Large Scale NAT
Note:
Large Scale NAT (LSN) feature is deprecated from NetScaler 14.1 release onwards.
Deprecated features are not removed immediately. The NetScaler appliance continues to support the deprecated feature until it is removed in a future release.
The Internet’s phenomenal growth has resulted in a shortage of public IPv4 addresses. Large Scale NAT (LSN/CGNAT) provides a solution to this issue, maximizing the use of available public IPv4 addresses by sharing a few public IPv4 addresses among a large pool of Internet users.
LSN translates private IPv4 addresses into public IPv4 addresses. It includes network address and port translation methods to aggregate many private IP addresses into fewer public IPv4 addresses. LSN is designed to handle NAT on a large scale. The NetScaler LSN feature is very useful for Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and carriers providing millions of translations to support a large number of users (subscribers) and at very high throughput.
LSN Architecture
The LSN architecture of an ISP using NetScaler products consists of subscribers (Internet users) in private address spaces accessing the Internet through a NetScaler appliance deployed in ISP’s core network. Subscribers are connected to the ISP through the ISP’s access network. Usually, subscribers for commercial use of the Internet are directly connected to the ISP’s access network. Serving those subscribers requires only one level of NAT (NAT44).
Noncommercial subscribers, however, are typically behind customer-premises equipment (CPE), such as routers and modems, that also implements NAT. These two levels of NAT create the NAT444 model. Deploying a NetScaler appliance in an ISP’s core network for LSN functionality is transparent to the subscribers and requires no configuration changes to subscribers or the CPEs.
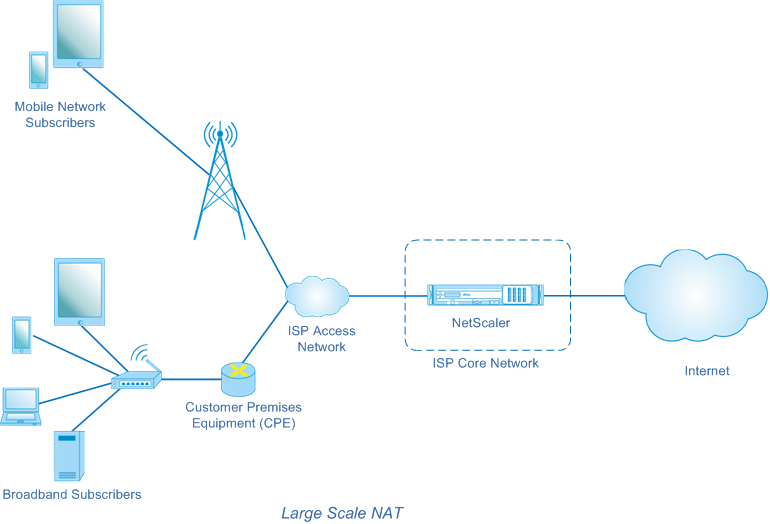
The NetScaler appliance receives all subscriber packets destined to the Internet. The appliance is configured with a pool of pre-defined NAT IP addresses to use for LSN. The NetScaler appliance uses its LSN feature to translate the source IP address (private) and port of the packet to the NAT IP address (public) and NAT port, and then sends the packet to its destination on the Internet. The appliance maintains a record of all active sessions that use the LSN feature. These sessions are called LSN sessions. The NetScaler appliance also maintains the mappings between subscriber IP address and port, and NAT IP address and port, for each session. These mappings are called LSN mappings. From LSN sessions and LSN mappings, the NetScaler appliance recognizes a response packet (received from the Internet) belonging to a particular session. The appliance translates the destination IP address and port of the response packet from NAT IP address:port to the subscriber IP address:port, and sends the translated packet to the subscriber.
LSN Features Supported on NetScaler appliance
The following describes some of the LSN features supported on NetScaler appliance:
NAT Resource Allocation
The NetScaler appliance allocates NAT IP addresses and ports, from its pre-defined NAT resource pool, to subscribers to translate their packets for transmission to external hosts (Internet). The NetScaler appliance supports the following types of NAT IP address and port allocation for subscribers:
-
Deterministic. The NetScaler appliance allocates a NAT IP address and a block of ports to each subscriber. The appliance sequentially allocates NAT resources to these subscribers. It assigns the first block of ports on the beginning NAT IP address to the beginning subscriber IP address. The next range of ports is assigned to the next subscriber, and so on, until the NAT address does not have enough ports for the next subscriber. At that point, the first port block on the next NAT address is assigned to the subscriber, and so on.
The NetScaler appliance logs the allocated NAT IP address and the port block for a subscriber. For a connection, a subscriber can be identified just by its mapped NAT IP address and port block. Because of this reason, the NetScaler appliance does not log any LSN session created or deleted. If the entire block of ports is being used, the NetScaler appliance drops any new connection from the subscriber.
-
Dynamic. The NetScaler appliance allocates a random NAT IP address and a port from the LSN NAT pool for a subscriber’s connection. When port block allocation is enabled in the configuration, the appliance allocates a random NAT IP address and a block of ports for a subscriber when it initiates a connection for the first time. The NetScaler appliance then allocates this NAT IP address and one of the ports from the allocated block to each subsequent connection from this subscriber. If the entire block of ports is being used, the appliance allocates a new random port block to the subscriber when it initiates a new connection. One of the port in the new port block is allocated for the new connection.
IP Pooling
The following NAT resource allocation options are available for subsequent sessions of a subscriber who was allocated a random NAT IP address and port for an existing session.
- Paired. The NetScaler appliance allocates the same NAT IP address for all sessions associated with the same subscriber. When no more ports are available for that address, the appliance drops any new connections from the subscriber. This option is needed for proper functioning of certain applications that require creation of multiple sessions on the same source IP address (for example in peer-to-peer applications that use RTP or RTCP protocol.
- Random. The NetScaler appliance allocates random NAT IP addresses, from the pool, for different sessions associated with the same subscriber.
Reusing LSN Mappings
The NetScaler appliance can reuse an existing LSN map for new connections originating from the same subscriber IP address and port. The NetScaler LSN feature supports the following types of LSN mapping reuse:
- Endpoint Independent. The NetScaler appliance reuses the LSN mapping for subsequent packets sent from the same subscriber IP address and port (X:x) to any external IP address and port. This type of LSN map reuse is useful for proper functioning of VOIP and peer-to-peer applications.
- Address dependent. The NetScaler appliance reuses the LSN mapping for subsequent packets sent from the same subscriber IP address and port (X:x) to the same external IP address (Y), regardless of the external port.
- Address port dependent. The NetScaler appliance reuses the LSN mapping for subsequent packets sent from the same internal IP address and port (X:x) to the same external IP address and port (Y:y) while the mapping is still active.
LSN Filtering
The NetScaler appliance can filter packets from external hosts based on the active LSN sessions and LSN mappings. Consider an example of an LSN mapping that includes the mapping of subscriber IP:port (X:x), NAT IP:port (N:n), and external host IP:port (Y:y). The NetScaler LSN feature supports the following types of filtering:
- Endpoint Independent. The NetScaler appliance filters out only those packets that are not destined to NAT IP:port (N:n), which represents subscriber IP:port (X:x), regardless of the external host IP address and port source (Z:z). The NetScaler appliance forwards any packets destined to X:x. In other words, sending packets from the subscriber to any external IP address is sufficient to allow packets from any external host to the subscriber. This type of filtering is useful for proper functioning of VOIP and peer-to-peer applications.
- Address dependent. The NetScaler appliance filters out packets not destined to NAT IP:port (N:n), which represents subscriber IP:port (X:x). In addition, the appliance filters out packets from external host IP address and port (Y:y) destined for N:n if the subscriber has not previously sent packets to Y:anyport (external port independent). In other words, receiving packets from a specific external host requires that the subscriber first send packets to that specific external host’s IP address.
- Address port dependent. The NetScaler appliance filters out packets not destined to NAT IP:port (N:n), which represents subscriber IP:port (X:x). In addition, the appliance filters out packets from external host IP address and port (Y:y) destined for N:n if the subscriber has not previously sent packets to Y:y. In other words, receiving packets from a specific external host requires that the subscriber first send packets to that specific external IP address and port.
Quotas
The NetScaler appliance can limit the number of NAT ports and sessions for each subscriber to ensure fair distribution of resources among subscribers. The NetScaler appliance can also limit the number of session for a subscriber group to ensure fair distribution of resources among different subscriber groups.
- Port quota. The NetScaler appliance can limit the LSN NAT ports to be used at a time by each subscriber for a specified protocol. For example, you could limit each subscriber to a maximum of 500 TCP NAT ports. When the LSN NAT mappings for a subscriber reach the limit, the NetScaler appliance does not allocate additional NAT ports of the specified protocol to that subscriber.
- Subscriber Session Limit. The number of concurrent session for a subscriber can be more than it port quota. The NetScaler appliance can limit the LSN sessions allowed for each subscriber for a specified protocol. When the number of LSN sessions reaches the limit for a subscriber, the NetScaler appliance does not allow the subscriber to open additional sessions of the specified protocol.
- Group Session Limit. The NetScaler appliance can limit the total number of LSN sessions allowed for a subscriber group for a specified protocol. When the total number of LSN sessions reaches the limit for a group for a specified protocol, the NetScaler appliance does not allow any subscriber of the group to open additional sessions of the specified protocol. For example, You limit a group to a maximum of 10000 UDP sessions. When the total number of UDP sessions for this group reaches 10000, the NetScaler appliance does not allow any subscriber of the group to open additional UDP sessions.
Application Layer Gateways
For some Application layer protocols, the IP addresses and protocol port numbers are also communicated in the packet’s payload. Application Layer Gateway for a protocol parses the packet’s payload and does necessary changes to ensure that the protocol continues to work over LSN.
The NetScaler appliance supports ALG for the following protocols:
- FTP
- ICMP
- TFTP
- PPTP
- SIP
- RTSP
Hairpin Support
The NetScaler appliance supports communication between subscribers or internal hosts using NAT IP addresses. This type of communication between two subscribers using NAT IP addresses is called hairpin flow. Hairpin flow is enabled by default, and you cannot disable it.