-
Distributing traffic across cluster nodes
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Traffic distribution in a cluster setup
In a cluster setup, external networks view the collection of NetScaler appliances as a single entity. So, the cluster must select a single node that must receive the traffic. The cluster does this selection by using the Equal Cost Multiple Path (ECMP) or cluster link aggregation traffic distribution mechanism. The selected node is called the flow receiver.
Note
For an L3 cluster (nodes across different networks), only the ECMP traffic distribution can be used.
The flow receiver gets the traffic and then, using internal cluster logic determines the node that must process the traffic. This node is called the flow processor. The flow receiver steers the traffic to the flow processor over the backplane if the flow receiver and the flow processor are on the same network. The traffic is steered through the tunnel if the flow receiver and the flow processor are on different networks.
Note
- The flow receiver and flow processor must be nodes capable of serving traffic.
- From NetScaler 11 onwards, you can disable steering on the cluster backplane. For more information, see Disabling Steering on the Cluster Backplane.
Figure 1. Traffic distribution in a cluster
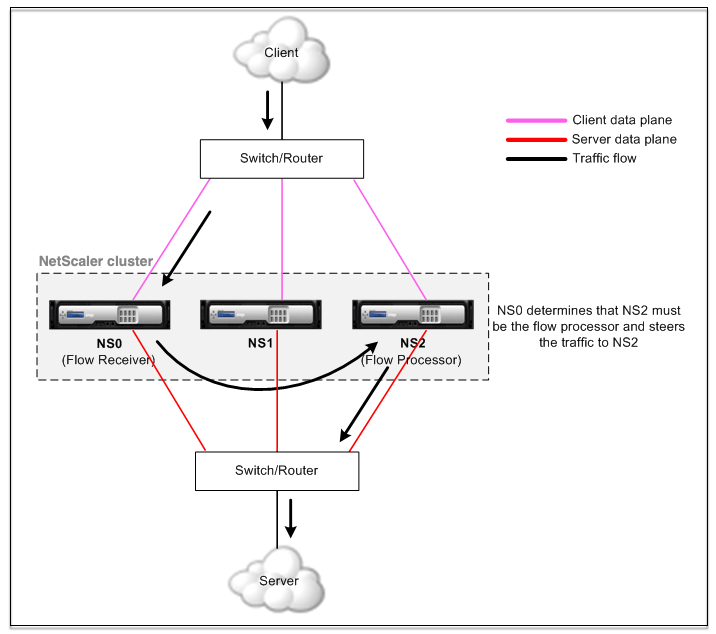
The preceding figure shows a client request flowing through the cluster. The client sends a request to a virtual IP (VIP) address. A traffic distribution mechanism configured on the client data plane selects one of the cluster nodes as the flow receiver. The flow receiver receives the traffic, determines the node that must process the traffic, and steers the request to that node (unless the flow receiver selects itself as the flow processor).
The flow processor establishes a connection with the server. The server processes the request and sends the response to the subnet IP (SNIP) address that sent the request to the server.
- If the SNIP address is a striped or partially striped IP address, the traffic distribution mechanism configured on the server data plane selects one of the cluster nodes as the flow receiver. The flow receiver receives the traffic, determines the flow processor, and steers the request to the flow processor through the cluster backplane.
- If the SNIP address is a spotted IP address, the node that owns the SNIP address receives the response from the server.
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.