Install Citrix SD-WAN VPX Standard Edition on Azure - Release Version 9.3
The Citrix SD-WAN Standard Edition for Azure logically bonds multiple network links into a single secure logical virtual path. The solution enables organizations to use connections from different service providers including Broadband, MPLS, 4G/LTE, Satellite, and point-to-point links to get high resiliency virtual WAN paths. SD-WAN for Azure enables organizations to have a direct secure connection from each branch to the applications hosted in Azure eliminating the need to backhaul cloud bound traffic through a data center. Some of the benefits of using SD-WAN in Azure are:
- Create direct connections from every location to Azure.
- Ensure an always on connection to Azure.
- Extend your secure perimeter to the cloud.
- Evolve to a simple, easy to manage branch network.
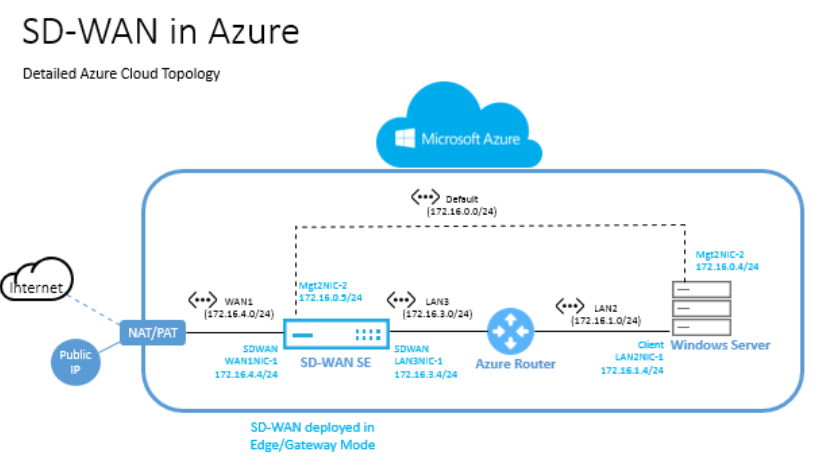
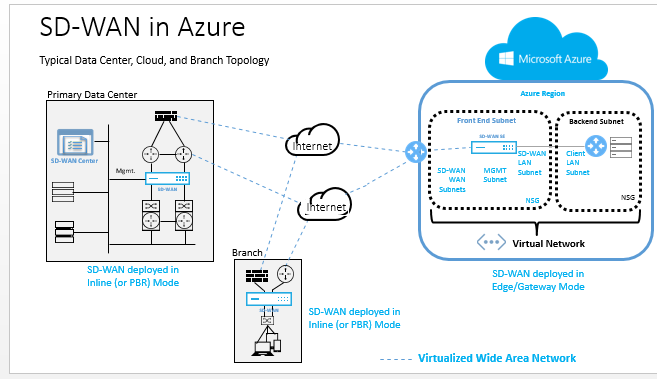
Topology - SD-WAN in Azure
Citrix SD-WAN Standard Edition can only be deployed in Gateway deployment mode in Azure. A Public IP address (Static/Dynamic) needs to be assigned to the WAN facing interface of SD-WAN in Azure.
Use case
An Azure VM is deployed within a specified region and can be connected to multiple branch locations through MPLS, Internet, or 4G/LTE. Within a Virtual Network (VNET) infrastructure, SD-WAN Standard Edition VHD (Virtual Hard Drive) is deployed in Gateway mode. The VNET has routes towards the Azure Gateway. The SD-WAN instance has a route towards the Azure Gateway for internet connectivity.
Connectivity between Data Center, Branch, and Cloud is achieved by using different transports methods utilizing multiple WAN paths simultaneously.
To deploy Citrix SD-WAN™ standard edition in Microsoft Azure
- In a web browser, type https://portal.azure.com/. Log into Microsoft Azure account. Search for SD-WAN Standard Edition.
- In the search results window, choose the following solution:
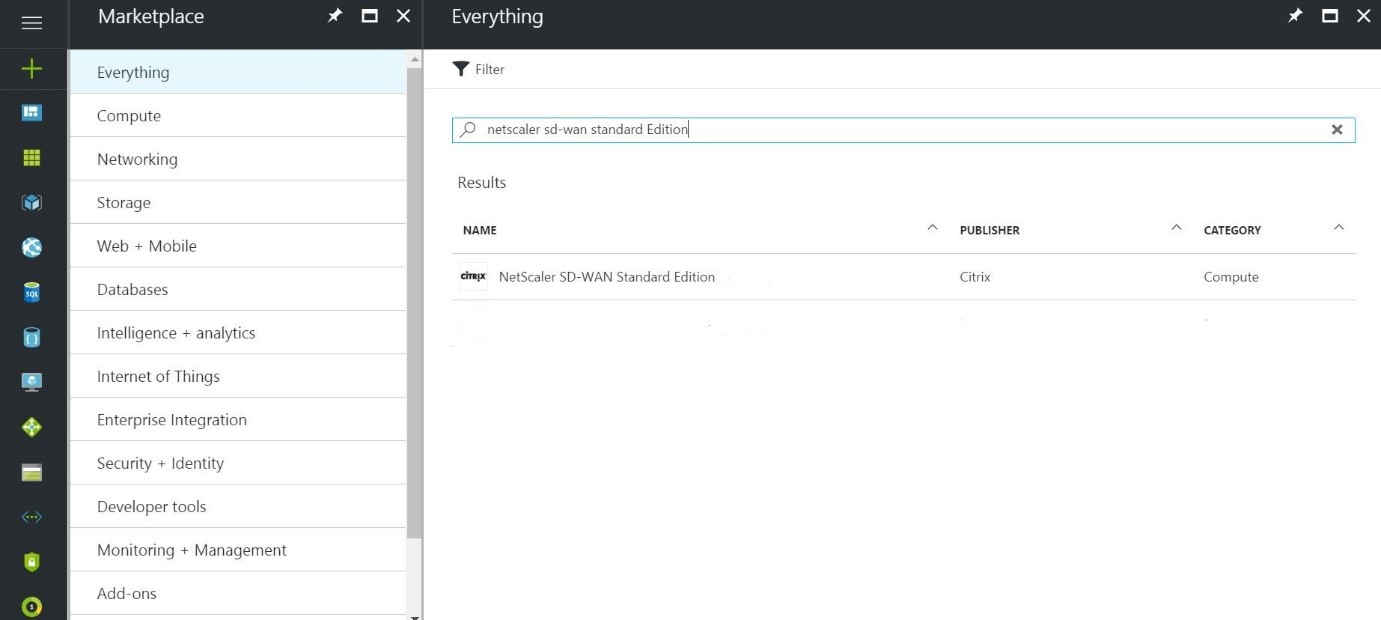
- Click create after going through the description and making sure the solution chosen is correct.
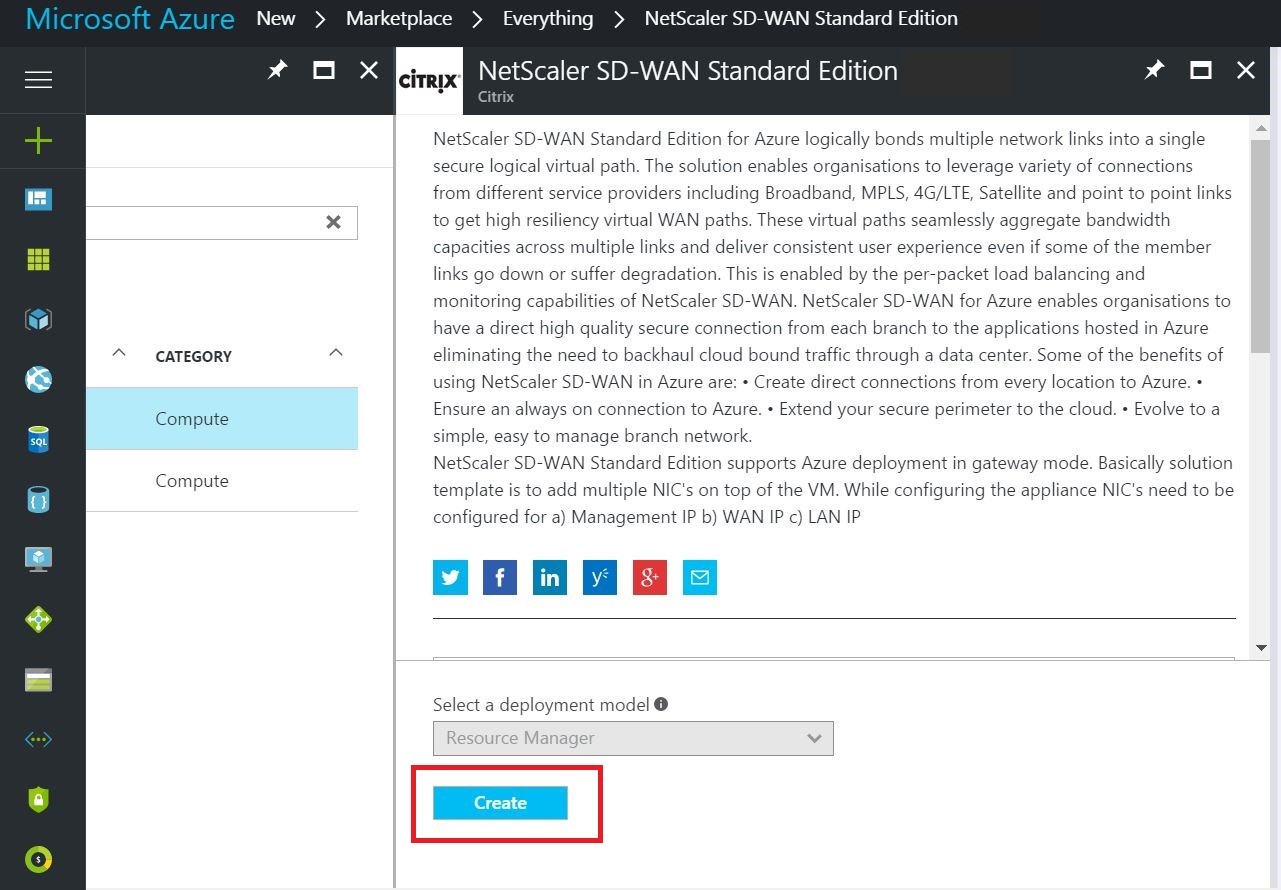
- After you click Create, a wizard prompting for details necessary to create the virtual machine in Azure appears. In the first step, choose the resource group in which you like to deploy the solution. A resource group is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. The resource group can include all the resources for the solution, or only those resources that you want to manage as a group. You can decide how you want to allocate resources to resource groups based on your deployment. Some important points to consider when defining your resource group are:
- All the resources in your group should share lifecycle. You deploy, update, and delete them together.
- If one resource, such as a database server must exist on a different deployment cycle, then it can be in another resource group.
- Each resource can only exist in one resource group.
- You can add or remove a resource to another resource group at any time.
- You can move a resource from one resource group to another resource group
- A resource group can contain resources that reside in different regions.
- A resource group can be used to scope access control for administrative actions.
- A resource can interact with resources in other resource groups. This interaction is common when the two resources are related but do not share lifecycle (for example, web apps connecting to a database).
In the following image, choose Create New.
Under Location, choose the region in which you want to deploy the solution. When creating a resource group, you must provide a location for that resource group. The resource group stores metadata about the resources that you are creating. Therefore, when you specify a location for the resource group, you are specifying where that metadata is stored.
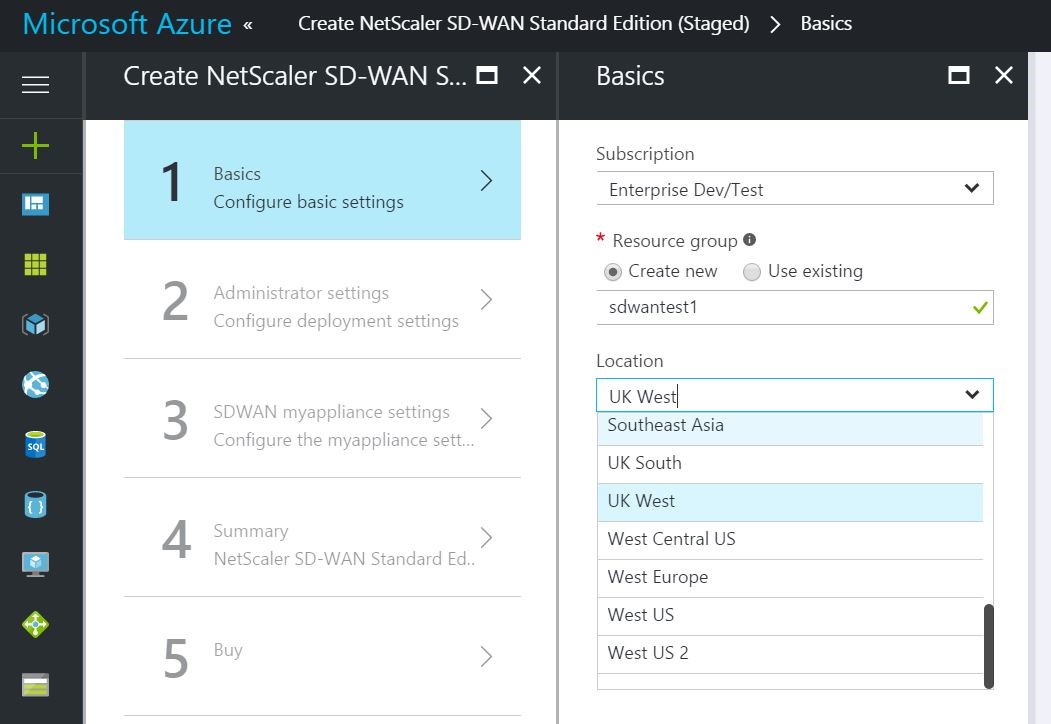
-
Provide a name for the Virtual Machine. Choose a username and strong password. The password must consist of an upper case letter, special character and must be more than nine characters. Click OK.
- Choose the instance in which you want to run the image. Currently, Standard_D3_V2 and Standard_D4_V2 are supported. If you are looking to achieve 200 Mbps of aggregated through put, then choose Standard_D4_V2 as the instance type.
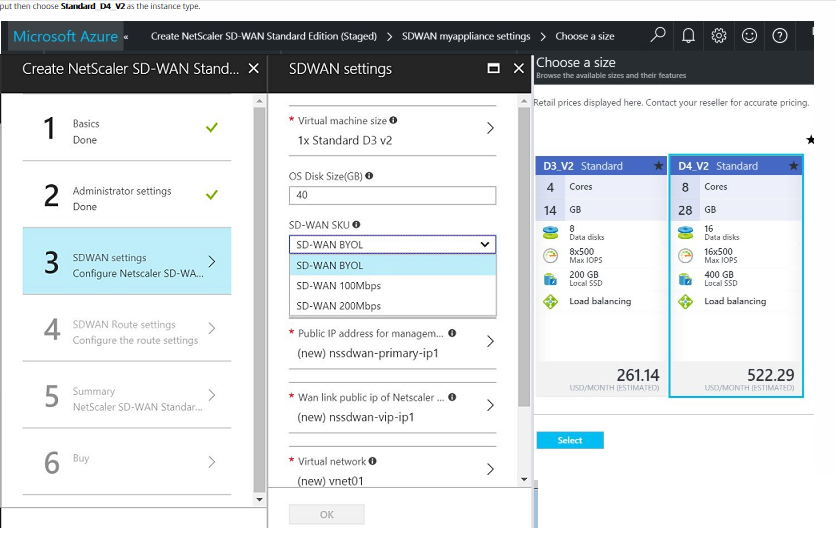
-
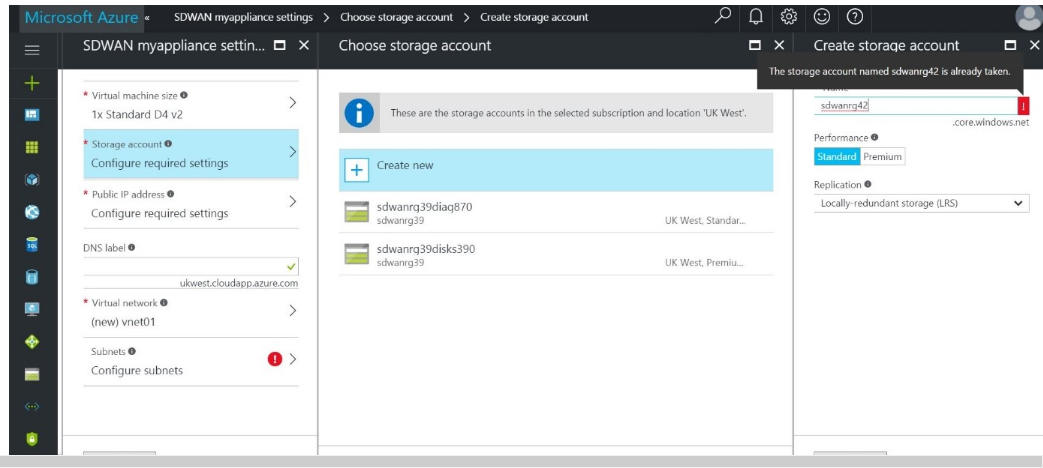
After choosing the image, choose the storage account. If you have an existing storage account, then you can choose that. In this step, you are creating a storage account as seen in the following image. A storage account stores the VHDs for the operating system’s temporary and more data disks.
- Choose a Public IP for the Virtual Machine. This would be assigned to the WAN facing interface of the solution. You can choose either a static or dynamic IP. However, it is recommended that you choose a static IP. The public IP that is assigned to the appliance here is provided by Azure and becomes the Virtual IP of the SD-WAN VM and would be used to communicate with the Master Control Node.
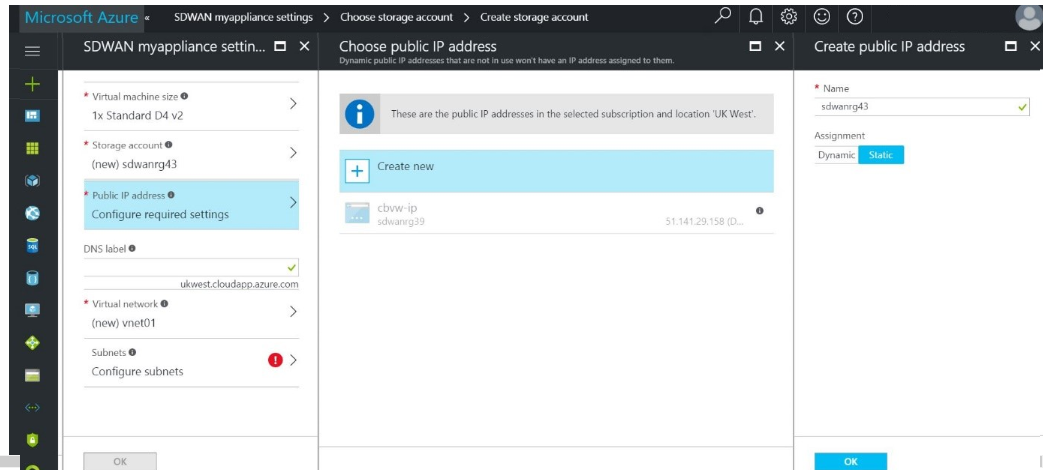
- After you have assigned an IP address, assign a DNS label. This DNS label must be able to uniquely identify the SD-WAN VM.
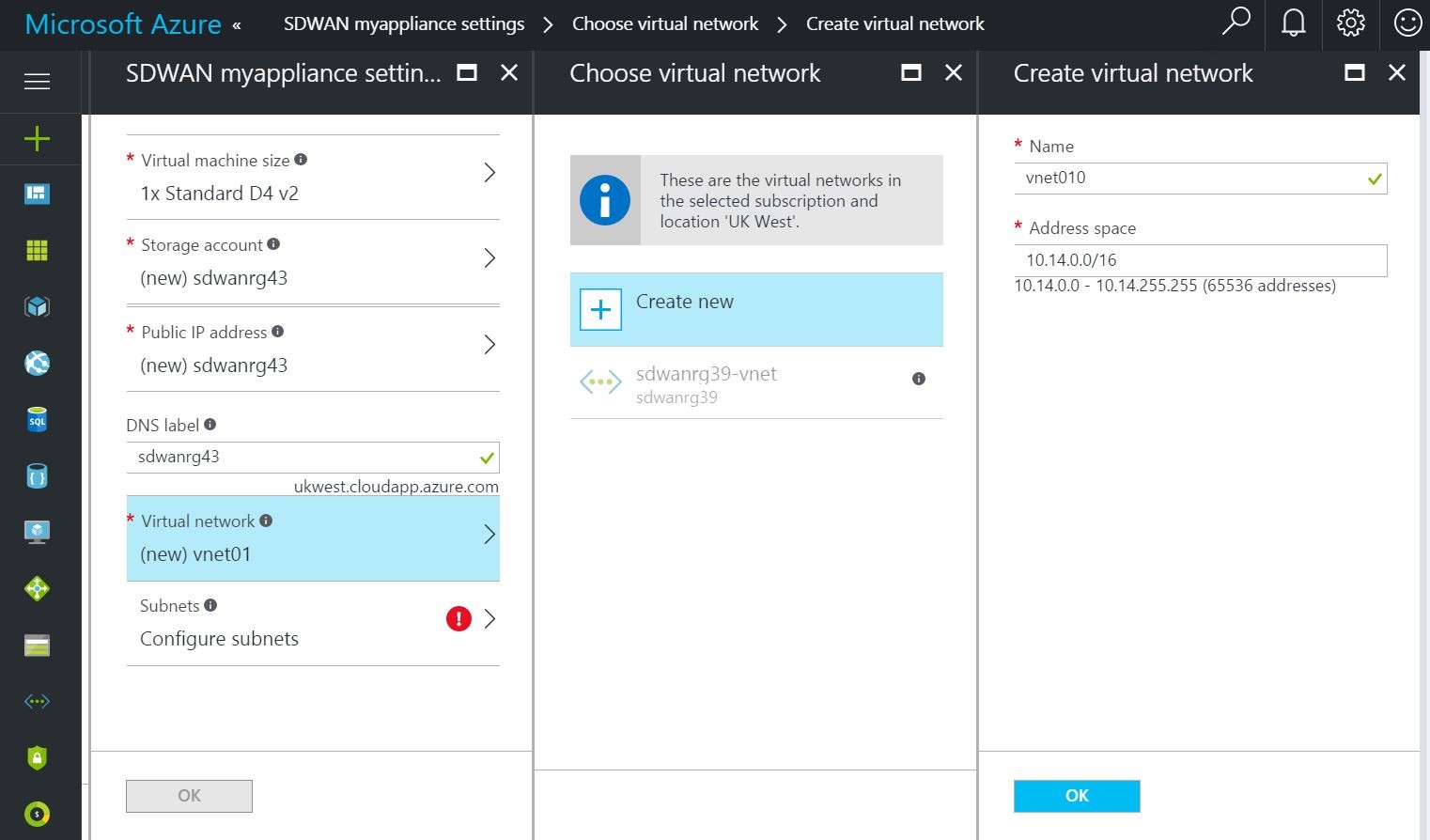
- Create a new Virtual Network (VNET) or use an existing VNET. This is the most critical step for deployment as this step chooses the subnets to be assigned to the interfaces of the SD-WAN VM.
-
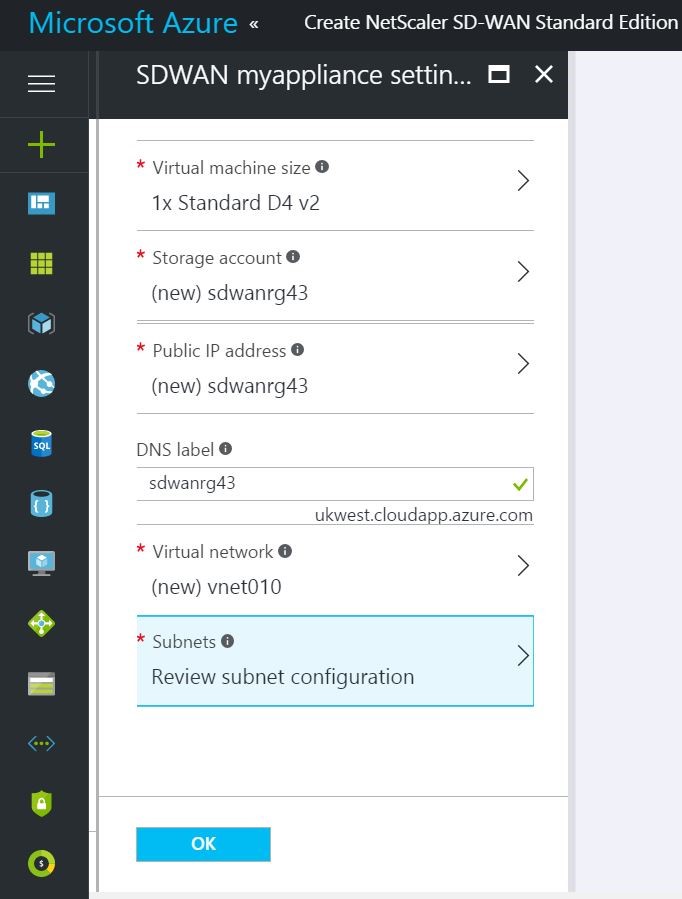
You can now assign the required subnets to each of the interfaces in the VM. The ordering for assigning subnets is WAN, LAN, and Management respectively. Choose as required and click OK.
NIC Associated network NIC 0 (default) Management subnet NIC 1 LAN subnet NIC 2 WAN subnet - Verify all the configuration details and click OK.
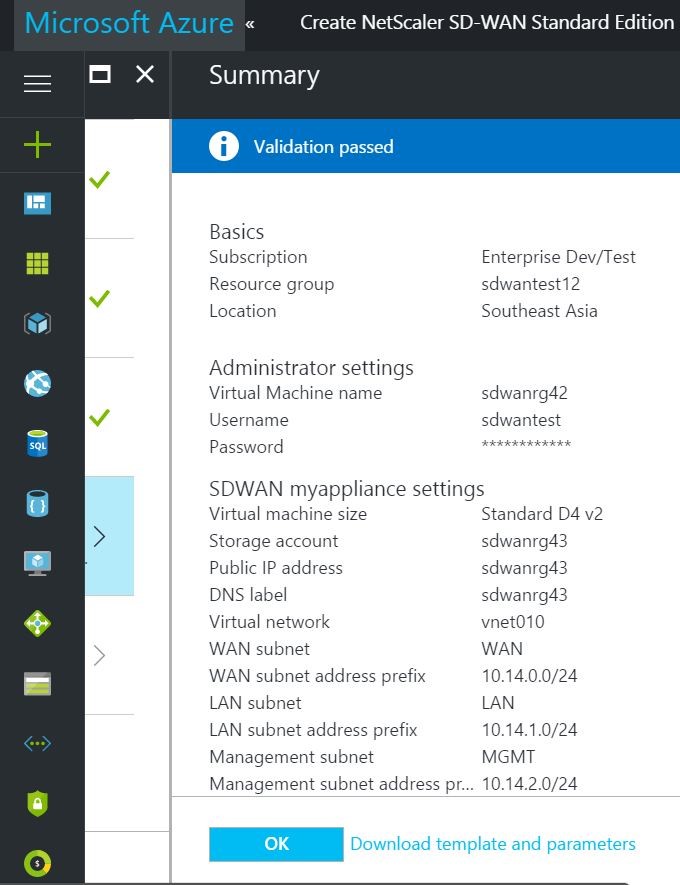
- All the configuration that you provided in previous steps is validated and applied. If you have configured correctly, then you should see that the validation passed message as follows. Click OK.
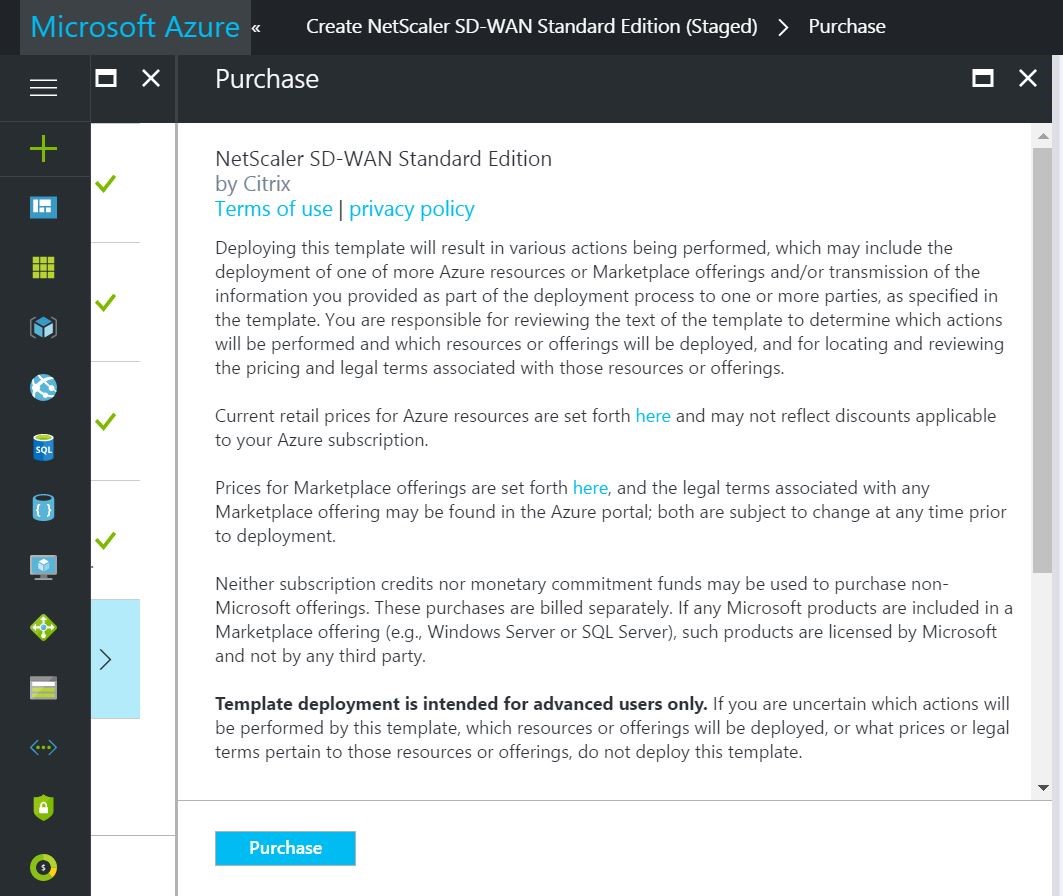
- After validation is passed, click on Purchase to purchase and create the image.
- After you make the purchase, the deployment starts and you can view the status in the notifications section.
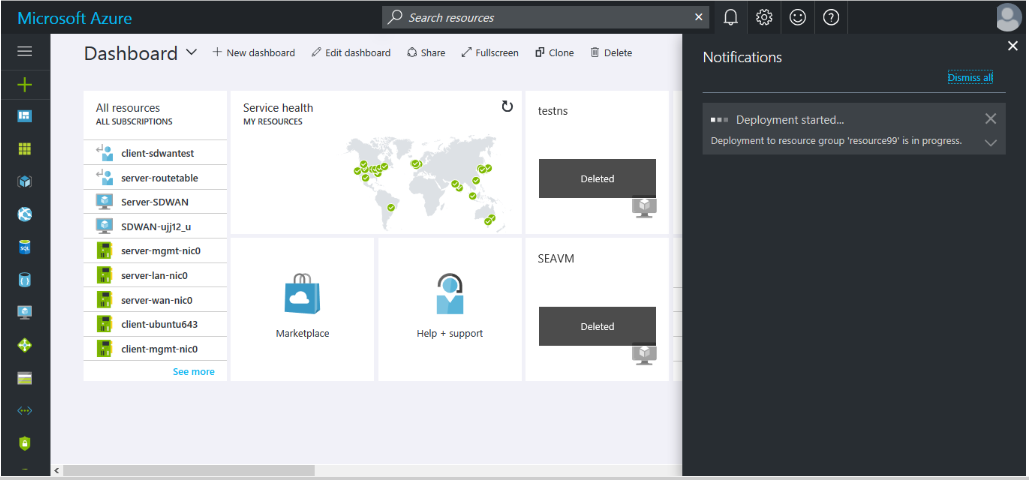
- You can get more details of your deployment by going to the resource group in which you are creating the deployment.
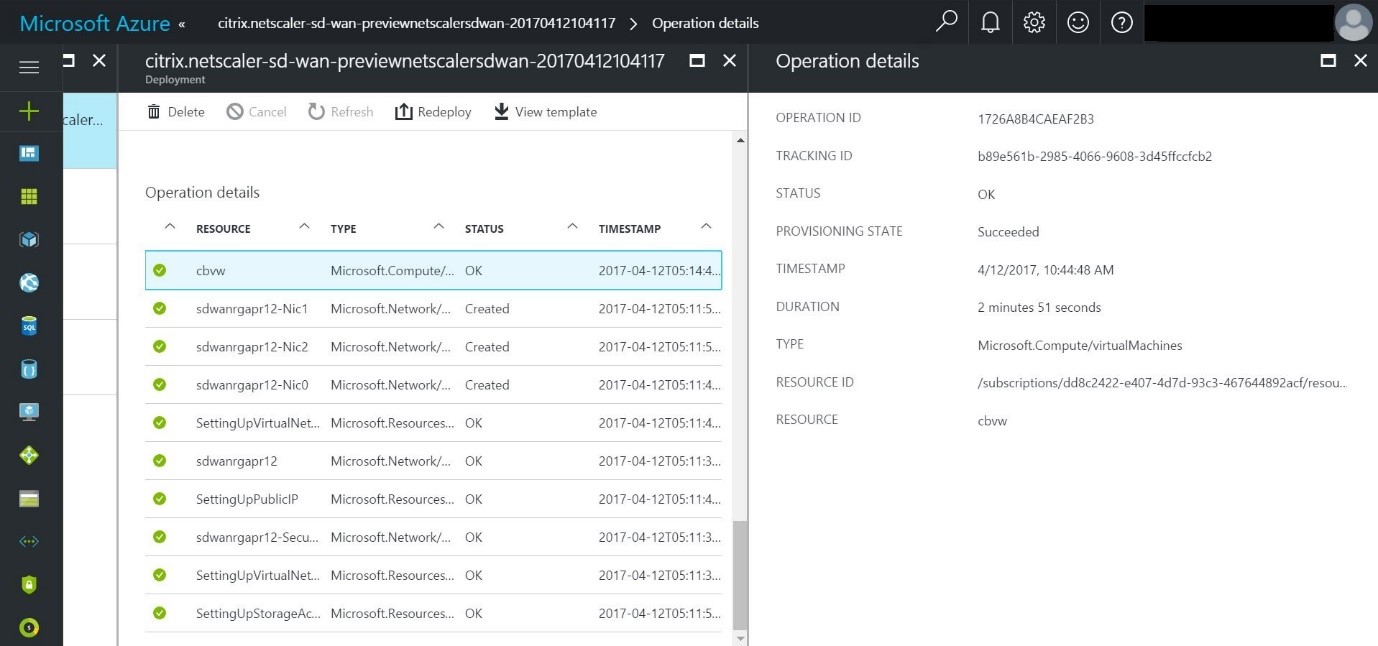
- Once the deployment has succeeded, please try to access the GUI through the public IP using the credentials that you have configured.
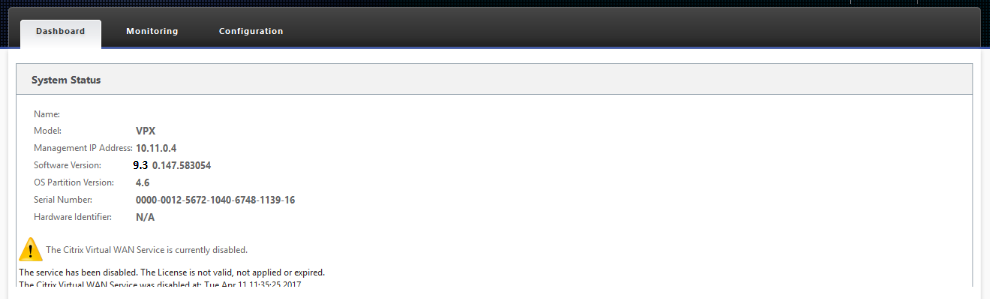
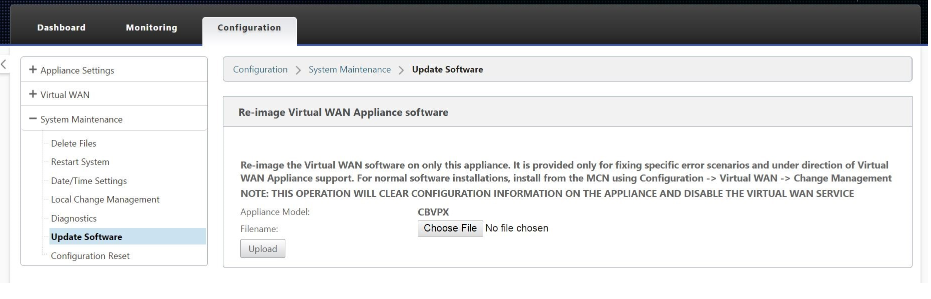
- Upgrade the software to the latest image by applying the latest 9.2.147 software image for VPX appliances by going into the update software option. This is a onetime operation only and is required when bringing up the image for the first time.
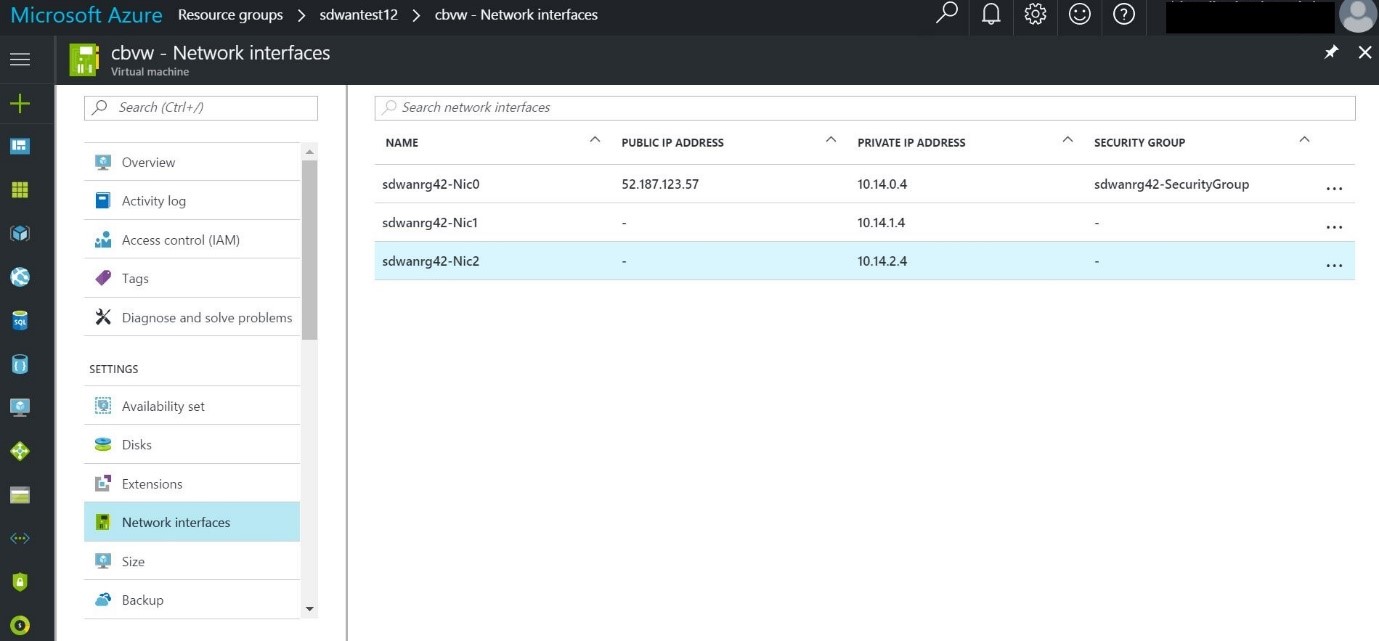
- After software is updated, you cannot access the GUI through the public IP as the public IP would be used for setting up the virtual paths. To access the GUI for managing the solution, create a Windows VM in the same vnet and connect to the management IP assigned to the appliance. The management IP is assigned to the last NIC (sdwanrg42-Nic2 as shown in the following image). You must connect to the GUI of the appliance through the management IP assigned to this NIC, 10.14.2.4 as follows.
- After you log in to the GUI, you will notice that the virtual service is disabled because SD-WAN on Azure works on a BYOL (Bring Your Own License) model. Please apply the license through the licensing tab, if you have the license already or order a new one by going to http://store.citrix.com.
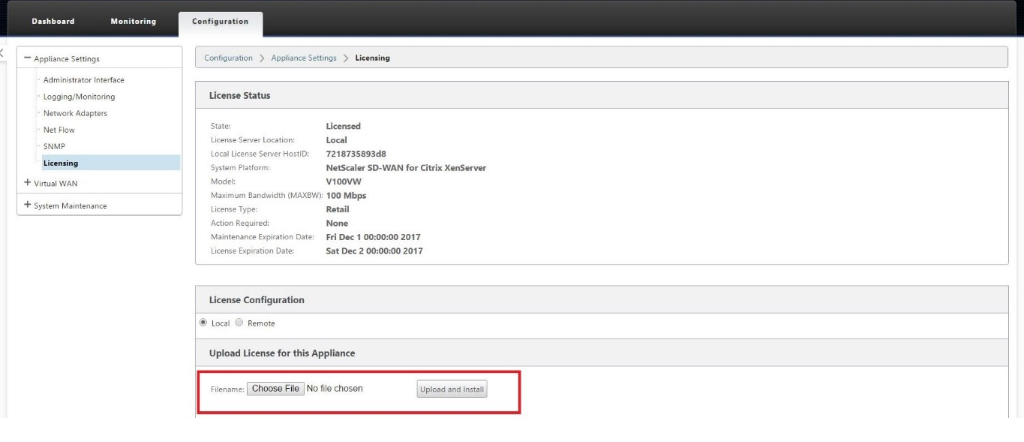
- After the license is applied, you can apply configuration to the appliance and use it like any other branch. For more information on configuring the appliance, please refer to: sd-wan licensing
Limitations - Microsoft Azure VMs
- After a VM is created and booted in Azure, the interfaces cannot be added or deleted. The VM profile (RAM/HD/CPUs) can be changed.
- There is no concept of MAC address spoofing in Azure Cloud. The LAN subnet of the SE-VPX and the LAN subnet of the Client/Server Host have to be different. This requires more routing configuration to be done in two places.
- Routes are added in the Virtual WAN configuration file directing all Virtual WAN data traffic coming from the WAN to the Client/Server LAN Subnet.
Microsoft Azure supports only gateway mode for deployments. Refer to the following article for more information about VPN gateway