-
-
-
Configure Virtual Router redundancy protocol
-
-
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Configure Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is a widely used protocol that provides device redundancy to eliminate the single point of failure inherent in the static default-routed environment. VRRP allows you to configure two or more routers to form a group. This group appears as a single default gateway with one virtual IP address and one virtual MAC address.
A back-up router automatically takes over if the primary / master router fails. In a VRRP set-up, the master router sends a VRRP packet known as an advertisement to the back-up routers. If the master router stops sending the advertisement, the back-up router sets the interval timer. If no advertisement is received within this hold period, the back-up router initiates the failover routine.
VRRP specifies an election process in which, the router with the highest priority becomes the master. If the priority is the same among the routers, the router with the highest IP address becomes the master. The other routers are in backup state. The election process is initiated again if the master fails, a new router joins the group, or an existing router leaves the group.
VRRP ensures a high availability default path without configuring dynamic routing or router discovery protocols on every end-host.
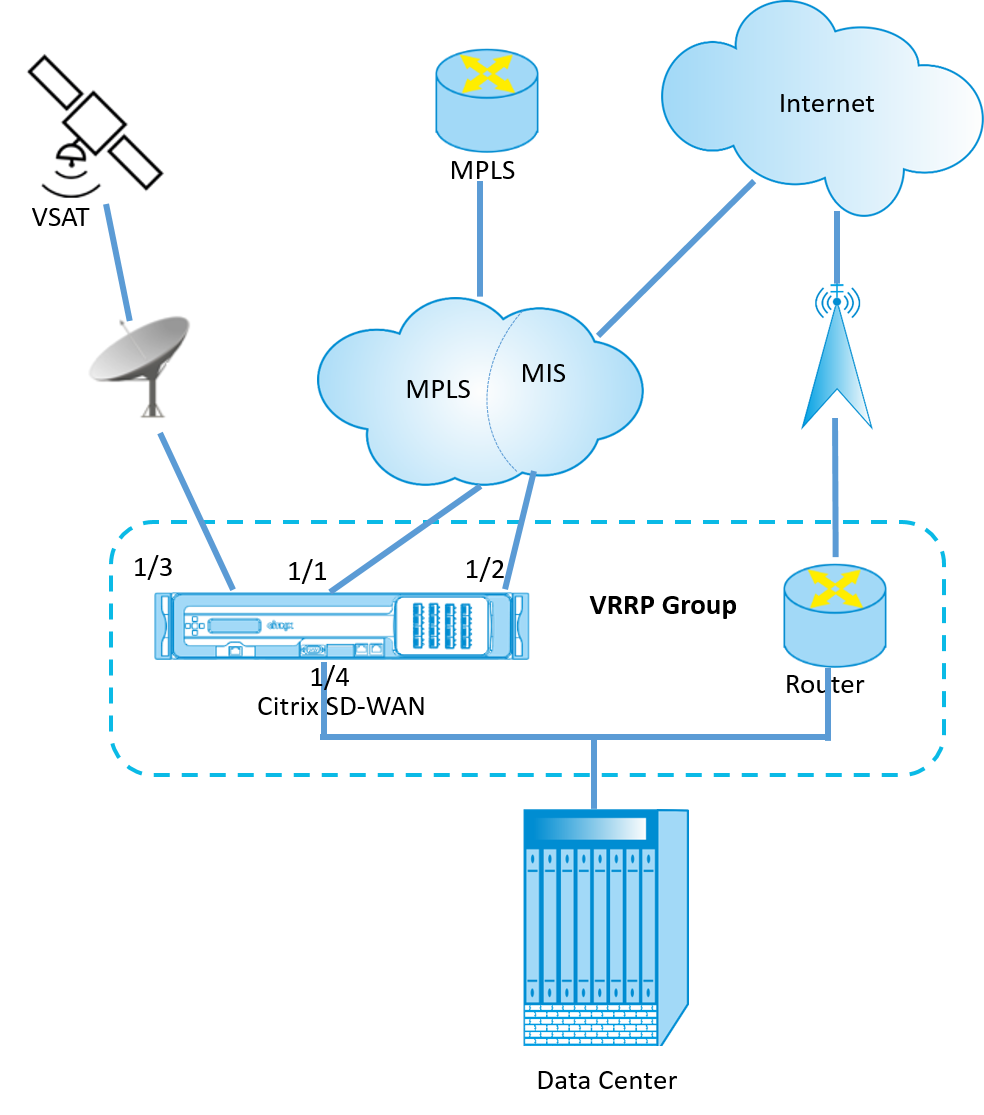
Citrix SD-WAN release version 10.1 supports VRRP version 2 and version 3 to inter-operate with any third party routers. The SD-WAN appliance acts as a master router and direct the traffic to use the Virtual Path Service between sites. You can configure the SD-WAN appliance as the VRRP master by configuring the Virtual Interface IP as the VRRP IP and by manually setting the priority to a higher value than the peer routers. You can configure the advertisement interval and the preempt option.
The below network diagram shows a Citrix SD-WAN appliance and a router configured as a VRRP group. The SD-WAN appliance is configured to be the master. If the SD-WAN appliance fails, the back-up router takes-over within milliseconds, ensuring that there is no downtime.
To configuring the VRRP instance:
- In the Configuration Editor, navigate to Sites > Site name > VRRP and click +.
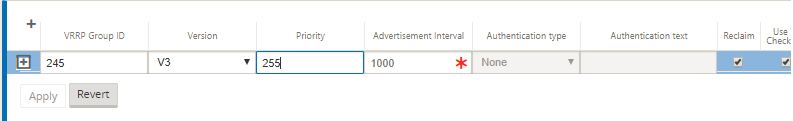
- Configure a VRRP instance. Enter the values for the following fields:
- VRRP group ID: The VRRP group ID. The group ID must be a value range is 1–255. The same group ID must be configured on the back-up routers too.
Note
Currently you can configure up to four groups only.
- Version: The VRRP protocol version. You can choose between VRRP protocol V2 and V3.
- Priority: The priority of the Citrix SD-WAN appliance for the VRRP group. The priority range is 1–254. Set this value to maximum (254) to make the SD-WAN appliance the master.
Note
If the router is the owner of the VRRP IP address, the Priority is set to 255 by default.
- Advertisement Interval: The frequency in milliseconds, with which the VRRP advertisements are sent when the SD-WAN appliance is the master. The default advertisement interval is one second.
- Authentication Type: You can choose Plain Text to enter an authentication string. The authentication string is sent as a plain text without any encryption in the VRRP Advertisements. Choose None, if you do not want to set up authentication.
- Authentication Text: The authentication string to be sent in the VRRP Advertisement. This option is enabled if the Authentication Type is Plain Text.
Note
Authentication is supported in VRRPv2 only.
- Reclaim: enables preemption when the priority of the SD-WAN appliance is highest in the VRRP group. This is used in the VRRP election process.
- Use V2 Checksum: enables compatibility with third party network devices for VRRPv3. By default, VRRPv3 uses the v3 checksum computation method. Certain third party devices might only support VRRPv2 checksum computation. In such cases, enable this option.
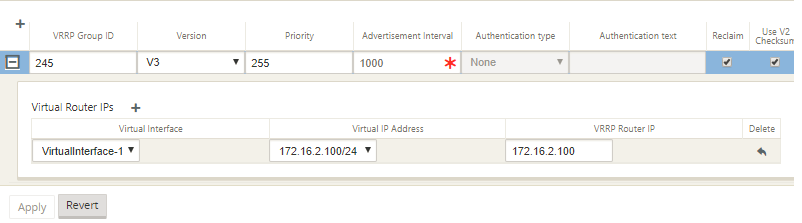
Configure the VRRP IP address. Enter values for the following fields and click Apply.
- Virtual Interface: The virtual interface to be used for VRRP. Choose one of the configured virtual interfaces.
- Virtual IP Address: The virtual IP address assigned to the virtual interface. Choose one of the configured virtual IP addresses for the virtual interface.
-
VRRP Router IP: The virtual router IP address for the VRRP group. By default, the Virtual IP address of the SD-WAN appliance is assigned as the virtual router IP address.
VRRP Statistics
You can view the VRRP statistics under Monitoring > VRRP Protocol.
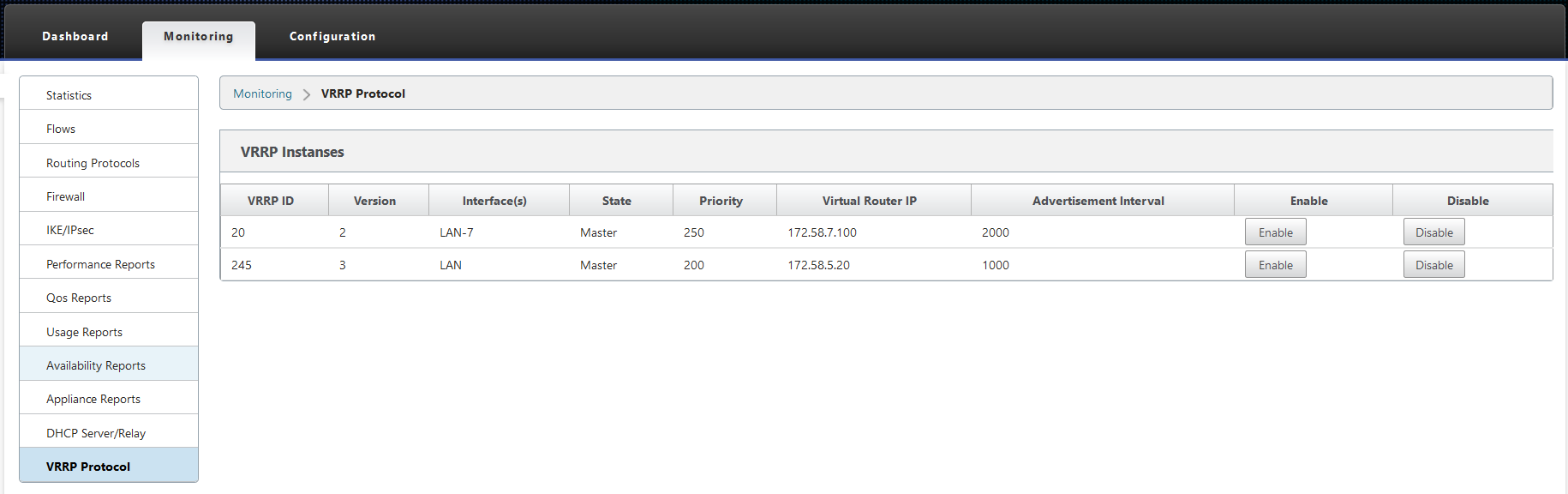
You can view the following statistics data:
- VRRP ID: The VRRP group ID
- Version: The VRRP protocol version.
- Interface: The virtual interface used for VRRP.
- State: The VRRP state of the SD-WAN appliance. It indicates whether the appliance is a master or a backup.
- Priority: The priority of the SD-WAN appliance for a VRRP Group
- Virtual Router IP: The virtual router IP address for the VRRP group.
- Advertisement Interval: The frequency of VRRP advertisements.
- Enable: Select this to enable the VRRP instance on the SD-WAN appliance.
- Disable: Select this to disable the VRRP instance on the SD-WAN appliance.
Limitations
- VRRP is supported in Gateway Mode deployment only.
- You can configure up to four VRRP IDs (VRID).
- Up to 16 virtual network interfaces can participate in VRID.
High Availability and VRRP
You can significantly reduce network downtime and traffic disruption by leveraging both the high availability and VRRP features on your SD-WAN network. Deploy a pair of Citrix SD-WAN appliance in active/standby roles along with a standby router to form the VRRP group. This group appears as a single default gateway with one virtual IP address and one virtual MAC address.
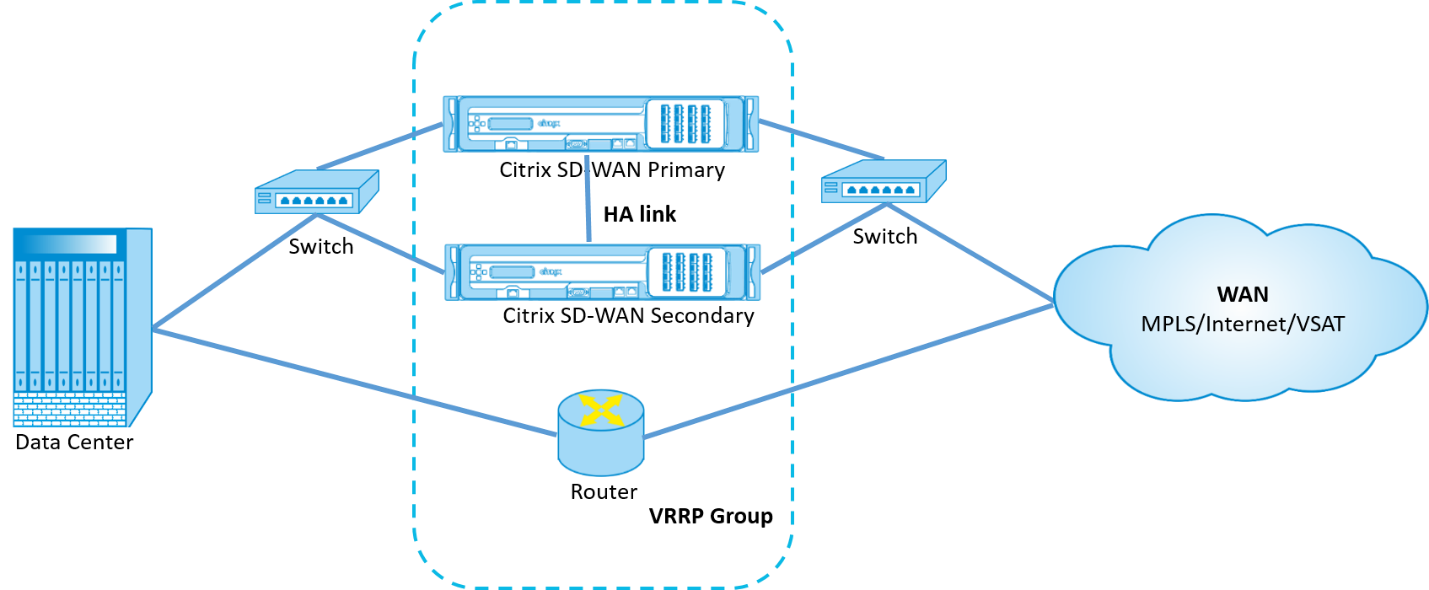
The following are 2 cases with the above deployment:
1st case: High availability failover timer on SD-WAN equals the VRRP failover timer.
The expected behavior is high availability switchover to happen before the VRRP switchover, that is the traffic continues to flow through the new Active SD-WAN appliance. In this case SD-WAN continues with the VRRP Master role.
2nd case: High availability failover timer on SD-WAN greater than the VRRP failover timer.
The expected behavior is the VRRP switchover to the router happens, that is the router becomes VRRP Master and traffic might momentarily flow through the router, bypassing the SD-WAN appliance.
But once the high availability switchover happens, SD-WAN again becomes VRRP Master, that is the traffic now flows through the new active SD-WAN appliance.
For more information on high availability deployment modes, see High Availability.
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.