-
Exploring the XenCenter workspace
-
-
-
-
-
Editing Workload Balancing Settings
-
Optimizing and Managing Power Automatically
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Optimizing and Managing Power Automatically
Note:
XenCenter YYYY.x.x is not yet supported for use with Citrix Hypervisor 8.2 CU1 in production environments. To manage your Citrix Hypervisor 8.2 CU1 production environment, use XenCenter 8.2.7. For more information, see the XenCenter 8.2.7 documentation.
You can install XenCenter 8.2.7 and XenCenter YYYY.x.x on the same system. Installing XenCenter YYYY.x.x does not overwrite your XenCenter 8.2.7 installation.
You can configure Workload Balancing to accept optimization recommendations automatically (Automation) and turn servers on or off automatically (Power Management).
Accepting optimization recommendations automatically
Workload Balancing lets you configure for it to accept optimization recommendations on your behalf and perform the optimization actions it recommends automatically. You can use this feature, which is known as Automation, to apply any recommendations automatically, including ones to improve performance or power down hosts. However, to power down hosts as virtual-machines usage drops, you must configure automation, power management, and Maximum Density mode.
By default, Workload Balancing does not accept optimizations automatically. Enable Automation if you want Workload Balancing to accept recommendations automatically. If you do not, Workload Balancing still prompts you to accept recommendations manually.
Workload Balancing does not automatically apply recommendations to hosts or virtual machines when the recommendations conflict with High Availability settings. If a pool becomes overcommitted by applying Workload Balancing optimization recommendations, XenCenter prompts you whether you want to continue applying the recommendation. When Automation is enabled, Workload Balancing does not apply any power-management recommendations that exceed the number of host failures to tolerate in the High Availability plan.
It is possible to tweak how Workload Balancing applies recommendations in automated mode. For information, see Advanced Settings.
Enabling Power Management
Power management is the ability to turn the power on or off for physical hosts. In a Workload Balancing context, this term refers to powering hosts in a pool on or off based on the pool’s total workload.
Configuring Workload Balancing power management on a host requires that:
- The hardware for the host server has remote power on/off capabilities
- The Host Power On feature is configured for the host
- The host has been explicitly selected as a host to participate in (Workload Balancing) Power Management
In addition, if you want Workload Balancing to power off hosts automatically, you also need to configure:
- Workload Balancing is configured to apply recommendations automatically
- Workload Balancing is configured to apply Power Management recommendations automatically
When the pool is in Maximum Density mode, if Workload Balancing detects unused resources, it recommends powering off hosts until it eliminates all excess capacity in the pool. If WLB detects the pool has insufficient host capacity to shut down servers, it recommends leaving the servers on until the pool workload decreases enough. When you configure Workload Balancing to power off extra servers automatically, it applies these recommendations automatically and, therefore, behaves in the same way.
When a host is set to participate in Power Management, Workload Balancing makes power-on/off recommendations as needed. If you turn on the option to apply Power Management recommendations automatically, you do so at the pool level. However, you can specify which hosts from the pool you want to participate in Power Management.
Understanding Power Management behavior
Before Workload Balancing recommends powering hosts on or off, it selects the hosts to transfer virtual machines to (that is, to “fill”). It does so in the following order:
- Filling the pool coordinator since it is the host that cannot be powered off.
- Filling the host with the most virtual machines.
- Filling subsequent hosts according to which hosts have the most virtual machines running.
When Workload Balancing fills the pool coordinator, it does so assuming artificially low (internal) thresholds for the pool coordinator. Workload Balancing uses these low thresholds as a buffer to prevent the pool coordinator from being overloaded.
Workload Balancing fills hosts in this order to encourage density.
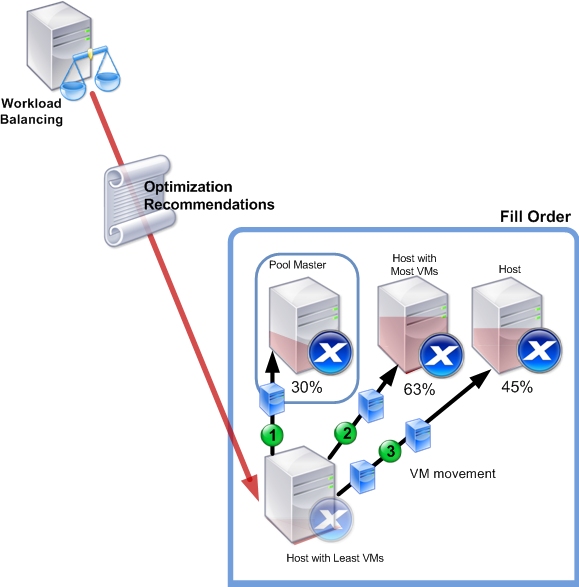
This illustration shows how, when consolidating VMs on hosts in Maximum Density mode, XenServer fills the pool coordinator first, the most loaded server second, and the least loaded server third.
If Workload Balancing detects a performance issue while the pool is in Maximum Density mode, it addresses the issue by recommending migrating workloads among the powered-on hosts. If Workload Balancing cannot resolve the issue using this method, it attempts to power on a host. (Workload Balancing determines which hosts to power on by applying the same criteria it would if the optimization mode was set to Maximum Performance.)
When WLB runs in Maximum Performance mode, it powers on hosts until resource utilization on all hosts in the pool falls below the High threshold.
While migrating one or more VMs, if WLB determines that increasing capacity would benefit the pool’s overall performance, it powers on hosts automatically or recommends doing so.
Important:
Workload Balancing only recommends powering on a host that Workload Balancing powered off.
Designing environments for Power Management and VM consolidation
When you are planning XenServer implementations and you intend to configure automatic VM consolidation and power management, consider your workload design. For example, you might want to:
-
Place Different Types of Workloads in Separate Pools. If you have distinct types of workloads or types of applications that perform better with certain types of hardware, consider whether to locate the VMs hosting these workloads in different pools.
Because power management and VM consolidation are managed at the pool level, design pools so they contain workloads that you want consolidated at the same rate. Factor in considerations such as those discussed in the Advanced Settings topic.
-
Exclude Hosts from Workload Balancing. Some hosts might have to be always on. For more information, see Excluding Hosts from Recommendations.
To apply optimization recommendations automatically
- In the Resources pane of XenCenter, select XenCenter > your resource pool.
- In the Properties pane, select the WLB tab.
- In the WLB tab, select Configure WLB.
- In the left pane, select Automation.
- Select one or more of the following check boxes:
- Automatically apply Optimization recommendations. When you select this option, you do not need to accept optimization recommendations manually. Workload Balancing automatically accepts the optimization and placement recommendations it makes.
-
Automatically apply Power Management recommendations. The behavior of this option varies according to the pool’s optimization mode:
- Maximum Performance Mode. When Automatically apply Power Management recommendations is enabled, Workload Balancing automatically powers on hosts when doing so improves the host performance.
- Maximum Density Mode. When Automatically apply Power Management recommendations is enabled, Workload Balancing automatically powers off hosts when resource utilization drops below the Low threshold. That is, Workload Balancing powers off hosts automatically during low usage periods.
- Do one of the following:
- If you want to configure power management, select Automation/Power Management and proceed to the following section.
- If you do not want to configure power management and you are finished configuring automation, select OK.
To select servers for power management
-
In the Power Management section, select the hosts that you want Workload Balancing to power on and off automatically.
Note:
Selecting hosts for power management recommendations without selecting Automatically apply Power Management recommendations results in Workload Balancing suggesting power management recommendations but not applying them automatically for you.
-
Click OK. If none of the physical servers in the resource pool support remote power management, Workload Balancing displays the message, No hosts support Power Management
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Cloud Software Group Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Cloud Software Group Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Cloud Software Group product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.