Use Machine Creation Services™ (MCS) to create Linux VMs
To use MCS to create Linux VMs, prepare a master image on your hypervisor. This process entails installing the VDA on the template VM, creating a Machine Catalog in Citrix Studio, creating a Delivery Group, and performing certain configuration tasks.
Note:
Unexpected results can occur if you try to prepare a master image on hypervisors other than Citrix Hypervisor™, Microsoft Azure, VMware vSphere, AWS, GCP, or Nutanix AHV.
Microsoft Azure, AWS, and GCP are not supported as of Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ 7 2003. But you can continue using the hosts in the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops service.
Supported distributions
| Winbind | SSSD | Centrify | PBIS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHEL 8.3 | Yes | No | No | No |
| CentOS 8.3 | Yes | No | No | No |
| RHEL 8.2 | Yes | No | No | No |
| CentOS 8.2 | Yes | No | No | No |
| RHEL 8.1 | Yes | No | No | No |
| CentOS 8.1 | Yes | No | No | No |
| RHEL 7.9 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| CentOS 7.9 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| RHEL 7.8 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| CentOS 7.8 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Ubuntu 18.04 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Ubuntu 16.04 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Debian 10.7 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| SUSE 12.5 | Yes | Yes | No | No |
Use MCS to create Linux VMs on Citrix Hypervisor
Step 1: Prepare a master image
A master image contains the operating system, non-virtualized applications, VDA, and other software. To prepare a master image, do the following:
Step 1a: Install Citrix VM Tools
Citrix VM Tools must be installed on the template VM for each VM to be able to use the xe CLI or XenCenter. VM performance can be slow unless the tools are installed. Without the tools, you cannot do any of the following:
- Cleanly shut down, restart, or suspend a VM.
- View the VM performance data in XenCenter.
- Migrate a running VM (through
XenMotion). - Create snapshots or snapshots with memory (checkpoints), and revert to snapshots.
- Adjust the number of vCPUs on a running Linux VM.
-
Run the following command to mount Citrix VM Tools named guest-tools.iso.
sudo mount /dev/cdrom /mnt <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the following command to install the
xe-guest-utilitiespackage based on your Linux distribution.For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo rpm -i /mnt/Linux/xe-guest-utilities_{package-version}_all.rpm <!--NeedCopy-->For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg -i /mnt/Linux/xe-guest-utilities_{package-version}_all.deb <!--NeedCopy-->For SUSE 12:
sudo rpm -i /mnt/Linux/xe-guest-utilities_{package-version}_all.rpm <!--NeedCopy--> -
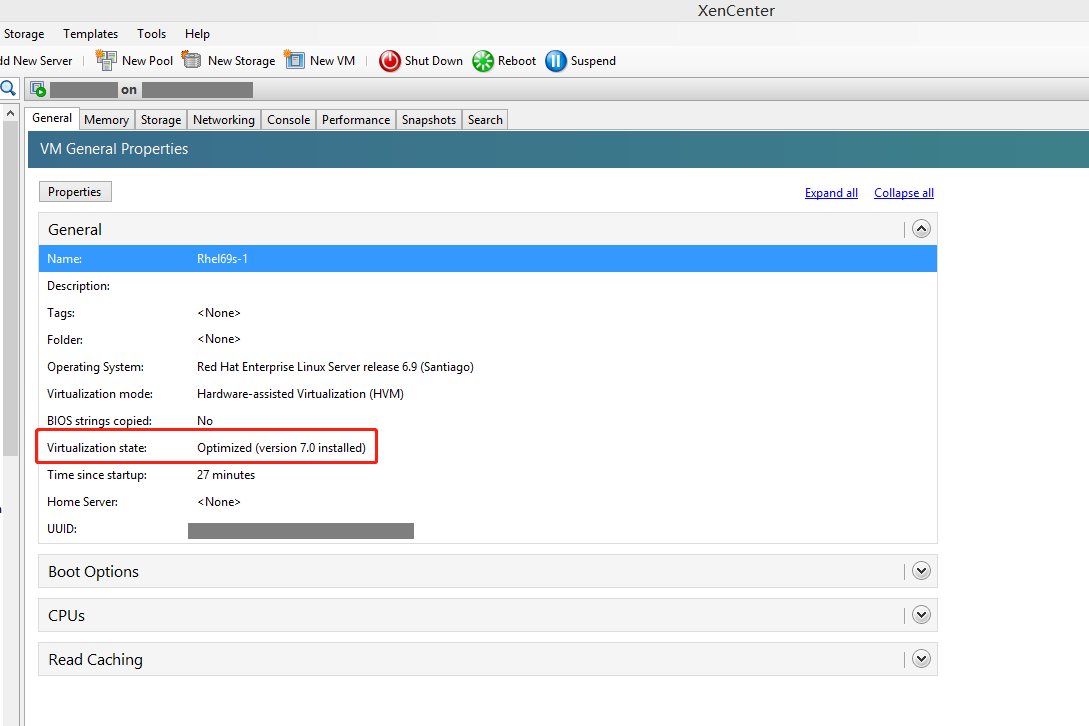
Check the virtualization state of the template VM on the General tab in XenCenter. If Citrix VM Tools are installed correctly, the virtualization state is Optimized:
Step 1b: (For Ubuntu 16.04 only) Install OpenJDK 11
On Ubuntu 16.04, install OpenJDK 11 by completing the following steps:
- Download the latest OpenJDK 11 from https://jdk.java.net/archive/.
- Run the
tar zxf openjdk-11.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzcommand to unzip the downloaded package. - (Optional) Run the
mv jdk-11.0.2/ <target directory>command to save OpenJDK in a target directory. - Run the
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java <custom directory>/bin/java 2000command to set up the Java runtime. - Run the
java -versioncommand to verify the version of Java.
Step 1c: Install the Linux VDA package on the template VM
Note:
To use a currently running VDA as the template VM, omit this step.
Before installing the Linux VDA package on the template VM, install .NET Core Runtime 3.1. For more information, see Installation overview.
Based on your Linux distribution, run the following command to set up the environment for the Linux VDA:
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo yum –y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg –i <PATH>/<Linux VDA DEB>
apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
For SUSE 12:
sudo zypper –i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 1d: Enable repositories to install the tdb-tools package
For RHEL 7 server:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
<!--NeedCopy-->
For RHEL 7 workstation:
subscription-manager repos --enable=rhel-7-workstation-optional-rpms
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 1e: Install the EPEL repository that contains ntfs-3g
Install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8/CentOS 8, RHEL 7/CentOS 7 so that running deploymcs.sh later installs the ntfs-3g package contained in it.
Step 1f: Manually install ntfs-3g on SUSE 12
On the SUSE 12 platform, there is no repository providing ntfs-3g. Download the source code, compile, and install ntfs-3g manually:
-
Install the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) compiler system and the make package:
sudo zypper install gcc sudo zypper install make <!--NeedCopy--> -
Download the ntfs-3g package.
-
Decompress the ntfs-3g package:
sudo tar -xvzf ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version>.tgz <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enter the path to the ntfs-3g package:
sudo cd ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install ntfs-3g:
./configure make make install <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 1g: Set up the runtime environment
Before running deploymcs.sh, do the following:
-
Change variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf. Themcs.confconfiguration file contains variables for setting MCS and the Linux VDA. The following are variables you can set as required:-
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDA: Determines whether to use the existing configurations of the currently running VDA. If set to Y, configuration files on MCS-created machines are the same as the equivalents on the currently running VDA. However, you still must configure thednsandAD_INTEGRATIONvariables. The default value is N, which means configuration files on MCS-created machines are determined by configuration templates on the master image. -
dns: Sets the DNS IP address. -
AD_INTEGRATION: Sets Winbind or SSSD. For a matrix of the Linux distributions and domain joining methods that MSC supports, see Supported distributions in this article. -
WORKGROUP: Sets the workgroup name (case-sensitive) if it is configured in AD.
-
-
On the template machine, add command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile for writing or updating registry values as required. This action prevents the loss of data and settings every time an MCS-provisioned machine restarts.Each line in the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile is a command for setting or updating a registry value.For example, you can add the following command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile to write or update a registry value respectively:create -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" --force <!--NeedCopy-->update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 1h: Create a master image
- Run
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh. -
(Optional) On the template VM, update the configuration templates to customize the relevant
/etc/krb5.conf,/etc/samba/smb.conf, and/etc/sssd/sssd.conffiles on all created VMs.For Winbind users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_krb5.conf.tmpland/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.For SSSD users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd.conf.tmpl,/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_krb5.conf.tmpl, and/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.Note:
Keep the existing format used in the template files and use variables such as $WORKGROUP, $REALM, $realm, and $AD_FQDN.
- On Citrix Hypervisor, shut down the template VM. Create and name a snapshot of your master image.
Step 2: Create a Machine Catalog
In Citrix Studio, create a Machine Catalog and specify the number of VMs to create in the catalog. Do other configuration tasks as needed. For more information, see Create a machine catalog using Studio.
Step 3: Create a Delivery Group
A Delivery Group is a collection of machines selected from one or more Machine Catalogs. The Delivery Group specifies which users can use those machines, and the applications and desktops available to those users. For more information, see Create Delivery Groups.
Use MCS to create Linux VMs on Azure
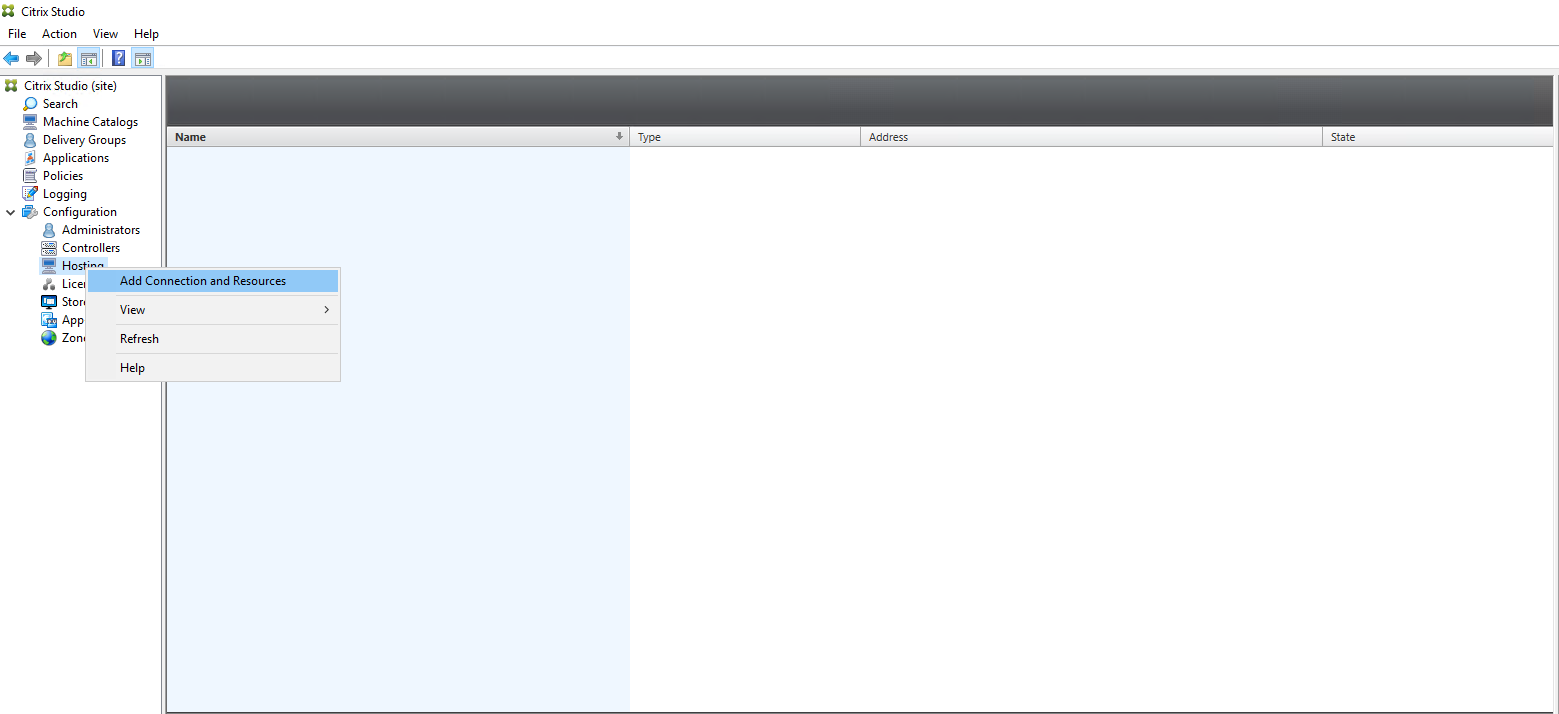
Step 1: Create a hosting connection to Azure in Citrix Studio
-
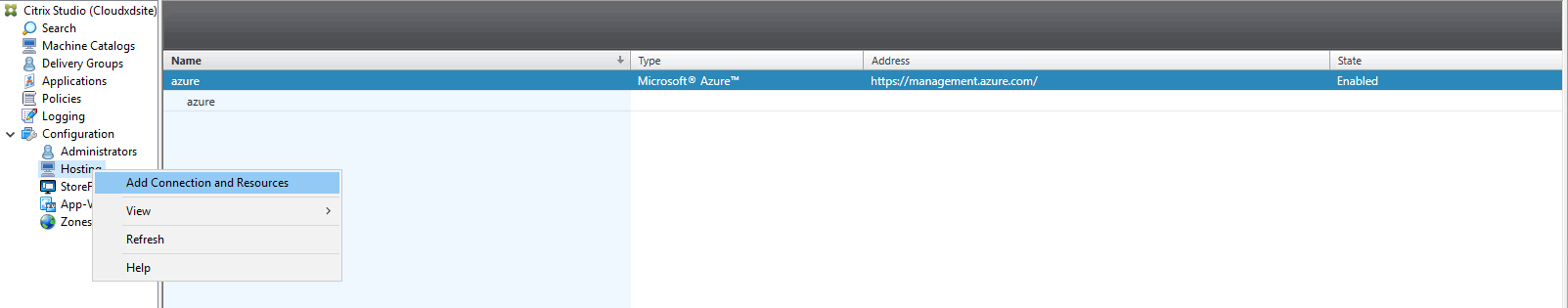
In Citrix Studio on Citrix Cloud™, choose Configuration > Hosting > Add Connection and Resources to create a connection to Azure.
-
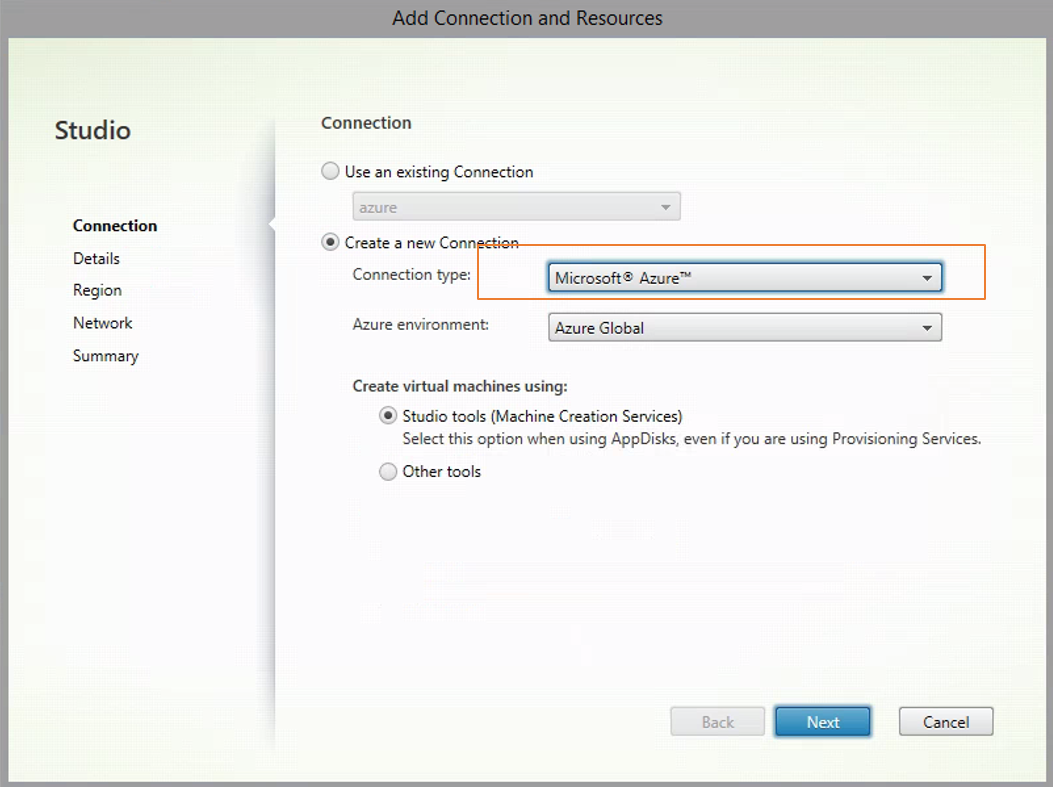
Choose Microsoft Azure as the connection type.
-
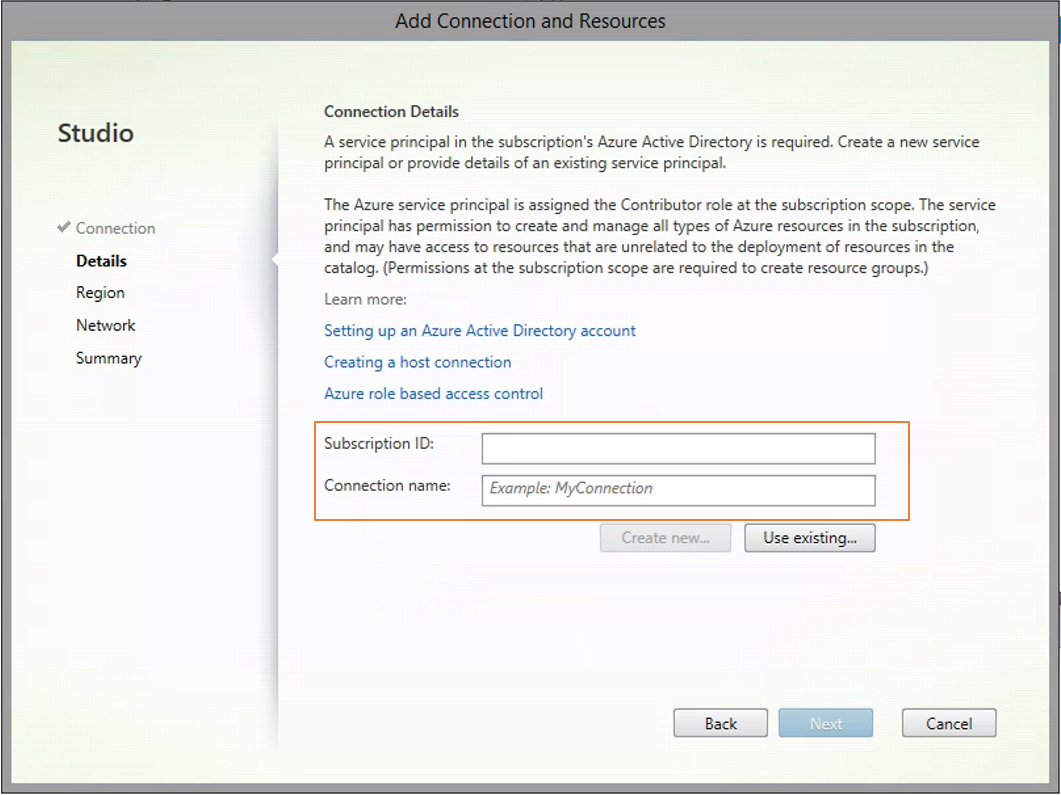
Type the subscription ID of your Azure account and your connection name.
A new connection appears in the hosting pane.
Step 2: Prepare a master image on the template VM
A master image contains the operating system, non-virtualized applications, VDA, and other software. To prepare a master image, do the following:
Step 2a: Configure cloud-init for Ubuntu 18.04
To ensure that a VDA host name persists when a VM is restarted or stopped, run the following command.
echo "preserve_hostname: true" > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99_hostname.cfg
<!--NeedCopy-->
Ensure that the following lines are present under the system_info section in the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg file:
system_info:
network:
renderers: ['netplan', 'eni', 'sysconfig']
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2b: (For Ubuntu 16.04 only) Install OpenJDK 11
On Ubuntu 16.04, install OpenJDK 11 by completing the following steps:
- Download the latest OpenJDK 11 from https://jdk.java.net/archive/.
- Run the
tar zxf openjdk-11.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzcommand to unzip the downloaded package. - (Optional) Run the
mv jdk-11.0.2/ <target directory>command to save OpenJDK in a target directory. - Run the
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java <custom directory>/bin/java 2000command to set up the Java runtime. - Run the
java -versioncommand to verify the version of Java.
Step 2c: Install the Linux VDA package on the template VM
Note:
To use a currently running VDA as the template VM, omit this step.
Before installing the Linux VDA package on the template VM, install .NET Core Runtime 3.1. For more information, see Installation overview.
Based on your Linux distribution, run the following command to set up the environment for the Linux VDA:
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo yum –y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg –i <PATH>/<Linux VDA DEB>
apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
For SUSE 12:
sudo zypper –i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2d: Install the EPEL repository that contains ntfs-3g
Install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8/CentOS 8, RHEL 7/CentOS 7 so that running deploymcs.sh later installs the ntfs-3g package contained in it.
Step 2e: Manually install ntfs-3g on SUSE 12
On the SUSE 12 platform, there is no repository providing ntfs-3g. Download the source code, compile, and install ntfs-3g manually:
-
Install the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) compiler system and the make package:
sudo zypper install gcc sudo zypper install make <!--NeedCopy--> -
Download the ntfs-3g package.
-
Decompress the ntfs-3g package:
sudo tar -xvzf ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version>.tgz <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enter the path to the ntfs-3g package:
sudo cd ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install ntfs-3g:
./configure make make install <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2f: Set up the runtime environment
Before running deploymcs.sh, do the following:
-
Change variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf. Themcs.confconfiguration file contains variables for setting MCS and the Linux VDA. The following are some of the variables, of whichdnsandAD_INTEGRATIONmust be set:Note: If a variable can be set with multiple values, put the values inside single quotes and separate them with spaces. For example, LDAP_LIST=’aaa.lab:389 bbb.lab:389.’
-
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDA: Determines whether to use the existing configurations of the currently running VDA. If set to Y, configuration files on MCS-created machines are the same as the equivalents on the currently running VDA. However, you still must configure thednsandAD_INTEGRATIONvariables. The default value is N, which means configuration files on MCS-created machines are determined by configuration templates on the master image. -
dns: Sets the DNS IP address. -
AD_INTEGRATION: Sets Winbind or SSSD (SSSD is not supported on SUSE). -
WORKGROUP: Sets the workgroup name (case-sensitive) if it is configured in AD.
-
-
On the template machine, add command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile for writing or updating registry values as required. This action prevents the loss of data and settings every time an MCS-provisioned machine restarts.Each line in the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile is a command for setting or updating a registry value.For example, you can add the following command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile to write or update a registry value respectively:create -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" --force <!--NeedCopy-->update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2g: Create a master image
- Run
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh. -
(Optional) On the template VM, update the configuration templates to customize the relevant
/etc/krb5.conf,/etc/samba/smb.conf, and/etc/sssd/sssd.conffiles on all created VMs.For Winbind users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_krb5.conf.tmpland/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.For SSSD users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd.conf.tmpl,/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_krb5.conf.tmpl, and/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.Note: Keep the existing format used in the template files and use variables such as $WORKGROUP, $REALM, $realm, and $AD_FQDN.
-
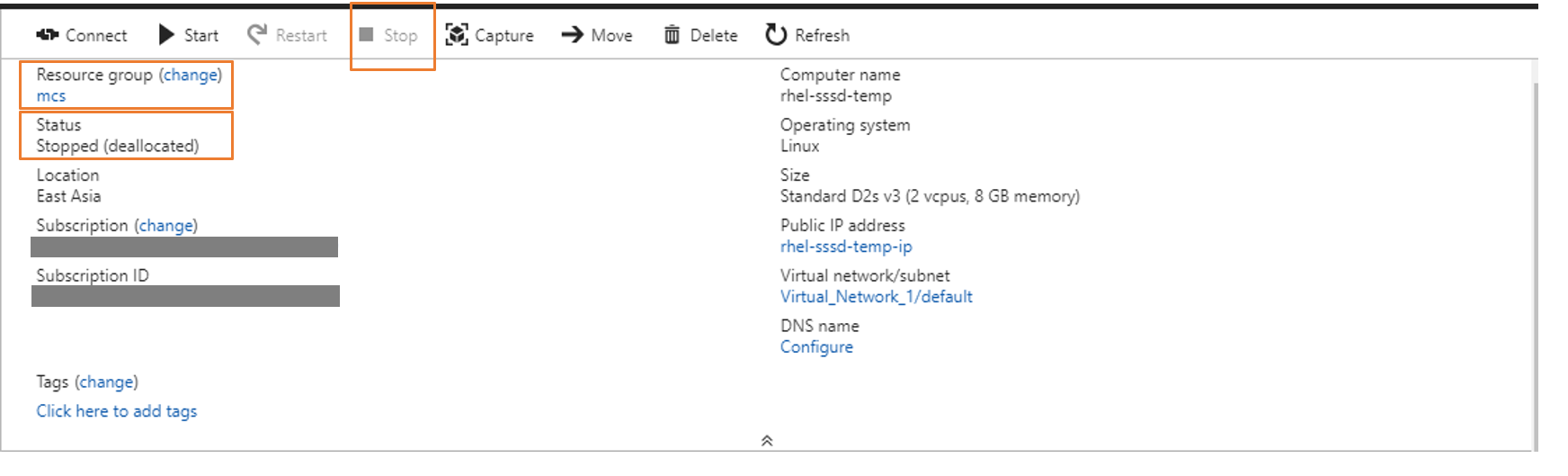
Install applications on the template VM and shut down the template VM from the Azure portal. Ensure that the power status of the template VM is Stopped (deallocated). Remember the name of the resource group here. You need the name to locate your master image on Azure.
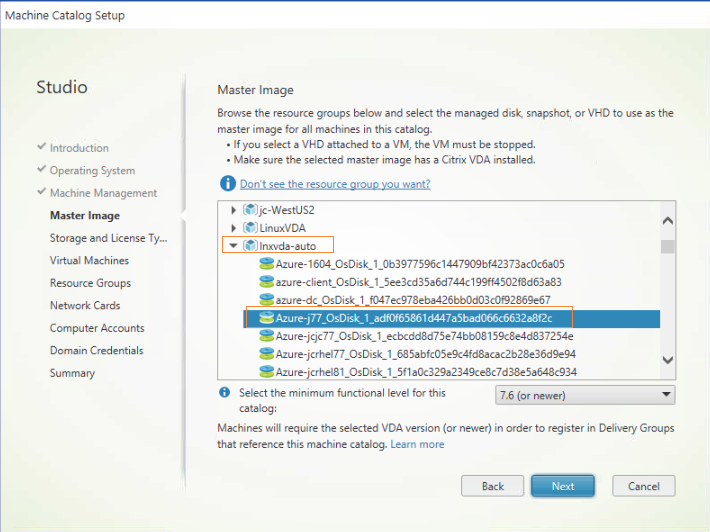
Step 3: Create a Machine Catalog
In Citrix Studio, create a Machine Catalog and specify the number of VMs to create in the catalog. When creating the Machine Catalog, choose your master image from the resource group where the template VM belongs and find the VHD of the template VM.
Do other configuration tasks as needed. For more information, see Create a machine catalog using Studio.
Step 4: Create a Delivery Group
A Delivery Group is a collection of machines selected from one or more Machine Catalogs. The Delivery Group specifies which users can use those machines, and the applications and desktops available to those users. For more information, see Create Delivery Groups.
Use MCS to create Linux VMs on VMware vSphere
Step 1: Create a hosting connection to VMware in Citrix Studio
-
Install vCenter Server in the vSphere environment. For more information, see VMware vSphere.
-
In Citrix Studio, choose Configuration > Hosting > Add Connection and Resources to create a connection to VMware vSphere.

-
Choose VMware vSphere as the connection type.
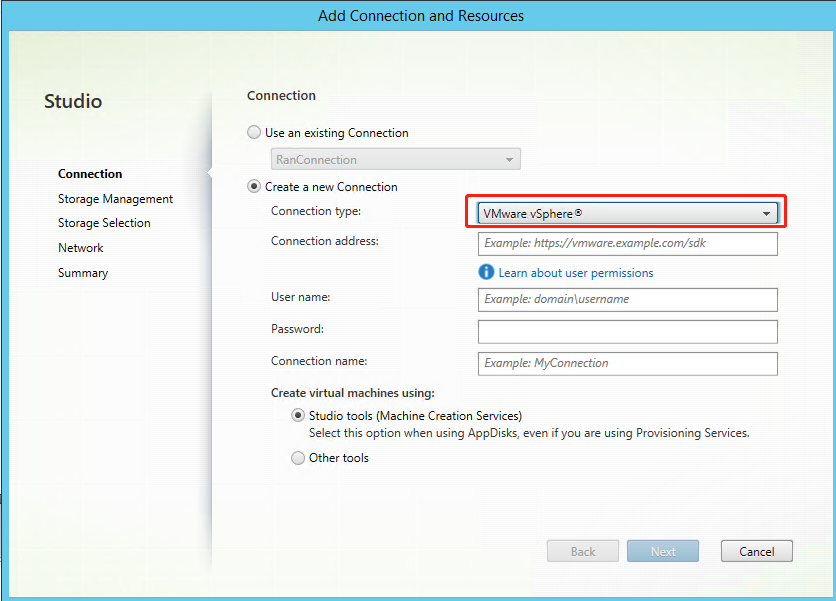
-
Type the connection address (the vCenter Server URL) of your VMware account, your user name and password, and your connection name.
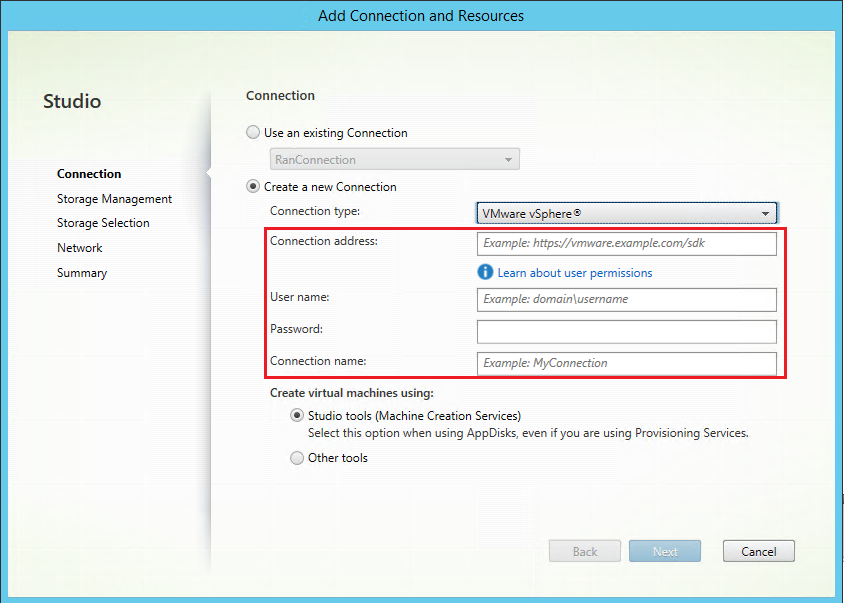
A new connection appears in the hosting pane.
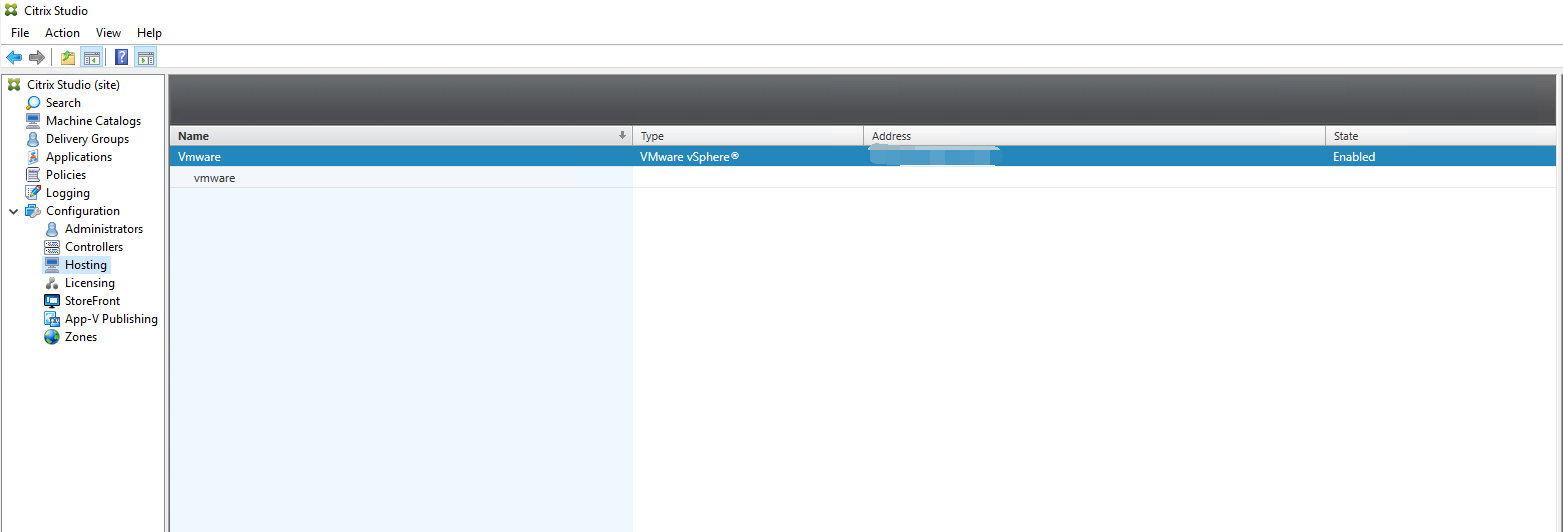
Step 2: Prepare a master image
A master image contains the operating system, non-virtualized applications, VDA, and other software. To prepare a master image, do the following:
Step 2a: (For Ubuntu 16.04 only) Install OpenJDK 11
On Ubuntu 16.04, install OpenJDK 11 by completing the following steps:
- Download the latest OpenJDK 11 from https://jdk.java.net/archive/.
- Run the
tar zxf openjdk-11.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzcommand to unzip the downloaded package. - (Optional) Run the
mv jdk-11.0.2/ <target directory>command to save OpenJDK in a target directory. - Run the
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java <custom directory>/bin/java 2000command to set up the Java runtime. - Run the
java -versioncommand to verify the version of Java.
Step 2b: Install the Linux VDA package on the template VM
Note:
To use a currently running VDA as the template VM, omit this step.
Before installing the Linux VDA package on the template VM, install .NET Core Runtime 3.1. For more information, see Installation overview.
Based on your Linux distribution, run the following command to set up the environment for the Linux VDA:
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo yum –y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg –i <PATH>/<Linux VDA DEB>
apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
For SUSE 12:
sudo zypper –i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2c: Install the EPEL repository that contains ntfs-3g
Install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8/CentOS 8, RHEL 7/CentOS 7 so that running deploymcs.sh later installs the ntfs-3g package contained in it.
Step 2d: Manually install ntfs-3g on SUSE 12
On the SUSE 12 platform, there is no repository providing ntfs-3g. Download the source code, compile, and install ntfs-3g manually:
-
Install the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) compiler system and the make package:
sudo zypper install gcc sudo zypper install make <!--NeedCopy--> -
Download the ntfs-3g package.
-
Decompress the ntfs-3g package:
sudo tar -xvzf ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version>.tgz <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enter the path to the ntfs-3g package:
sudo cd ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install ntfs-3g:
./configure make make install <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2e: Set up the runtime environment
Before running deploymcs.sh, do the following:
-
Change variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf. Themcs.confconfiguration file contains variables for setting MCS and the Linux VDA. The following are some of the variables, of whichdnsandAD_INTEGRATIONmust be set:Note: If a variable can be set with multiple values, put the values inside single quotes and separate them with spaces. For example, LDAP_LIST=’aaa.lab:389 bbb.lab:389.’
-
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDA: Determines whether to use the existing configurations of the currently running VDA. If set to Y, the configuration files on MCS-created machines are the same as the equivalents on the currently running VDA. However, you still must configure thednsandAD_INTEGRATIONvariables. The default value is N, which means configuration files on MCS-created machines are determined by configuration templates on the master image. -
dns: Sets the DNS IP address. -
AD_INTEGRATION: Sets Winbind or SSSD (SSSD is not supported on SUSE). -
WORKGROUP: Sets the workgroup name (case-sensitive) if it is configured in AD.
-
-
On the template machine, add command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile for writing or updating registry values as required. This action prevents the loss of data and settings every time an MCS-provisioned machine restarts.Each line in the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile is a command for setting or updating a registry value.For example, you can add the following command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile to write or update a registry value respectively:create -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" --force <!--NeedCopy-->update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2f: Create a master image
- Run
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh. -
(Optional) On the template VM, update the configuration templates to customize the relevant /etc/krb5.conf, /etc/samba/smb.conf, and /etc/sssd/sssd.conf files on all created VMs.
For Winbind users, update the /etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_krb5.conf.tmpl and /etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_smb.conf.tmpl templates.
For SSSD users, update the /etc/xdl/mcs/sssd.conf.tmpl, /etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_krb5.conf.tmpl, and /etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_smb.conf.tmpl templates.
Note: Keep the existing format used in the template files and use variables such as $WORKGROUP, $REALM, $realm, and $AD_FQDN.
- After you finish installing applications on the template VM, shut down the template VM from the VMware. Take a snapshot of the template VM.
Step 3: Create a Machine Catalog
In Citrix Studio, create a Machine Catalog and specify the number of VMs to create in the catalog. When creating the Machine Catalog, choose your master image from the snapshot list.
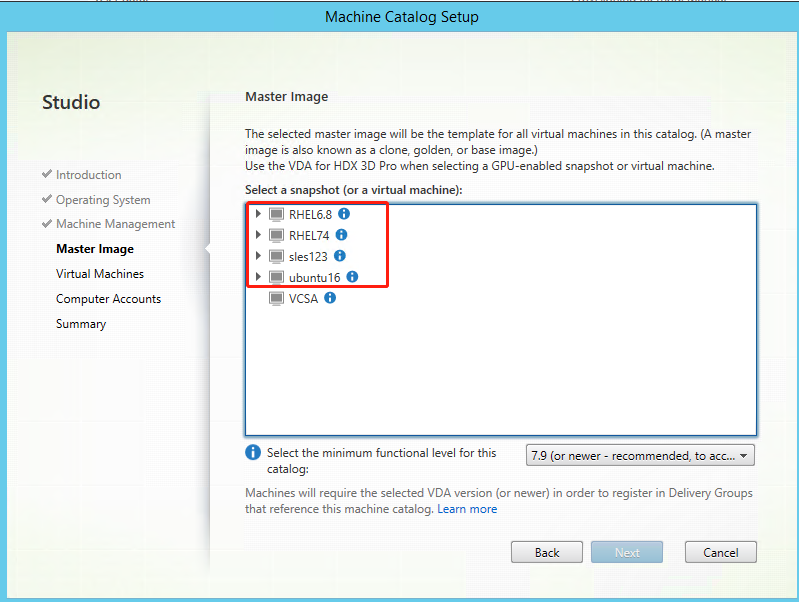
Do other configuration tasks as needed. For more information, see Create a machine catalog using Studio.
Step 4: Create a Delivery Group
A Delivery Group is a collection of machines selected from one or more Machine Catalogs. The Delivery Group specifies which users can use those machines, and the applications and desktops available to those users. For more information, see Create Delivery Groups.
Use MCS to create Linux VMs on AWS
Step 1: Create a hosting connection to AWS in Citrix Studio
-
In Citrix Studio on Citrix Cloud, choose Configuration > Hosting > Add Connection and Resources to create a connection to AWS.
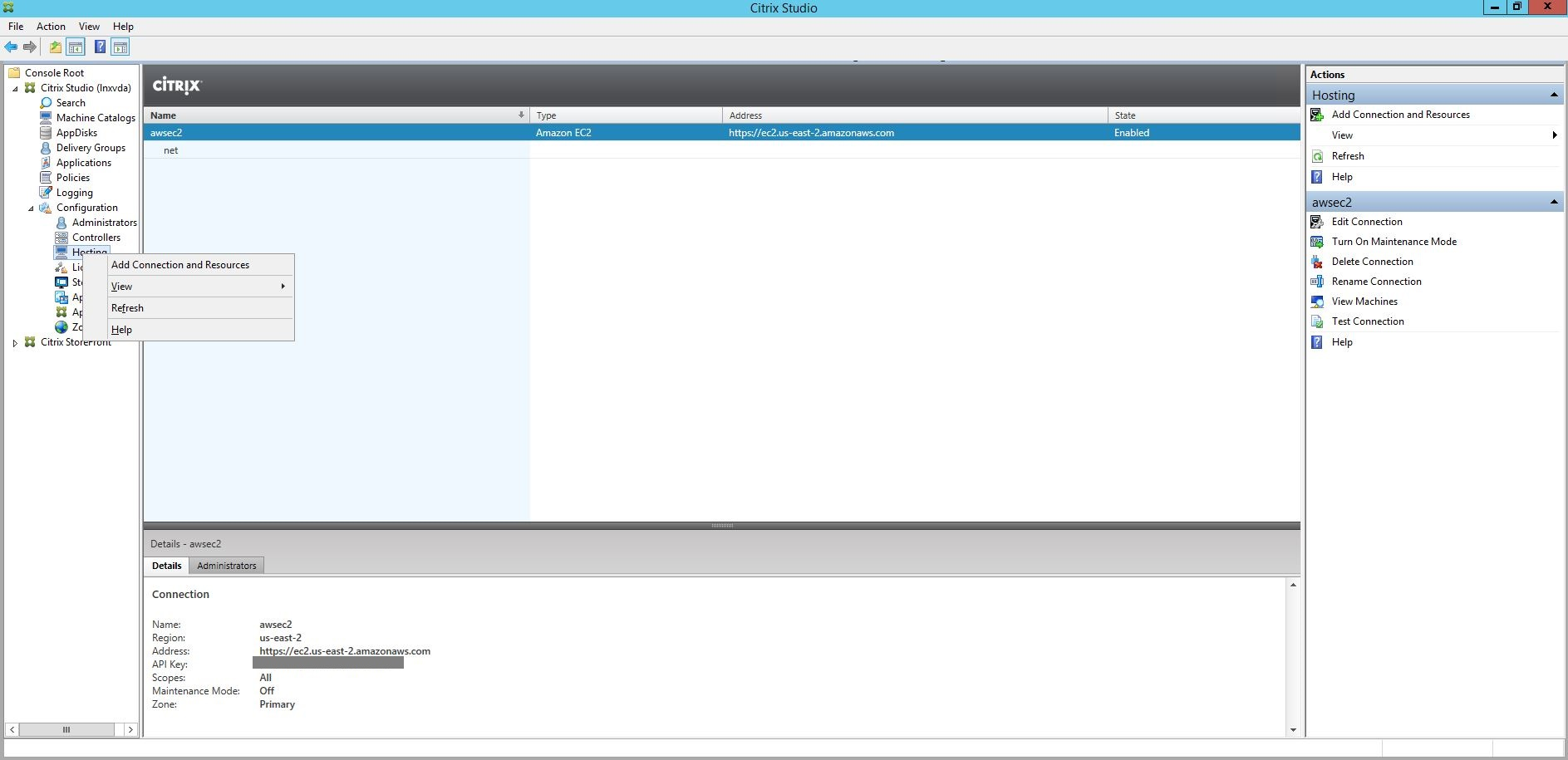
-
Choose Amazon EC2 as the connection type.
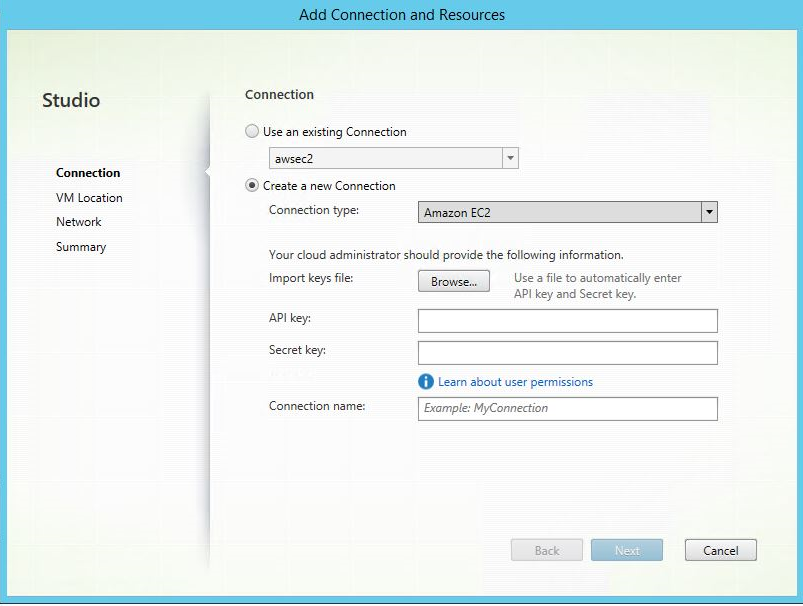
-
Type the API key and secret key of your AWS account and type your connection name.
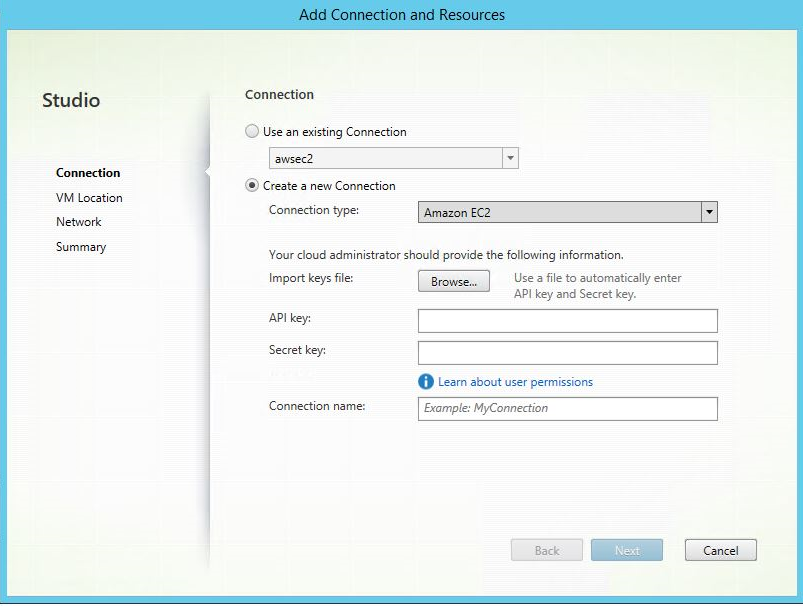
The API key is your access key ID and the Secret key is your secret access key. They are considered as an access key pair. If you lose your secret access key, you can delete the access key and create another one. To create an access key, do the following:
- Sign in to the AWS services.
- Navigate to the Identity and Access Management (IAM) console.
- On the left navigation pane, choose Users.
- Select the target user and scroll down to select the Security credentials tab.
- Scroll down and click Create access key. A new window appears.
- Click Download .csv file and save the access key to a secure location.
A new connection appears in the hosting pane.
Step 2: Prepare a master image
A master image contains the operating system, non-virtualized applications, VDA, and other software. To prepare a master image, do the following:
Step 2a: Configure cloud-init
-
To ensure that a VDA host name persists when an EC2 instance is restarted or stopped, run the following command to preserve the VDA host name.
echo "preserve_hostname: true" > /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99_hostname.cfg <!--NeedCopy-->For Ubuntu 18.04, ensure that the following lines are present under the system_info section in the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg file:
system_info: network: renderers: ['netplan', 'eni', 'sysconfig'] <!--NeedCopy--> -
To use SSH for remotely accessing MCS-created VMs on AWS, enable password authentication because no key name is attached to those VMs. Do the following as needed.
-
Edit the
cloud-initconfiguration file, /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg. Ensure that the ssh_pwauth: true line is present. Remove or comment the set-password line and the following lines if they exist.users: - default <!--NeedCopy--> - If you plan to use the default user
ec2-userorubuntucreated bycloud-init, you can change the user password by using thepasswdcommand. Keep the new password in mind for later use to log in to the MCS-created VMs. -
Edit the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile to ensure that the following line is present:PasswordAuthentication yes <!--NeedCopy-->Save the file and run the
sudo service sshd restartcommand.
-
Step 2b: (For Ubuntu 16.04 only) Install OpenJDK 11
On Ubuntu 16.04, install OpenJDK 11 by completing the following steps:
- Download the latest OpenJDK 11 from https://jdk.java.net/archive/.
- Run the
tar zxf openjdk-11.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzcommand to unzip the downloaded package. - (Optional) Run the
mv jdk-11.0.2/ <target directory>command to save OpenJDK in a target directory. - Run the
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java <custom directory>/bin/java 2000command to set up the Java runtime. - Run the
java -versioncommand to verify the version of Java.
Step 2c: Install the Linux VDA package on the template VM
Note:
To use a currently running VDA as the template VM, omit this step.
Before installing the Linux VDA package on the template VM, install .NET Core Runtime 3.1. For more information, see Installation overview.
Based on your Linux distribution, run the following command to set up the environment for the Linux VDA:
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo yum –y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg –i <PATH>/<Linux VDA DEB>
apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
For SUSE 12:
sudo zypper –i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2d: Install the EPEL repository that contains ntfs-3g
Install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8/CentOS 8, RHEL 7/CentOS 7 so that running deploymcs.sh later installs the ntfs-3g package contained in it.
Step 2e: Manually install ntfs-3g on SUSE 12
On the SUSE 12 platform, there is no repository providing ntfs-3g. Download the source code, compile, and install ntfs-3g manually:
-
Install the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) compiler system and the make package:
sudo zypper install gcc sudo zypper install make <!--NeedCopy--> -
Download the ntfs-3g package.
-
Decompress the ntfs-3g package:
sudo tar -xvzf ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version>.tgz <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enter the path to the ntfs-3g package:
sudo cd ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install ntfs-3g:
./configure make make install <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2f: Set up the runtime environment
Before running deploymcs.sh, do the following:
-
Change variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf. Themcs.confconfiguration file contains variables for setting MCS and the Linux VDA. The following are some of the variables, of whichdnsandAD_INTEGRATIONmust be set:Note: If a variable can be set with multiple values, put the values inside single quotes and separate them with spaces. For example, LDAP_LIST=’aaa.lab:389 bbb.lab:389.’
-
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDA: Determines whether to use the existing configurations of the currently running VDA. If set to Y, the configuration files on MCS-created machines are the same as the equivalents on the currently running VDA. However, you still must configure thednsandAD_INTEGRATIONvariables. The default value is N, which means configuration files on MCS-created machines are determined by configuration templates on the master image. -
dns: Sets the DNS IP address. -
AD_INTEGRATION: Sets Winbind or SSSD (SSSD is not supported on SUSE). -
WORKGROUP: Sets the workgroup name (case-sensitive) if it is configured in AD.
-
-
On the template machine, add command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile for writing or updating registry values as required. This action prevents the loss of data and settings every time an MCS-provisioned machine restarts.Each line in the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile is a command for setting or updating a registry value.For example, you can add the following command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile to write or update a registry value respectively:create -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" --force <!--NeedCopy-->update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 2g: Create a master image
- Run
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh. -
(Optional) On the template VM, update the configuration templates to customize the relevant
/etc/krb5.conf,/etc/samba/smb.conf, and/etc/sssd/sssd.conffiles on all created VMs.For Winbind users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_krb5.conf.tmpland/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.For SSSD users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd.conf.tmpl,/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_krb5.conf.tmpl, and/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.Note: Keep the existing format used in the template files and use variables such as $WORKGROUP, $REALM, $realm, and $AD_FQDN.
-
Install applications on the template VM and shut down the template VM from the AWS EC2 portal. Ensure that the instance state of the template VM is Stopped.
-
Right-click the template VM and select Image > Create Image. Type information and make settings as needed. Click Create Image.
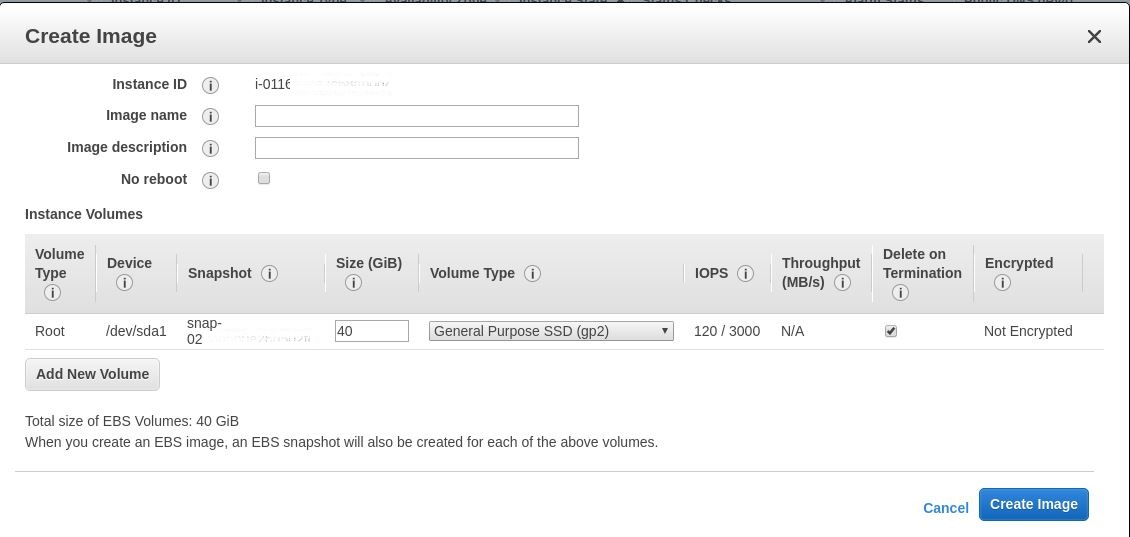
Step 3: Create a Machine Catalog
In Citrix Studio, create a Machine Catalog and specify the number of VMs to create in the catalog. When creating the Machine Catalog, choose your machine template (the master image you created earlier) and select one or more security groups.
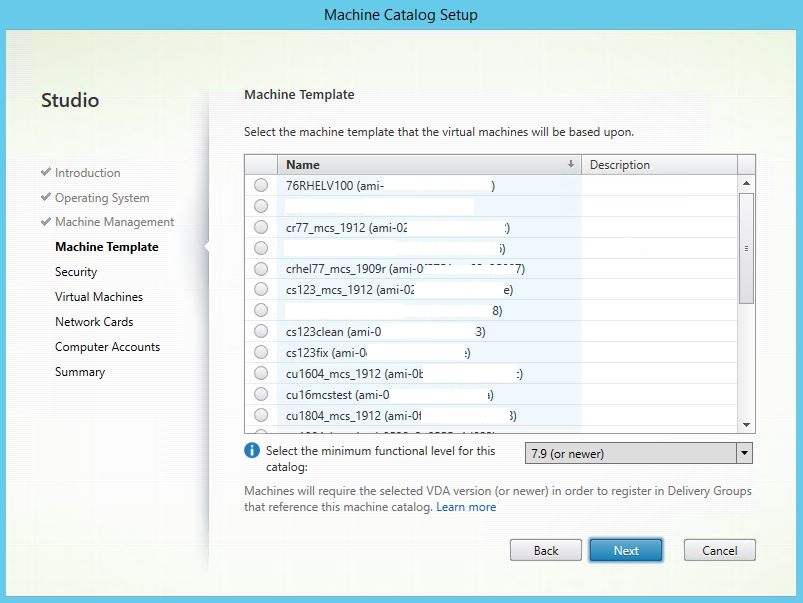
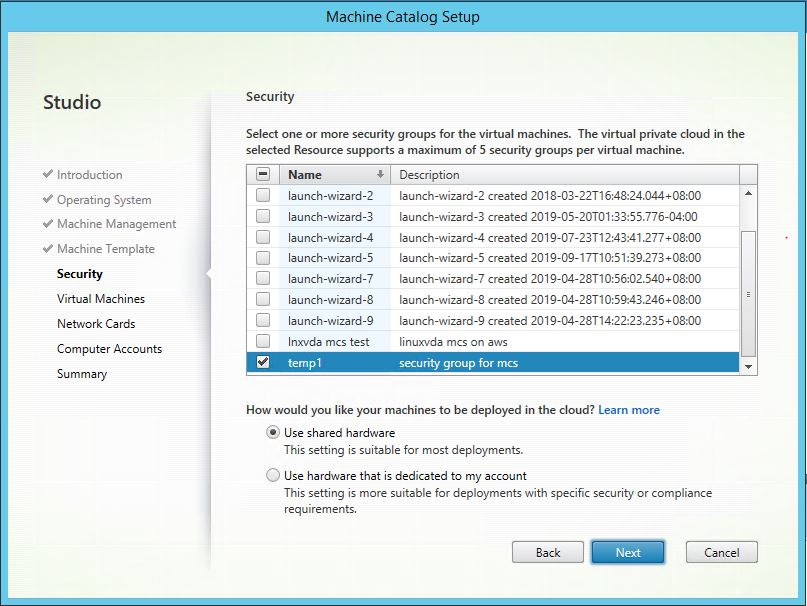
Do other configuration tasks as needed. For more information, see Create a machine catalog using Studio.
Step 4: Create a Delivery Group
A Delivery Group is a collection of machines selected from one or more Machine Catalogs. The Delivery Group specifies which users can use those machines, and the applications and desktops available to those users. For more information, see Create Delivery Groups.
Use MCS to create Linux VMs on GCP
Step 1: Set up your GCP environment
For more information, see Google Cloud Platform virtualization environments.
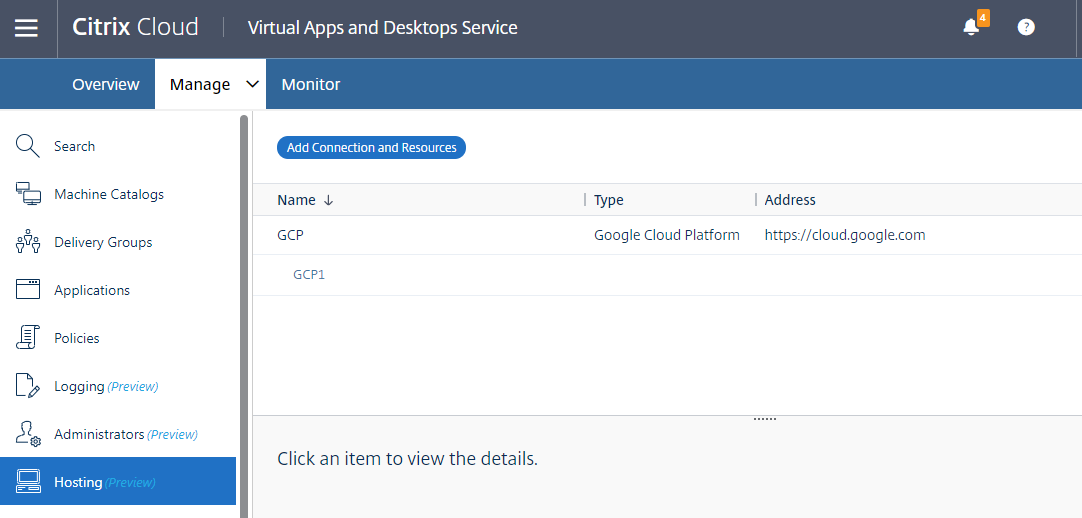
Step 2: Create a hosting connection to GCP in Citrix Studio
-
In Citrix Studio on Citrix Cloud, choose Configuration > Hosting > Add Connection and Resources to create a connection to GCP.
-
Choose Google Cloud Platform as the connection type.
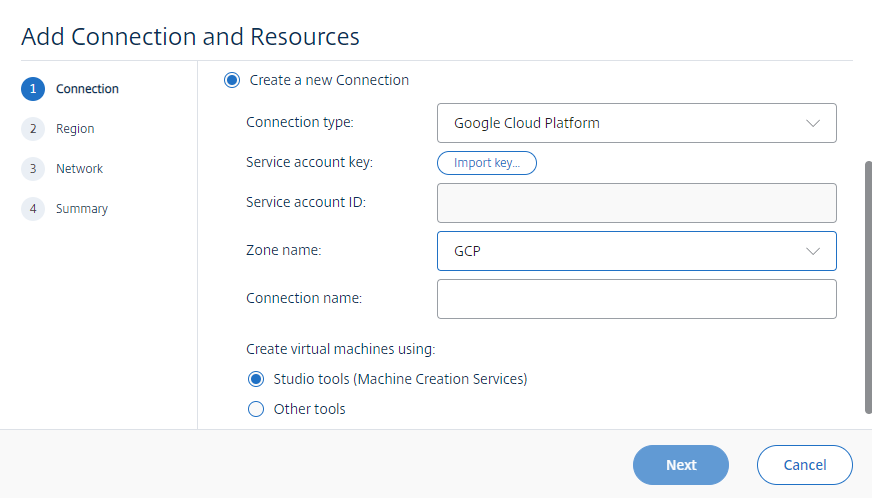
-
Import the service account key of your GCP account and type your connection name.
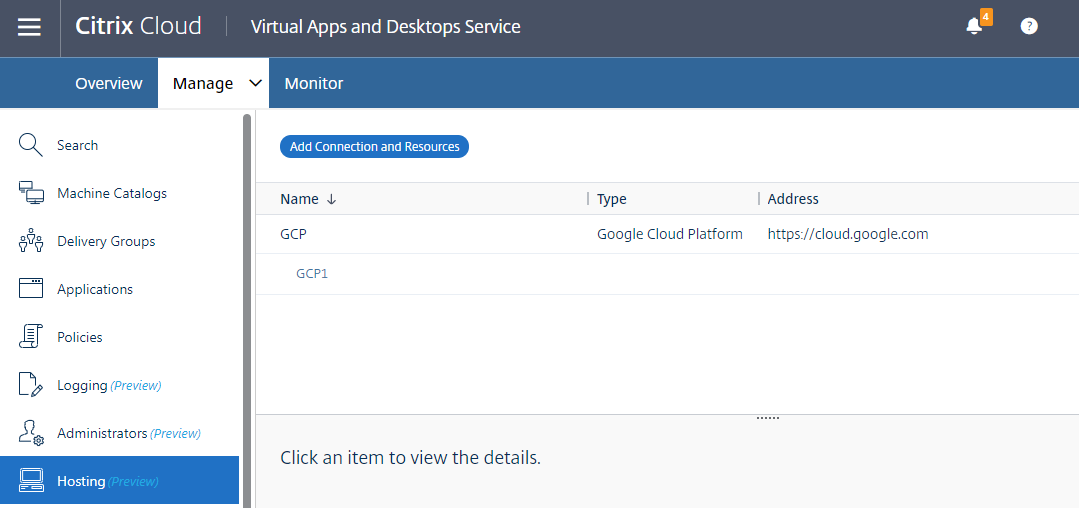
A new connection appears in the hosting pane.
Step 3: Prepare a master image
A master image contains the operating system, non-virtualized applications, VDA, and other software. To prepare a master image, do the following:
Step 3a: (For Ubuntu 16.04 only) Install OpenJDK 11
On Ubuntu 16.04, install OpenJDK 11 by completing the following steps:
- Download the latest OpenJDK 11 from https://jdk.java.net/archive/.
- Run the
tar zxf openjdk-11.0.2_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzcommand to unzip the downloaded package. - (Optional) Run the
mv jdk-11.0.2/ <target directory>command to save OpenJDK in a target directory. - Run the
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java <custom directory>/bin/java 2000command to set up the Java runtime. - Run the
java -versioncommand to verify the version of Java.
Step 3b: Install the Linux VDA package on the template VM
Note:
To use a currently running VDA as the template VM, omit this step.
Before installing the Linux VDA package on the template VM, install .NET Core Runtime 3.1. For more information, see Installation overview.
Based on your Linux distribution, run the following command to set up the environment for the Linux VDA:
For RHEL/CentOS:
sudo yum –y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
For Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo dpkg –i <PATH>/<Linux VDA DEB>
apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
For SUSE 12:
sudo zypper –i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 3c: Install the EPEL repository that contains ntfs-3g
Install the EPEL repository on RHEL 8/CentOS 8, RHEL 7/CentOS 7 so that running deploymcs.sh later installs the ntfs-3g package contained in it.
Step 3d: Manually install ntfs-3g on SUSE 12
On the SUSE 12 platform, there is no repository providing ntfs-3g. Download the source code, compile, and install ntfs-3g manually:
-
Install the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) compiler system and the make package:
sudo zypper install gcc sudo zypper install make <!--NeedCopy--> -
Download the ntfs-3g package.
-
Decompress the ntfs-3g package:
sudo tar -xvzf ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version>.tgz <!--NeedCopy--> -
Enter the path to the ntfs-3g package:
sudo cd ntfs-3g_ntfsprogs-<package version> <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install ntfs-3g:
./configure make make install <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 3e: Set up the runtime environment
Before running deploymcs.sh, do the following:
-
Change variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf. Themcs.confconfiguration file contains variables for setting MCS and the Linux VDA. The following are some of the variables, of whichdnsandAD_INTEGRATIONmust be set:Note: If a variable can be set with multiple values, put the values inside single quotes and separate them with spaces. For example, LDAP_LIST=’aaa.lab:389 bbb.lab:389.’
-
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDA: Determines whether to use the existing configurations of the currently running VDA. If set to Y, the configuration files on MCS-created machines are the same as the equivalents on the currently running VDA. However, you still must configure thednsandAD_INTEGRATIONvariables. The default value is N, which means configuration files on MCS-created machines are determined by configuration templates on the master image. -
dns: Sets the DNS IP address. -
AD_INTEGRATION: Sets Winbind or SSSD (SSSD is not supported on SUSE). -
WORKGROUP: Sets the workgroup name (case-sensitive) if it is configured in AD.
-
-
On the template machine, add command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile for writing or updating registry values as required. This action prevents the loss of data and settings every time an MCS-provisioned machine restarts.Each line in the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile is a command for setting or updating a registry value.For example, you can add the following command lines to the
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.regfile to write or update a registry value respectively:create -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" --force <!--NeedCopy-->update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Clipboard\ClipboardSelection" -v "Flags" -d "0x00000003" <!--NeedCopy-->
Step 3f: Create a master image
- Run
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh. -
(Optional) On the template VM, update the configuration templates to customize the relevant
/etc/krb5.conf,/etc/samba/smb.conf, and/etc/sssd/sssd.conffiles on all created VMs.For Winbind users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_krb5.conf.tmpland/etc/xdl/mcs/winbind_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.For SSSD users, update the
/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd.conf.tmpl,/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_krb5.conf.tmpl, and/etc/xdl/mcs/sssd_smb.conf.tmpltemplates.Note:
Keep the existing format used in the template files and use variables such as $WORKGROUP, $REALM, $realm, and $AD_FQDN.
- After you finish installing applications on the template VM, shut down the template VM from the VMware. Take a snapshot of the template VM.
Step 4: Create a Machine Catalog
In Citrix Studio, create a Machine Catalog and specify the number of VMs to create in the catalog. When creating the Machine Catalog, choose your master image from the snapshot list.

Do other configuration tasks as needed. For more information, see Create a machine catalog using Studio.
Step 5: Create a Delivery Group
A Delivery Group is a collection of machines selected from one or more Machine Catalogs. The Delivery Group specifies which users can use those machines, and the applications and desktops available to those users. For more information, see Create Delivery Groups.
Use MCS to upgrade your Linux VDA
To use MCS to upgrade your Linux VDA, do the following:
-
Ensure that you installed .NET Core Runtime 3.1 before you upgrade your Linux VDA to the current release.
-
Upgrade your Linux VDA on the template machine:
For RHEL 7 and CentOS 7:
sudo rpm -U XenDesktopVDA-<version>.el7_x.x86_64.rpm <!--NeedCopy-->For RHEL 8 and CentOS 8:
sudo rpm -U XenDesktopVDA-<version>.el8_x.x86_64.rpm <!--NeedCopy-->For SUSE 12:
sudo rpm -U XenDesktopVDA-<version>.sle12_x.x86_64.rpm <!--NeedCopy-->For Ubuntu 16.04:
sudo dpkg -i xendesktopvda_<version>.ubuntu16.04_amd64.deb <!--NeedCopy-->For Ubuntu 18.04:
sudo dpkg -i xendesktopvda_<version>.ubuntu18.04_amd64.deb <!--NeedCopy-->For Ubuntu 20.04:
sudo dpkg -i xendesktopvda_<version>.ubuntu20.04_amd64.deb <!--NeedCopy--> -
Edit
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.confand/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs_local_setting.reg. -
Take a new snapshot.
-
In Citrix Studio, select the new snapshot to update your Machine Catalog. Wait before each machine restarts. Do not restart a machine manually.
Automate machine account password updates
Machine account passwords, by default, expire 30 days after the machine catalog is created. To prevent password expiration and to automate machine account password updates, do the following:
-
Add the following entry to /etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf before running /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh.
UPDATE_MACHINE_PW="enabled" -
After running /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh, open /etc/cron.d/mcs_update_password_cronjob to set the update time and frequency. The default setting updates machine account passwords weekly at 2:30AM, Sunday.
After each machine account password update, the ticket cache on the Delivery Controller becomes invalid and the following error might appear in /var/log/xdl/jproxy.log:
[ERROR] - AgentKerberosServiceAction.Run: GSSException occurred. Error: Failure unspecified at GSS-API level (Mechanism level: Checksum failed)
To eliminate the error, clear the ticket cache regularly. You can schedule a cache cleanup task on all Delivery Controllers or on the domain controller.
Enable FAS on MCS-created VMs
You can enable FAS on MCS-created VMs that run on the following distributions:
| Winbind | SSSD | Centrify | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHEL 8, CentOS 8 | Yes | No | No |
| RHEL 7, CentOS 7 | Yes | Yes | No |
| Ubuntu 20.04 | Yes | No | No |
| Ubuntu 18.04 | Yes | No | No |
| Ubuntu 16.04 | Yes | No | No |
| Debian 10.7 | Yes | No | No |
| SUSE 12.5 | Yes | No | No |
Enable FAS when you are preparing a master image on the template VM
-
Run the script
opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.shand set all environment variables such as the list of FAS servers. For more information about the environment variables, see Easy install.sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.sh <!--NeedCopy--> -
Import the root CA certificate.
sudo cp root.pem /etc/pki/CA/certs/ <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run ctxfascfg.sh.
- Set variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf.- Set the value of
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDAto Y. - Set the
FAS_LISTvariable to your FAS server address or multiple FAS server addresses that are separated by semicolons and enclosed by double quotes, for example,FAS_LIST="<FAS_SERVER_FQDN>;<FAS_SERVER_FQDN>". - Set the other variables as required, such as
VDI_MODE.
- Set the value of
- Run the script
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/deploymcs.sh.
Enable FAS on an MCS-created VM
If FAS is not enabled on the template machine as described earlier, you can enable FAS on each MCS-created VM.
To enable FAS on an MCS-created VM, do the following:
-
Set variables in /etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.conf.
- Set the value of
Use_Existing_Configurations_Of_Current_VDAto Y. - Set the
FAS_LISTvariable to your FAS server address. - Set the other variables as required, such as
VDI_MODE.
- Set the value of
-
Import the root CA certificate.
sudo cp root.pem /etc/pki/CA/certs/ <!--NeedCopy--> -
Run the
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxfascfg.shscript.
Note:
You must set all necessary variables in
/etc/xdl/mcs/mcs.confbecause these variables are called upon VM startup.
In this article
- Supported distributions
- Use MCS to create Linux VMs on Citrix Hypervisor
- Use MCS to create Linux VMs on Azure
- Use MCS to create Linux VMs on VMware vSphere
- Use MCS to create Linux VMs on AWS
- Use MCS to create Linux VMs on GCP
- Use MCS to upgrade your Linux VDA
- Automate machine account password updates
- Enable FAS on MCS-created VMs