Farm
Use the information in this section to configure a farm using the Citrix Provisioning™ console. This section includes information about the following elements:
- General tab
- Security tab
- Groups tab
- Licensing tab
- Options tab
- Virtual disk Version tab
- Status tab
- Registration tab
- Encryption tab
- Logging tab
The tables that follow identify and describe properties on each tab of the Farm Properties dialog.
General tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter or edit the name of this farm. |
| Description | Enter or edit a description for this farm. |
This tab displays warning messages if the farm is not entitled.
Security tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Add | Click Add to apply farm administrator privileges to a group. Select each box next to the groups to which you want to apply farm administrator read-only privileges. |
| Remove | Select the groups that you want to remove from the administrator role. Click Remove to remove the selected groups. |
Groups tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Add button | Click the Add button to open the Add System Groups dialog. To display all security groups, leave the text box set to the default *. To display groups, type part of the name using wildcards *. For example, if you want to see MY_DOMAIN\Builtin\Users, type: User*, Users, or ser. However, if you type MY_DOMAIN\Builtin\*, you get all groups, not just those groups in the MY_DOMAIN\Builtin path. Select the checkboxes next to each group included in this farm. Note: Filtering on groups was introduced in 5.0 SP2 for efficiency purposes. |
| Remove button | Click the Remove button to remove existing groups from this farm. Highlight the groups to which privileges do not apply. |
Licensing tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| License server name | Display the FQDN or IP Address of the license server. |
| License server port | Enter the port number that the license server uses or accept the default, which is 27000. |
| Web Services for Licensing Port | Enter the port number that the web services for licensing uses or accept the default, which is 8083. |
Options tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto add | When using this feature, select the site used by new target devices. If the No default site is chosen, the site of that Citrix Provisioning server that logs in the target device is used. Use the No default site setting if your farm has site scoped PXE/TFTP servers. Important: Enable this feature when adding new target devices. Enabling this feature results in computers being added without the approval of a farm administrator. |
| Auditing | Enable or disable the auditing feature for this farm. |
| Offline database support | Enable or disable the offline database support option. This option allows servers within this farm to use a snapshot of the database in case the connection is lost. |
Note:
The Send anonymous statistics and usage information checkbox, which enables the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP), is no longer available.
Virtual disk version tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert if number of versions from base image exceeds | Set an alert if the number of versions from the base image is exceeded. |
| Default access mode for new merge versions | Select the access mode for the virtual disk version after a merge completes. Options include; Maintenance, Test (default), or Production. Note: If the access mode is set to Production and a test version exists, the state of the resulting auto-merged version is automatically set to Maintenance or Test. If a Maintenance version exists, an automatic merge is not performed. |
| Merge after automated virtual disk update, if over the alert threshold | Enable automatic merge. Enable the automatic merge feature if the number or virtual disk versions exceeds the alert threshold. The minimum value is 3 and the maximum value is 100. |
Status tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Status of the farm | Provides database status information, information on group access rights being used, and information on joining status of farm to Citrix Cloud or a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ site. |
Registration tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| State | If you are joining your farm to Citrix Cloud, then this field provides information on the joining status of your farm to Citrix Cloud and customer ID and name. If you are joining your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps™ and Desktops site, then this field provides information on the joining status of your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, and site name. |
| Unregistered servers | Lists the servers in the farm that are not yet registered to Citrix Cloud™ or a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site. |
Encryption tab
Using this tab, you can:
- Monitor the encryption key rotation status
- See the list of Citrix Provisioning servers that are waiting on key distribution
- Rotate the encryption key
Key rotation distributes a new database encryption key to all the Citrix Provisioning servers in the farm. After the distribution is complete, the database is re-encrypted with this new key. This process ensures enhanced database security.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| State | States of the encryption that are Distributing keys, Re-encrypting Database, and Idle. |
| Offline servers | Lists the servers in the farm that are offline. |
The descriptions of the states of the encryption are as follows:
Distributing Keys: This is the first state of key rotation. In this state, the new database encryption key is being synchronized with all the Citrix Provisioning servers. The farm remains in the Distributing Keys state until all the servers have the latest encryption key. To retrieve the new encryption key, a Citrix Provisioning server:
- must be active (that is, must not be offline) until it gets the new encryption key. You can turn off the server once it gets the new encryption key.
Re-encrypting Database: This is the next state after Distributing Keys. In this state, after all the Citrix Provisioning servers in the farm get the new encryption key, the encrypted fields in the database are re-encrypted with this new encryption key.
Idle: This is the next state after re-encrypting the database. This state implies that the key rotation process is complete. The Rotate Encryption Key button is enabled when the encryption status is Idle. After you click Rotate Encryption Key, the state changes to Distributing Keys.
Note:
- Each encryption key cycling job takes a minimum of 5 to 10 minutes to move to the next state. However, the process is delayed if there are offline Citrix Provisioning servers.
- You might see a Citrix Provisioning server that initiated the key rotation in the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution even after the server in the farm gets the new encryption key immediately. Wait for approximately 5 minutes for that server to finish its key rotation process, after which it moves out of the list.
- You cannot add new Citrix Provisioning servers in the farm when the state is Distributing Keys or Re-encrypting Database.
- If you create a new farm using the Configuration Wizard, wait for the state to change to Idle and only then add new Citrix Provisioning servers to the farm.
- To add a Citrix Provisioning server to an existing farm, ensure that at least one server that has the encryption key is active (that is, must not be offline) so that the new server gets the encryption key. If no server is online, the new server fails to get added to the farm. In that case, ensure at least one server is active, and then rerun the Configuration Wizard on the new server that you want to add.
- Do not delete the Provisioning Services keys from the registry. If they get deleted, there must be at least one Citrix Provisioning Server in the farm that has the encryption data with which the database and registry fields were encrypted. We recommend taking registry backups including the
HKLM\Software\Citrix\ProvisioningServicesregistry key.
Using PowerShell and MCLI commands to rotate encryption key
You can now use PowerShell and MCLI commands to rotate encryption keys. Before using the commands, make sure that encryption status is Idle.
Using PvsPsSnapIn:
- Open the PowerShell window.
- Install the PowerShell Snap-In. The path where the
Citrix.PVS.SnapIn.dllis installed is:C:\Program Files\Citrix\Provisioning Services Console\Citrix.PVS.SnapIn.dll -
Run
Start-PvsRotateEncryptionKeysto start the key rotation process. After you run the command, the key rotation status changes to Distributing Keys.Note:
If you run the command
Start-PvsRotateEncryptionKeyswhen the key rotation status isDistributing KeysorRe-encrypting Database, you get an error because the key rotation is in process and keys can be rotated only when the key rotation status is Idle. -
Run
Get-PvsKeyRotationPendingServerscommand to get the list of servers in the farm that are waiting on key distribution and servers that are offline.Note:
- When the key rotation status is:
- Distributing Keys, you get the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution.
- Re-encrypting Database or Idle, you get the list of servers that are offline.
- You might see a Citrix Provisioning server that initiated the key rotation in the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution even after the server in the farm gets the new encryption key immediately. Wait for approximately 5 minutes for that server to finish its key rotation process, after which it moves out of the list.
- When the key rotation status is:
- Turn on any server that is offline. Ensure that the servers in the farm can communicate with each other.
-
After the key rotation process is complete, the status of the key rotation must change to Idle. Run the command
Get-PvsFarmto verify the key rotation status. The values of the propertyEncryptionStatus:- 0: Idle state
- 1: Distributing Keys
- 2: Re-encrypting Database
Note:
Each encryption key cycling job takes a minimum of 5 to 10 minutes to move to the next status. However, the process is delayed if there are offline Citrix Provisioning servers and servers waiting on key distribution.
Using MCLI.exe:
- Open the PowerShell window.
-
Run
.\MCLI.exe Run CycleEncryptionKeysto start the key rotation process. After you run the command, the key rotation status changes toDistributing Keys.Note:
If you run the command
.\MCLI.exe Run CycleEncryptionKeyswhen the key rotation status is Distributing Keys or Re-encrypting Database, you get an error because the key rotation is in process and keys can be rotated only when the key rotation status is Idle. -
Run
.\MCLI.exe Get PendingServerscommand to get the list of servers in the farm that are waiting on key distribution and servers that are offline.Note:
- When the key rotation status is:
- Distributing Keys, you get the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution.
- Re-encrypting Database or Idle, you get the list of servers that are offline.
- You might see a Citrix Provisioning server that initiated the key rotation in the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution even after the server in the farm gets the new encryption key immediately. Wait for approximately 5 minutes for that server to finish its key rotation process, after which it moves out of the list.
- When the key rotation status is:
- Turn on any server that is offline. Ensure that the servers in the farm can communicate with each other.
-
After the key rotation process is complete, the status of the key rotation must change to Idle. Run the command
.\MCLI.exe Get Farm -fto verify the key rotation status. The values of the propertyEncryptionStatus:- 0: Idle state
- 1: Distributing Keys
- 2: Re-encrypting Database
Note:
Each encryption key cycling job takes a minimum of 5–10 minutes to move to the next status. However, the process is delayed if there are offline Citrix Provisioning servers and servers waiting on key distribution.
Using McliPsSnapIn:
- Open the PowerShell window.
- Install the PowerShell Snap-In. The path where the
Citrix.PVS.SnapIn.dllis installed is:Import-Module "C:\Program Files\Citrix\Provisioning Services Console\McliPSSnapIn.dll" -
Run
Mcli-Run CycleEncryptionKeysto start the key rotation process. After you run the command, the key rotation status changes to Distributing Keys.Note:
If you run the command
Mcli-Run CycleEncryptionKeyswhen the key rotation status is Distributing Keys or Re-encrypting Database, you get an error because the key rotation is in process and keys can be rotated only when the key rotation status is Idle. -
Run
Mcli-Get PendingServersto get the list of servers in the farm that are waiting on key distribution and servers that are offline.Note:
- When the key rotation status is:
- Distributing Keys, you get the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution.
- Re-encrypting Database or Idle, you get the list of servers that are offline.
- You might see a Citrix Provisioning server that initiated the key rotation in the list of servers that are waiting on key distribution even after the server in the farm gets the new encryption key immediately. Wait for approximately 5 minutes for that server to finish its key rotation process, after which it moves out of the list.
- When the key rotation status is:
- Turn on any server that is offline. Ensure that the servers in the farm can communicate with each other.
-
After the key rotation process is complete, the status of the key rotation must change to Idle. Run the command
Mcli-Get Farmto verify the key rotation status. The values of the propertyEncryptionStatus:- 0: Idle state
- 1: Distributing Keys
- 2: Re-encrypting Database
Note:
Each encryption key cycling job takes a minimum of 5–10 minutes to move to the next status. However, the process is delayed if there are offline Citrix Provisioning servers and servers waiting on key distribution.
Logging tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Default log level for new target devices
|
Sets the default log level for all new target devices in a farm. The log levels are
|
Using the console to configure a farm
Run the Configuration Wizard on a provisioning server when creating a farm, adding new provisioning servers to an existing farm, or reconfiguring an existing provisioning server.
If all provisioning servers in the farm share configuration settings such as site and store information, consider Running the Configuration Wizard Silently.
Starting the configuration wizard
The Configuration Wizard starts automatically after Citrix Provisioning software is installed. The wizard can also be started by selecting Start > All Programs > Citrix > Citrix Provisioning > Citrix Provisioning Configuration Wizard.
Configuration wizard settings
Before running the Configuration Wizard, be prepared to make the following selections:
- Network topology
- Identify the farm
- Identify the database
- Create a store for a new farm
- Identify the site
- Join Citrix Cloud or Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
- Select the license server
- Configure user account settings
- Select network addresses for the stream service
- Configure bootstrap Server
- Finish the configuration
Note:
If errors occur during processing, the log is written to a
ConfigWizard.logfile atC:\ProgramData\Citrix\Provisioning Services\Log\.
The binary files (ETL files) are also logged by the Configuration Wizard. The log is written to a ConfigWizard.etl file at C:\ProgramData\Citrix\Provisioning Services\Log\. Only the latest log files are retained.
Tip:
The Configuration Wizard was modified at release 7.12 to include support for Linux streaming. See the installation article for information about the Linux streaming component.
Network topology
Complete the network configuration steps that follow.
-
Select the network service to provide IP addresses
Note: Use existing network services if possible. If existing network services cannot be used, choose to install the network services that are made available during the installation process.
To provide IP addresses to target devices, select from the following network service options:
- If the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) service is on this server, select the radio button next to one of the following network services to use, then click Next:
- Microsoft DHCP
- Citrix Provisioning BOOTP service
- Other BOOTP or DHCP service
- If the DHCP service is not on this server, select the radio button next to The service is running on another computer, then click Next.
- If the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) service is on this server, select the radio button next to one of the following network services to use, then click Next:
-
Select the network service to provide PXE boot information
Each target device downloads a boot file from a TFTP server.
Select the network service to provide target devices with PXE boot information:
- If you use Citrix Provisioning to deliver PXE boot information, select The service that runs on this computer. Then select from either of the following options, then click Next:
- Microsoft DHCP (options 66 and 67)
- Citrix Provisioning PXE Service
- If Citrix Provisioning does not deliver PXE boot information, select the The information is provided by a service on another device option, then click Next.
- If you use Citrix Provisioning to deliver PXE boot information, select The service that runs on this computer. Then select from either of the following options, then click Next:
Identify the farm
- Select from the following farm options:
-
Farm is already configured
- On the Farm Configuration dialog, select the option Farm is already configured, and click Next. This option appears only if a farm has been previously configured on this server.
-
Enter database administrator credentials in the pop-up dialog. Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the current login. Click Ok.
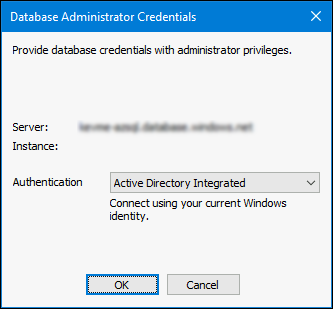
- Continue to the Configure user account settings procedure.
-
Create the farm
- On the Farm Configuration dialog, select the option Create a Farm, and click Next.
- On the Databse Server dialog,
-
Use the Browse button to browse for existing SQL databases and instances in the network, or type the database server name and instance.
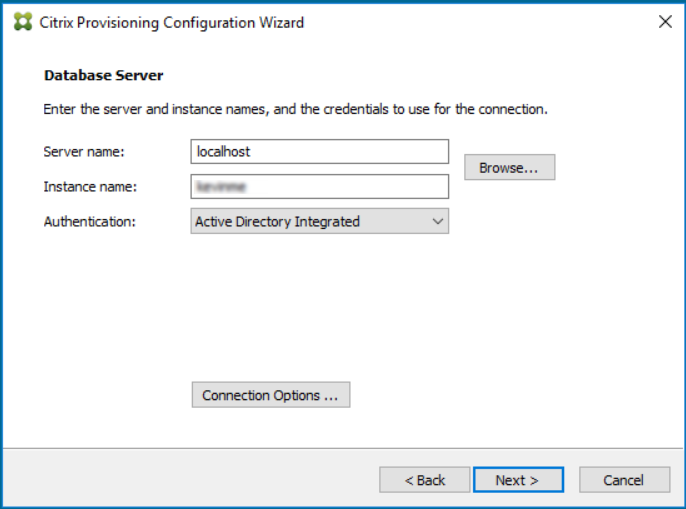
Note:
The combination of the database name and farm name must not exceed 54 characters. In such cases, the farm name displays as a truncated entry in the Existing Farms screen.
- To enable multi-subnet failover for SQL server, specify a database mirror failover partner, or enter a TCP port number, click Connection Options ….
- Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the services’ user account. Enter the database credentials that the Stream and SOAP services will use.
- Click Next.
-
-
Enter database administrator credentials in the pop-up dialog. Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the current login. Click Ok.

- Select the database location.
-
On the New Farm dialog, enter the database and farm names, and security groups.
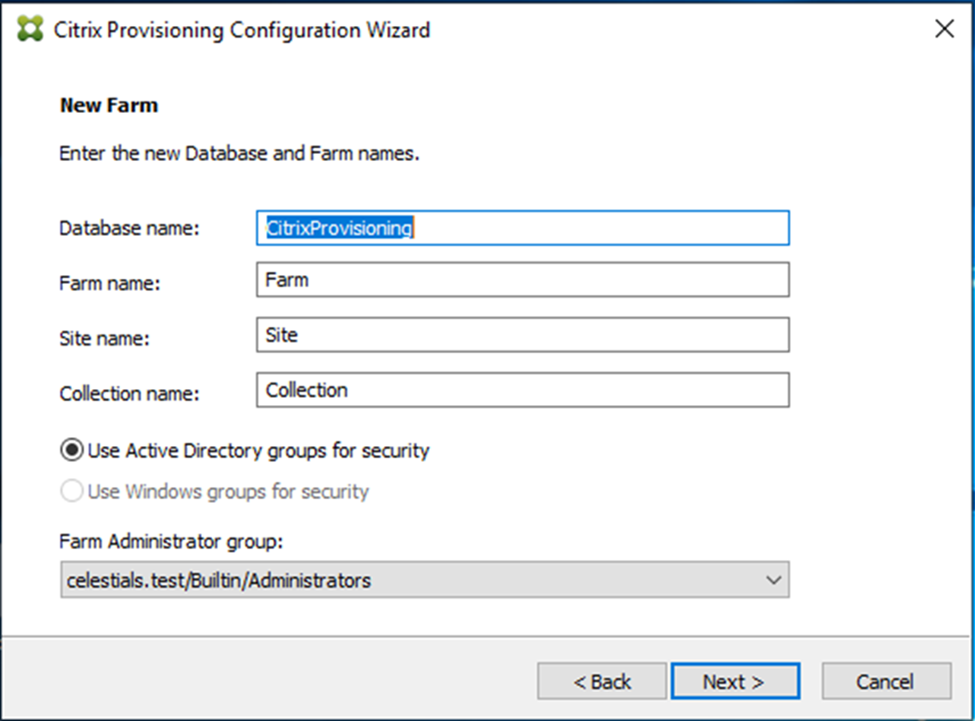
Note:
The Active Directory security group includes Built in groups, which are local to the current machine. Avoid using these groups as administrators, except for test environments. Some group names might be misleading and appear to be domain groups, but are local domain groups. For example,
ForestA.local/Builtin/Administrators.
-
Join an existing farm
- On the Farm Configuration dialog, select the option Join Existing Farm to add this provisioning server to an existing farm, then click Next.
- On the Databse Server dialog:
-
Use the Browse button to browse for the appropriate SQL database and instance within the network.

- Select the farm name that displays by default, or scroll to select the farm to join. Note: More than one farm can exist on a single server. This configuration is common in test implementations.
- To enable multi-subnet failover for SQL server, specify a database mirror failover partner, or enter a TCP port number, click Connection Options ….
- Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the services’ user account. Enter the database credentials that the Stream and SOAP services will use.
- Click Next.
-
-
Enter database administrator credentials in the pop-up dialog. Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the current login. Click Ok.

-
On the Existing Farm dialog, enter the farm database name, and click Verify. In case you do not have the farm database name, you can click Scan to scan for the farm database names.
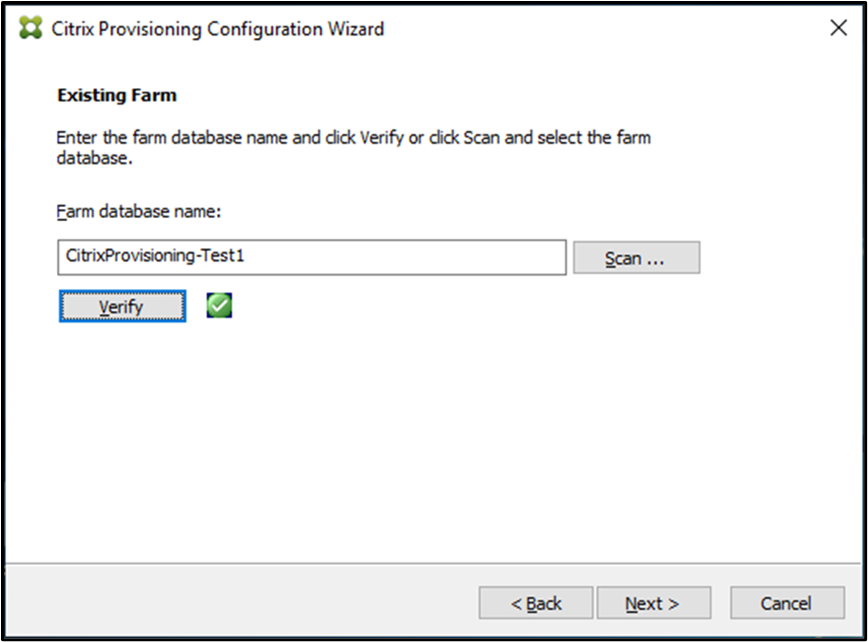
- Select from the following site options, then click Next:
- Existing Site: Select the site from the menu to join an existing site.
- New Site: Create a site by typing the name of the new site and a collection.
- Continue to select a store or enter a new store and default path.
-
Identify the database
Only one database exists within a farm. To identify the database:
-
If the database server location and instance have not yet been selected, complete the following procedure.
- On the Database Server dialog, click Browse to open the SQL Servers dialog.
-
From the list of SQL Servers, select the name of the server where this database exists. Specify the instance to use (to use the default instance, SQLEXPRESS, leave the instance name blank). In a test environment, this configuration can be a staged database.
Note:
Rerunning the Configuration Wizard to add extra provisioning server database entries, populates the Server Name and Instance Name text boxes. By default, SQL Server Express installs as an instance named SQLEXPRESS.
- Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the services’ user account. Enter the database credentials that the Stream and SOAP services will use.
- Click Next. If this database is a new farm, continue on to the Defining a Farm procedure.
-
To change the database to a new database
- On the old database server, perform a backup of the database to a file.
- On the new database server, restore the database from the backup file.
- Run the Configuration Wizard on each Citrix Provisioning server.
- Select Join existing farm on the Farm Configuration dialog.
- Enter the new database server and instance on the Database Server dialog.
- Select Active Directory Integrated authentication if you want to use the services’ user account. Enter the database credentials that the Stream and SOAP services will use.
- Select the restored database on the Existing Farm dialog.
- Select the site that the provisioning server was previously a member of on the Site dialog.
- Click Next until the Configuration Wizard finishes.
-
Define a farm. Select the security group to use:
-
Use Active Directory groups for security
Note:
When selecting the Active Directory group to act as the farm administrator from the menu, choices include any group the current user belongs to. This list includes Built in groups, which are local to the current machine. Avoid using these groups as administrators, except for test environments. Some group names might be misleading and appear to be domain groups, but are local domain groups. For example,
ForestA.local/Builtin/Administrators. -
Use Windows groups for security
-
-
Click Next.
Continue on to select the license server.
Create a store for a new farm
A new store can be created and assigned to the Citrix Provisioning server being configured:
Note: The Configuration Wizard only allows a server to create or join an existing store if it is new to the database. If a server exists in the database and it rejoins a farm, the Configuration Wizard might prompt the user to join a store or create a store. During this process, the selection is ignored.
- On the New Store page, name the new Store.
- Browse or enter the default path (for example: C:\PVSStore) to use to access this store, then click Next. If an invalid path is selected, an error message appears. Reenter a valid path, then continue. The default write cache location for the store is located under the store path for example: C:\PVSStore\WriteCache.
Identify the site
When joining an existing farm, identify the site where this provisioning server is a member. Identify a site by either creating a site or selecting an existing site within the farm. When a site is created, a default target device collection is automatically created for that site.
Join Citrix Cloud or Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
Using the Join Citrix Cloud or CVAD page, you can choose to join your farm with Citrix Cloud, a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, or choose to not join your farm.
Important:
- The Join Citrix Cloud or CVAD page appears only when the farm is NOT joined. If you select to join the farm to Citrix Cloud or Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, you do not see this page again.
- If you want to revert to a non-cloud joined or non-Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site joined farm, you must recreate the farm.
If you choose to join your farm with Citrix Cloud, then you can additionally:
- Provision Citrix Provisioning targets using the DaaS Studio.
If you choose to join your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, then you can additionally:
- Provision Citrix Provisioning targets using the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops Web Studio.
Note:
- For successfully joining your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, when running the Configuration Wizard, use a Windows login that has Machine Catalog Administrator or higher privileges in Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops.
- If you want to join your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, you must provision an SSL server certificate on all the servers in the farm. You can do this at a later step. See Creating self-signed certificates with PoSH.
-
On the Join Citrix Cloud or CVAD page, select one of the following:
- Do not join
- Join your farm with Citrix Cloud
- Join your farm with your Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
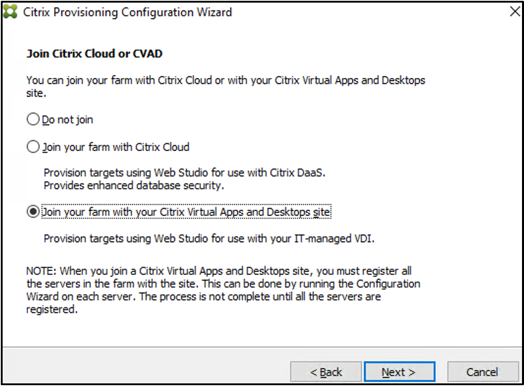
-
Click Next. If you choose to join your farm with Citrix Cloud or a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, then click Yes to confirm the action.
If you select to join your farm to Citrix Cloud or a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, see the required topics:
- If you select to join with Citrix Cloud
- If you select to join with a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
If you select to not join your farm, do the steps from Select the license server.
Note:
If you select to not join your farm, you see the Join Citrix Cloud or CVAD page every time you run the Configuration Wizard.
If you select to join with Citrix Cloud
If you select to join your farm with Citrix Cloud, follow these key steps:
- Using the Citrix Cloud Registration page, register all the Citrix Provisioning Servers with Citrix Cloud. However, if a server is already registered and the registration is still valid, the page is skipped, and you directly go to the Resource Location page. If a server was previously registered, however, the registration has become invalid, then you are prompted to register again. For more information on how to register, see Register with Citrix Cloud.
- Using the Resource Location page, select a resource location for the Citrix Provisioning target site. For more information on how to select the resource location, see Select a Resource Location.
- Continue with the steps from Select the license server.
Register with Citrix Cloud
Once you select to join your farm with Citrix Cloud, every server needs to be registered. Registration allows all the Citrix Provisioning Servers to authenticate and communicate with Citrix Cloud without the need to log in to Citrix Cloud. To register, do the following:
On the Citrix Cloud Registration page, do the following:
-
Review the page. If this is the first server to register, the page indicates that no customer has been established for the farm yet. Otherwise, you can see the customer ID on the page that is registered with the servers in the farm.
Note:
All the servers in the farm must register with the same customer account
-
Click Next to start the registration with Citrix Cloud. A message appears indicating that the Configuration Wizard is registering.
On the Confirm the Citrix Cloud Registration dialog:
- Follow the instructions as provided in the dialog to manually confirm the registration. This action requires you to log in to Citrix Cloud as account administrator.
- After the registration is confirmed, the dialog automatically closes. Do not press Cancel unless you wish to abort the Configuration Wizard.
Note:
If for some reason, you delete an unregistered Citrix Provisioning server when all the other servers are registered, the farm’s state is still considered partially joined. To resolve the issue, run the Configuration Wizard on any of the Citrix Provisioning servers that is joined to Citrix Cloud. Select the option Farm is already configured.
Select a Resource Location
On the Resource Location page:
-
Select a resource location for the Citrix Provisioning target site. You can also select No resource location from the options if:
- you do not use DaaS Web Studio to provision Citrix Provisioning targets.
- you use DaaS Web Studio to provision Citrix Provisioning targets, however, not for the specified Citrix Provisioning target site.
Note:
If a resource location has already been configured for the site, and you select a different resource location from the list, you get a confirmation pop-up after you click Next.
Continue with the steps from Select the license server.
If you select to join with a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
If you select to join your farm with a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site, you must select a Delivery Controller™ in the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site that you want to join.
Key steps:
- Using the Citrix Virtual Desktops™ Controller page, select a Delivery Controller. For more information, see Select a Delivery Controller.
- Continue with the steps from Select the license server.
Select a Delivery Controller
You must select a Delivery Controller in the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site that you want to join.
On the Citrix Virtual Desktops Controller page:
-
Review the page. If this is the first server to register, the page indicates that no Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site has joined the farm yet. In that case, select a Delivery Controller to establish the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site that the farm will join. If this is not the first server to register, you can see the name of the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site with which servers in the farm are registered.
Note:
All the servers in the farm must connect to the same Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site.
-
Click Next. The controller address is validated. You get an authorization error if you are not using a Windows login that has Machine Catalog Administrator or higher privileges on the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site.
Continue with the steps from Select the license server.
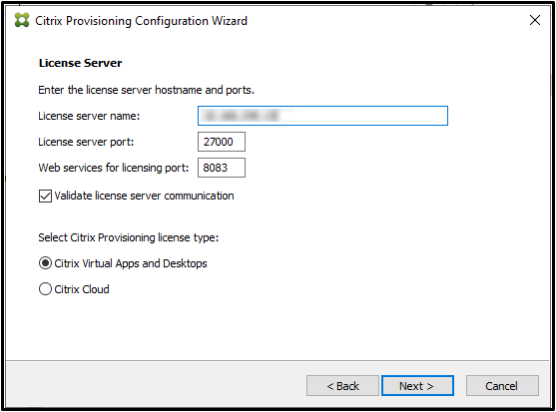
Select the license server
-
Enter the fully-qualified domain name of the license server. You can use a hostname, or an IP address if that is supported by the license server’s server certificate.
Note:
Every server certificate indicates the hostnames that can be used to connect to the server. The default server certificate on the license server only allows connections using the server’s fully qualified domain name. However, you can also use a hostname or IP address if that is supported by the license server’s server certificate. If the hostname is invalid for the server certificate that is used to connect (hostname mismatch), supported hostnames are suggested.
-
Enter the port number of License Server Port and Web Services for Licensing Port.
Default value of Licensing Server Port is 27000.
Default value of Web Services for Licensing Port is 8083.
The provisioning server must be able to communicate with both the licensing server port and web services for licensing port on the license server to get the appropriate product licenses.
-
The checkbox Validate license server communication is selected by default. This option verifies that the server can communicate with the license server and that the appropriate version of the license server is used. If the server is not able to communicate with the license server, or the wrong version of the license server is being used, an error message appears. You cannot proceed.
Note:
When you validate license server communication, the license server’s server certificate is also validated. If the license server is using a self-signed certificate that is valid but not trusted, you are prompted to add trust for the certificate. You can decline if you decide not to trust the certificate.
-
Select the license to be used.
Note:
- If you have a DaaS (Citrix Cloud) license, then select Citrix Cloud.
- If you have an on-premises Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops license or are operating independently of Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, then select Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops.
-
Click Next to continue on to configure user account settings.
Enable or disable scrambling of licensing telemetry data
Considering the sensitivity of information sent in the license telemetry, Citrix provides you an option to enable or disable scrambling of licensing telemetry data. Scrambling is enabled by default. However, you can disable scrambling on each new farm created using MCLI or PVS SnapIn commands.
The following table lists the data that is scrambled:
| Key | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
dvc -> dvcName |
Indicates the friendly name for the device. | E6oNXGy6fihiwi6cHdS/sg== |
workerSid |
Indicates a Unique identifier for the VDA used for the session. | GF/5+DT7Hb7DJIvIW+bYQA== |
Scrambling is enabled by default. To disable scrambling, do the following:
Use PvsPsSnapIn
- Open a PowerShell window.
- Install the PowerShell Snap-In using
Add-PSSnapin citrix*. -
Run the following command:
Set-PvsFarm -IsUsageDataScrambled:$true <!--NeedCopy-->
MCLI.exe
- Open the PowerShell window.
-
Run the following command:
MCLI.exe Set Farm -r isUsageDataScrambled=1 <!--NeedCopy-->
You can generate a mapping report (CSV list) of scrambled values to clear text values covering any data uploaded in the last one year using PowerShell commands.
- Open the PowerShell window.
-
Run the following command:
Get-pvsscrambleddatareport <!--NeedCopy-->
Sample mapping report:
| ScrambledData | Value |
|---|---|
| DjeASlHiVz5kDa+Ffm5DUg== | aaaa-m-2019 |
Note:
The scrambled data is retained for one year. The data older than a year is discarded.
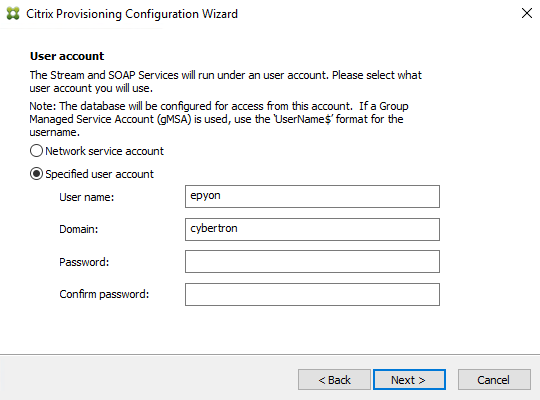
Configure user account settings
The Stream and Soap services run under a user account. Configure data reader and data writer database roles automatically using the Configuration Wizard to provide database access privileges to a user account.
-
On the User Account dialog, select the user account that the Stream and Soap services run under:
- Specified user account (required when using a Windows Share; workgroup or domain user account). Type the user name, domain, and password information in the appropriate text boxes.
- Network service account (minimum privilege local account that authenticates on the network as computers domain machine account). There are features that don’t work if you select Network service account. Therefore, the support for Network service account is deprecated from Citrix Provisioning version 2503.1.
-
Click Next, then continue on to selecting network cards for the Stream Service.
Group managed service accounts
Citrix Provisioning supports Group Managed Service Accounts (gMSA). These accounts are managed domain accounts providing automatic password management and simplified SPN management over multiple servers.
Deploy certificates
You must select a certificate for all the servers in the farm if you want to:
- Join your farm to a Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
- Use the Imaging Wizard for Linux targets
- Provision targets using the Citrix Provisioning API
Use the Citrix Provisioning Configuration Wizard to add the proper certificate from the local Computer personal certificates (My) store.
Note:
We recommend to use a CA-signed certificate but you can use a self-signed certificate if necessary.
For deploying a certificate:
- Import the certificate into
Mystore on the Citrix Provisioning server. - Install the root of trust of the certificate in the trusted root store of the client machines where connections are made (PVSAPI, Linux machine that is imaged and Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops Delivery Controller).
Note:
The set of operations depends on whether you use a CA-signed certificate or self-signed certificate.
- Run the Configuration Wizard. On the SSL Configuration page, select the certificate to use.
Use a CA-signed certificate
The CA-signed certificate must include both public and private key and the private key must be exportable.
-
Import the certificate into
Mystore on the Citrix Provisioning server.Import-Certificate -FilePath <crt file> -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My <!--NeedCopy--> -
If the certificate authority root certificate is not in the trusted root store (
Cert:\LocalMachine\Root) on every client machine, then add it on all client machines. However, this step is usually not required when using a public CA-signed certificate.
Use a self-signed certificate
-
Create a self-signed certificate.
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName $PVS_SERVER_FQDN -CertStoreLocation cert:\LocalMachine\My $cert_thumbprint = $cert.Thumbprint <!--NeedCopy-->Note:
When you create a certificate, you can specify multiple
-DnsName, separated by a comma. This adds Subject Alternative Names to the certificate, one for eachDnsName. When using the PVS API, you can connect using any of these names. Example: You can use -DnsName “servername.domain”, “servername”. Then, using PVS API connect with -PvsServerAddress “servername.domain” or -PvsServerAddress “servername”. -
Export the certificate to the
.cerfile without its private key.Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath $CERT_FILE <!--NeedCopy--> -
On each client machine, import the exported self-signed into the
Cert:\LocalMachine\Roottrusted root store on the client.$file = ( Get-ChildItem -Path $CERT_FILE ) $file | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root <!--NeedCopy-->
Use Configuration Wizard to deploy certificate
Use the Citrix Provisioning Configuration Wizard to add the proper certificate from the local Computer personal certificates (My) store.
The SSL Configuration page displays the certificate that is imported into My store on the Citrix Provisioning Server.
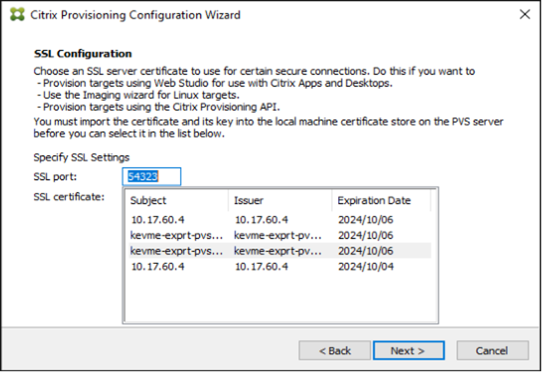
Tip:
When the Soap SSL Configuration page first loads, the certificate is highlighted which gives the appearance that it is selected. Ensure that the certificate is selected, it appears as a blue item in the table.
Select network addresses for the stream service
-
Select the checkbox next to each of the network addresses that the Stream Service can use. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses that are assigned to the Citrix Provisioning Server are displayed. You can proceed with one of the following combinations:
- Only IPv4 address
- Only IPv6 address
- Combination of both IPv4 and IPv6 address
-
Enter the base port number that is used for network communications in the First communications port: text box.
Note:
A minimum of 20 ports are required within the range. All provisioning servers within a farm must use the same port assignments.
-
Select the Soap Server port (default is 54321) to use for Console access, then click Next.
Continue on to select the bootstrap server.
Configure the bootstrap server
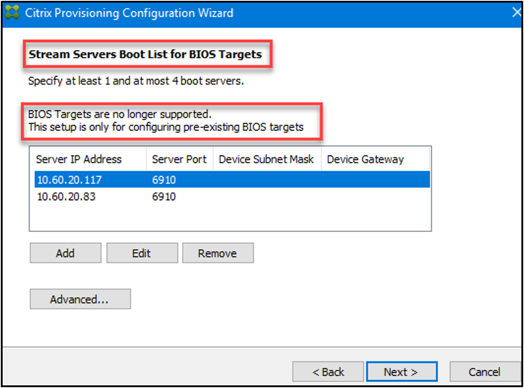
Note:
BIOS targets are no longer supported. These instructions are only for configuring pre-existing BIOS targets.
- Select Provisioning Servers to use for the boot process:
-
Use the Add button to add more provisioning servers to the list. The Edit button to edit existing information, or to remove the server from the list. Use the Move up or Move down buttons to change the server boot preference order. The maximum length for the server name is 15 characters. Do not enter the FQDN for the server name. In a high availability implementation, at least two provisioning servers must be selected as boot servers.
-
Optionally, highlight the IP address of the provisioning server that target devices boot from, then click Advanced. The Advanced Stream Servers Boot List appears.
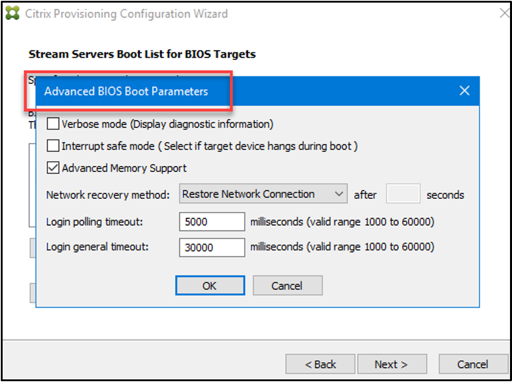
The following list describes advanced settings that you can choose from. After making your selections, click OK to exit the dialog, then click Next to continue.
- Verbose mode: Select the Verbose Mode option if you want to monitor the boot process on the target device (optional) or view system messages.
- Interrupt safe mode: Select Interrupt Safe Mode if you are having trouble with your target device failing early in the boot process. This option enables debugging of target device drivers that exhibit timing or boot behavior problems.
- Advanced memory support: This setting enables the bootstrap to support newer Windows OS versions and is enabled by default. Disable this setting on Windows Server OS 32 bit versions that do not support PXE. Or if your target device is hanging or behaving erratically in early boot phase.
-
Network recovery method:
-
Restore Network Connections: Selecting this option results in the target device attempting indefinitely to restore its connection to the provisioning server.
Note:
Because the Seconds field does not apply, it becomes inactive when selecting the Restore Network Connections option.
- Reboot to Hard Drive: (A hard drive must exist on the target device). Selecting this option instructs the target device to perform a hardware reset to force a reboot after failing to re-establish communications for a defined number of seconds. The user determines the number of seconds to wait before rebooting. Assuming the network connection cannot be established, PXE fails, and the system reboots to the local hard drive. The default number of seconds is 50, to be compatible with high availability configurations.
-
Restore Network Connections: Selecting this option results in the target device attempting indefinitely to restore its connection to the provisioning server.
- Logon polling timeout: Enter the time in milliseconds between retries when polling for provisioning servers. Each server is sent a login request packet in sequence. The first responding server is used. In non-HA configurations, this time-out simply defines how often to retry the single available server with the initial login request. This time-out defines how quickly the round-robin routine switches from one server to the next in trying to find an active server. The valid range is from 1,000 milliseconds to 60,000 milliseconds.
- Log in general timeout: Enter the time-out in milliseconds for all login associated packets, except the initial login polling time-out. The time-out is longer than the polling time-out because the server needs time to contact all associated servers, some of which are unreachable. Unreachable servers require retries and time-outs from the provisioning server to the other provisioning servers to determine if they online. The valid range is from 1,000 milliseconds to 60,000 milliseconds.
-
- Verify that all configuration settings are correct, then click OK.
Finish the configuration
On the Finish page, additional data about server registration is presented in the Summary section.
- Run the Configuration Wizard to configure all the servers in the farm.
- Click Finish on the Finish page after configuration is complete.
After you click Finish, the Configuration Wizard creates the SPN before the SOAP service starts. If the SPN creation fails, you get a warning message.
If you run Citrix Provisioning Services in an environment with NTLM disabled, it is necessary that SPNs for the Citrix Provisioning Services be associated with the domain account that runs the Citrix Provisioning Services. For each Citrix Provisioning server, two SPNs are created and these are set on the AD account that is used for the Citrix Provisioning Services:
-
PVSSoap/<PVS-server-fqdn>, and PVSSoap/<PVS-server-hostname>
The Configuration Wizard creates these SPNs for the Citrix Provisioning services which means that Kerberos is always used. However, the Configuration Wizard must be run by a user that is a member of the Domain Administrators group. If the Configuration Wizard is run using a user who is not a member of the Domain Administrators group, then ask a domain administrator to create the SPNs as follows:
For each Citrix Provisioning Server, run:
setspn -S PVSSoap/X-fqdn -U Y\Z
setspn -S PVSSoap/X-hostname -U Y\Z
<!--NeedCopy-->
Where, X is the Citrix Provisioning Server and Y\Z is the domain account that the services will run as on that server.
Verify Citrix Provisioning server registration
To verify the Citrix Provisioning server registration:
- Log in to
<customer>.cloud.com. - Go to Identity and Access Management > API Access > Product Registrations. You can see the current registrations.
Restore database
You can restore the database from a backup when using enhanced database encryption if you rotate the keys between taking the backup and restoring the database.
To restore the database when using enhanced encryption:
- Take a backup of the database using SQL Server Management Studio when the key rotation state is Idle.
-
Restore the database.
- Wait for the key rotation state to be Idle if a key rotation is in progress.
- Stop all Citrix Provisioning Services on all Citrix Provisioning Servers in the farm - SOAP, stream process, and Citrix Provisioning API. This action ensures that all active connections to the database are closed.
- Restore the database using SQL Server Management Studio.
-
Get the Citrix Provisioning Servers online.
- Run the Configuration Wizard on all the servers in the farm. After you click Finish, the system displays a prompt to indicate that the database has been restored and key rotation is required. Click OK.
-
Rotate the key using one of the following:
-
Go to the Citrix Provisioning Console > Farm > Properties > Encryption tab. For more information, see Encryption tab.
Note:
After you launch the Citrix Provisioning Console, the farm icon is replaced with a warning icon. The General, Encryption, and Status tabs of Farm > Properties also display a warning message to indicate that the database has been restored and key rotation is required. The warning icon and the message disappear after you rotate the key.
-
Use the PowerShell command
Start-PvsRotateEncryptionKeys. For more information, see Using PowerShell and MCLI commands to rotate encryption key.
-
Downgrade
If the Citrix Provisioning farm is using enhanced encryption (Cloud join: Citrix Provisioning version 2303 and later, or any join: Citrix Provisioning version 2405 and later) and if the VM needs to be reused to install an older version of the Citrix Provisioning software, then run the Downgrade.ps1 script to clear the enhanced encryption fields from the registry.
Important:
- You must back up the database before upgrading to Citrix Provisioning version 2303 or later. This restores the database using the original encryption
- The
Downgrade.ps1script is included in the Citrix Provisioning ISO. It is located under\Tools\Scripts folder.
Downgrade to an earlier release
- Stop all Citrix Provisioning services on all Citrix Provisioning servers in the farm - SOAP, stream process, and Citrix Provisioning API.
On each Citrix Provisioning server in the farm:
- Uninstall Citrix Provisioning server and console version 2303 or later.
- Run PoSH script (Downgrade.ps1) to delete the enhanced encryption fields from registry values. Mention the version to which you want to downgrade.
- (Optional) If the farm was joined to cloud then manually unregister it from Citrix Cloud.
- Install Citrix Provisioning server and console to a version that you want to downgrade to.
- Run the Configuration Wizard on a provisioning server. The wizard behaves as if there are no values in the registry. Select Join Existing Farm on the Farm Configuration dialog to add this provisioning server to an existing farm. Reconfigure the provisioning server.
- Repeat the steps for every Citrix Provisioning server in the farm.
Delete registrations of Citrix Provisioning servers from Citrix Cloud
- Stop all Citrix Provisioning Services on all Citrix Provisioning servers in the farm - SOAP, stream process, and Citrix Provisioning API.
- Restore the database from the backup.
On each Citrix Provisioning server in the farm:
- Run the PoSH script (Downgrade.ps1) to delete registry values. The script disables the features that are included in Citrix Provisioning version 2303 or later.
-
(Optional) Manually deregister the Citrix Provisioning server from Citrix Cloud.
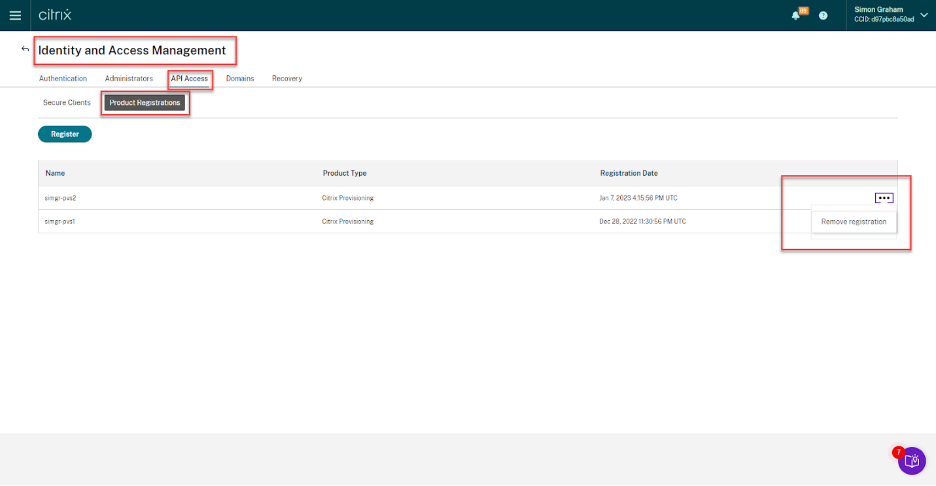
- Log in to
<customer>.cloud.comwith an administrator account. - Go to Identity and Access Management > API Access > Product Registrations.
-
Use the ••• menu to remove registrations from Citrix Cloud.
- Log in to
- Run the Configuration Wizard on a provisioning server. The wizard behaves as if there are no values in the registry. Select Join Existing Farm on the Farm Configuration dialog to add this provisioning server to an existing farm. Reconfigure the provisioning server.
- Repeat the steps for every Citrix Provisioning server in the farm.
In this article
- General tab
- Security tab
- Groups tab
- Licensing tab
- Options tab
- Virtual disk version tab
- Status tab
- Registration tab
- Encryption tab
- Logging tab
- Using the console to configure a farm
- Starting the configuration wizard
- Configuration wizard settings
- Network topology
- Identify the farm
- Identify the database
- Create a store for a new farm
- Identify the site
- Join Citrix Cloud or Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops site
- Select the license server
- Configure user account settings
- Select network addresses for the stream service
- Configure the bootstrap server
- Finish the configuration
- Verify Citrix Provisioning server registration
- Restore database
- Downgrade