Smart cards
You can use a smart card connected to the client device for authentication when logging on to a Linux virtual desktop session. This feature is implemented through smart card redirection over the ICA® smart card virtual channel. You can also use the smart card within the session. Use cases include:
- Adding a digital signature to a document
- Encrypting or decrypting an email
- Authenticating to a website
The Linux VDA uses the same configuration as the Windows VDA for this feature. For more information, see the Configure the smart card environment section in this article.
Note:
Using a mapped smart card within a Linux VDA session to sign on to Citrix Gateway isn’t supported.
Support for limited Linux distributions and AD integration methods
-
Smart card pass-through authentication supports limited Linux distributions and AD integration methods. See the following matrix:
Winbind SSSD Centrify Quest Debian 12.12 Yes Yes Yes Yes Debian 13 Yes Yes Yes No RHEL 10/9.7/9.6/9.4 Yes Yes Yes Yes RHEL 8.10 Yes Yes Yes Yes Rocky Linux 10/9.7/9.6/9.4 Yes Yes Yes Yes Rocky Linux 8.10 Yes Yes Yes Yes Ubuntu 24.04 Yes Yes Yes Yes Ubuntu 22.04 Yes Yes Yes Yes
Prerequisites
The availability of smart card pass-through authentication is contingent on the following conditions:
-
Your Linux VDA can register with the Delivery Controller™ and you can open the published Linux desktop sessions using Windows credentials.
-
Smart cards supported by OpenSC are used. For more information, see Ensure that OpenSC supports your smart card.
Ensure that OpenSC supports your smart card
OpenSC is a widely used smart card driver on RHEL 7.4+. As a fully compatible replacement of CoolKey, OpenSC supports many types of smart cards (see Smart Card Support in Red Hat Enterprise Linux).
In this article, the YubiKey smart card is used as an example to illustrate the configuration. YubiKey is an all-in-one USB CCID PIV device that can easily be purchased from Amazon or other retail vendors. The OpenSC driver supports YubiKey.
If your organization requires some other more advanced smart card, prepare a physical machine with a supported Linux distribution and the OpenSC package installed. For information about the OpenSC installation, see Install the smart card driver. Insert your smart card, and run the following command to verify that OpenSC supports your smart card:
pkcs11-tool --module opensc-pkcs11.so --list-slots
<!--NeedCopy-->
Configuration
Prepare a root certificate
A root certificate is used to verify the certificate on the smart card. Complete the following steps to download and install a root certificate.
-
Get a root certificate in PEM format, typically from your CA server.
You can run a command similar to the following to convert a DER file (*.crt, *.cer, *.der) to PEM. In the following command example, certnew.cer is a DER file.
openssl x509 -inform der -in certnew.cer -out certnew.pem <!--NeedCopy--> -
Install the root certificate to the
openssldirectory. The certnew.pem file is used as an example.cp certnew.pem <path where you install the root certificate> <!--NeedCopy-->To create a path for installing the root certificate, run
sudo mdkir -p <path where you install the root certificate>.
Configure the smart card environment
You can use the ctxsmartlogon.sh script to configure the smart card environment or complete the configuration manually.
(Option 1) Use the ctxsmartlogon.sh script to configure the smart card environment
Note:
The ctxsmartlogon.sh script adds PKINIT information to the default realm. You can change this setting through the /etc/krb5.conf configuration file.
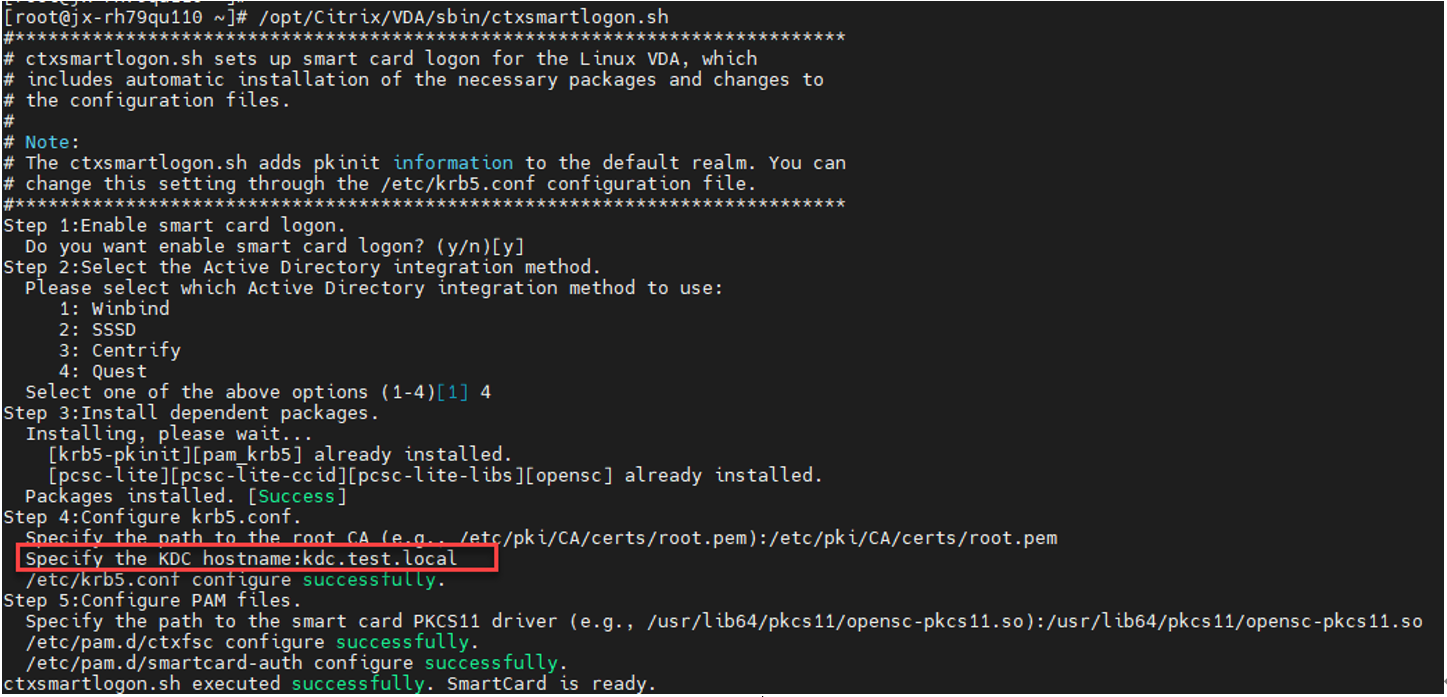
Before using smart cards for the first time, run the ctxsmartlogon.sh script to configure the smart card environment.
Tip:
If you have used SSSD for domain joining, restart the SSSD service after you run ctxsmartlogon.sh. For RHEL 8 and later, as PAM_KRB5 is moved to the EPEL repository, the script will try to enable EPEL in those distributions.
sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxsmartlogon.sh
<!--NeedCopy-->
The results resemble the following:
Note:
If you use Quest as the domain joining method, you are required to specify the host name of the Key Distribution Center (KDC). For example:
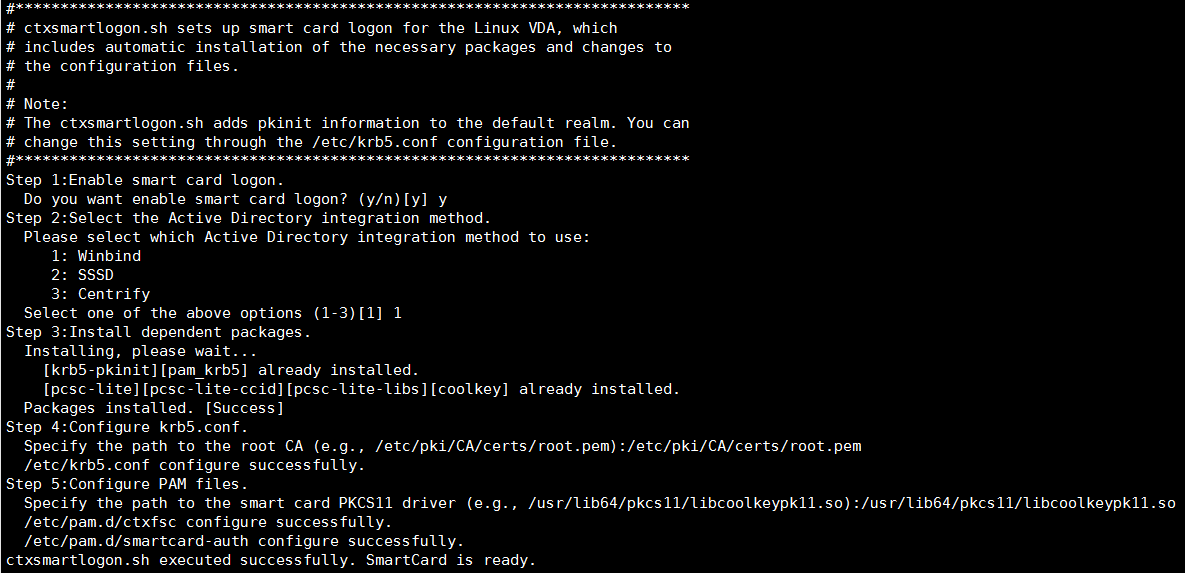
You can also disable smart cards by running the ctxsmartlogon.sh script:
sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxsmartlogon.sh
<!--NeedCopy-->
The results resemble the following:
(Option 2) Configure the smart card environment manually
The Linux VDA uses the same smart card environment with the Windows VDA. In the environment, multiple components must be configured, including the Domain Controller, Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA), Internet Information Services, Citrix StoreFront, and Citrix Workspace app. For information about the configuration based on the YubiKey smart card, see Knowledge Center article CTX206156.
Before moving to the next step, make sure that:
- You have configured all components correctly.
- You have downloaded the private key and user certificate to the smart card.
- You can successfully log on to the VDA using the smart card.
Install the PC/SC Lite packages
PCSC Lite is an implementation of the Personal Computer/Smart Card (PC/SC) specification in Linux. It provides a Windows smart card interface for communicating to smart cards and readers. Smart card redirection in the Linux VDA is implemented on the PC/SC level.
Run the following command to install the PC/SC Lite packages:
RHEL 9.x/8.x, Rocky Linux 9.x/8.x:
yum install pcsc-lite pcsc-lite-ccid pcsc-lite-libs
<!--NeedCopy-->
Ubuntu 24.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Debian 12.x, Debian 11.11:
apt-get install -y libpcsclite1 libccid
<!--NeedCopy-->
Install the smart card driver
OpenSC is a widely used smart card driver. If OpenSC is not installed, run the following command to install it:
RHEL 9.x/8.x, Rocky Linux 9.x/8.x:
yum install opensc
<!--NeedCopy-->
Ubuntu 24.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Debian 12.x, Debian 11.11:
apt-get install -y opensc
<!--NeedCopy-->
Install the PAM modules for smart card authentication
Run the following command to install the pam_krb5 and krb5-pkinit modules.
RHEL 9.x/8.x, Rocky Linux 9.x/8.x:
yum install krb5-pkinit
<!--NeedCopy-->
Ubuntu 24.04, Ubuntu 22.04:
apt-get install libpam-krb5 krb5-pkinit
<!--NeedCopy-->
Debian 12.x, Debian 11.11:
apt-get install -y libpam-krb5 krb5-pkinit
<!--NeedCopy-->
The pam_krb5 module is a pluggable authentication module. PAM-aware applications can use pam_krb5 to check passwords and obtain ticket-granting tickets from the Key Distribution Center (KDC). The krb5-pkinit module contains the PKINIT plug-in that allows clients to obtain initial credentials from the KDC using a private key and a certificate.
Configure the pam_krb5 module
The pam_krb5 module interacts with the KDC to get Kerberos tickets using certificates in the smart card. To enable pam_krb5 authentication in PAM, run the following command:
authconfig --enablekrb5 --update
<!--NeedCopy-->
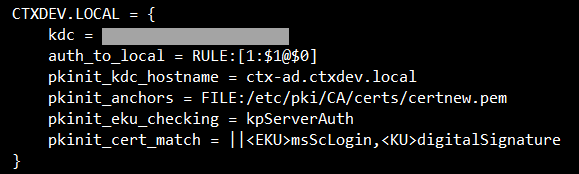
In the /etc/krb5.conf configuration file, add PKINIT information according to the actual realm.
Note:
The pkinit_cert_match option specifies matching rules that the client certificate must match before it is used to attempt PKINIT authentication. The syntax of the matching rules is:
[relation-operator] component-rule …
where relation-operator can be either &&, meaning all component rules must match, or ||, meaning only one component rule must match.
Here is an example of a generic krb5.conf file:
EXAMPLE.COM = {
kdc = KDC.EXAMPLE.COM
auth_to_local = RULE:[1:$1@$0]
pkinit_anchors = FILE:<path where you install the root certificate>/certnew.pem
pkinit_kdc_hostname = KDC.EXAMPLE.COM
pkinit_cert_match = ||<EKU>msScLogin,<KU>digitalSignature
pkinit_eku_checking = kpServerAuth
}
<!--NeedCopy-->
The configuration file resembles the following after you add the PKINIT information.
Configure PAM authentication
PAM configuration files tell what modules are used for PAM authentication. To add pam_krb5 as an authentication module, add the following line to the /etc/pam.d/smartcard-auth file:
auth [success=done ignore=ignore default=die] pam_krb5.so preauth_options=X509_user_identity=PKCS11:<path to the pkcs11 driver>/opensc-pkcs11.so
The configuration file resembles the following after modification if SSSD is used.
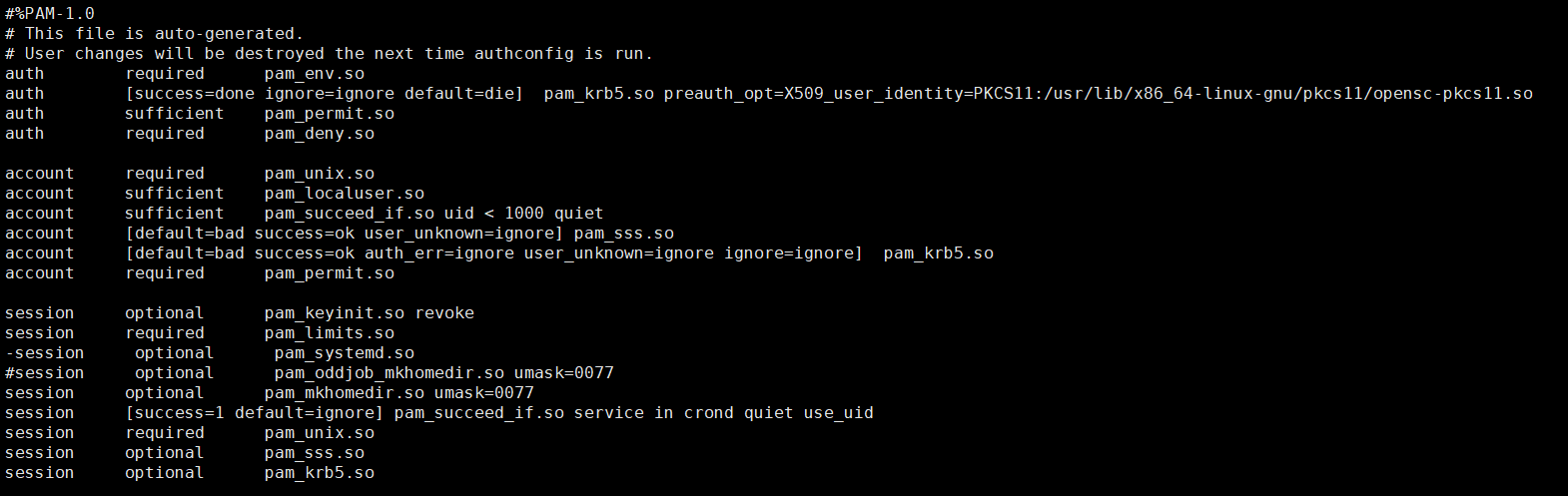
(Optional) Single sign-on by using smart cards
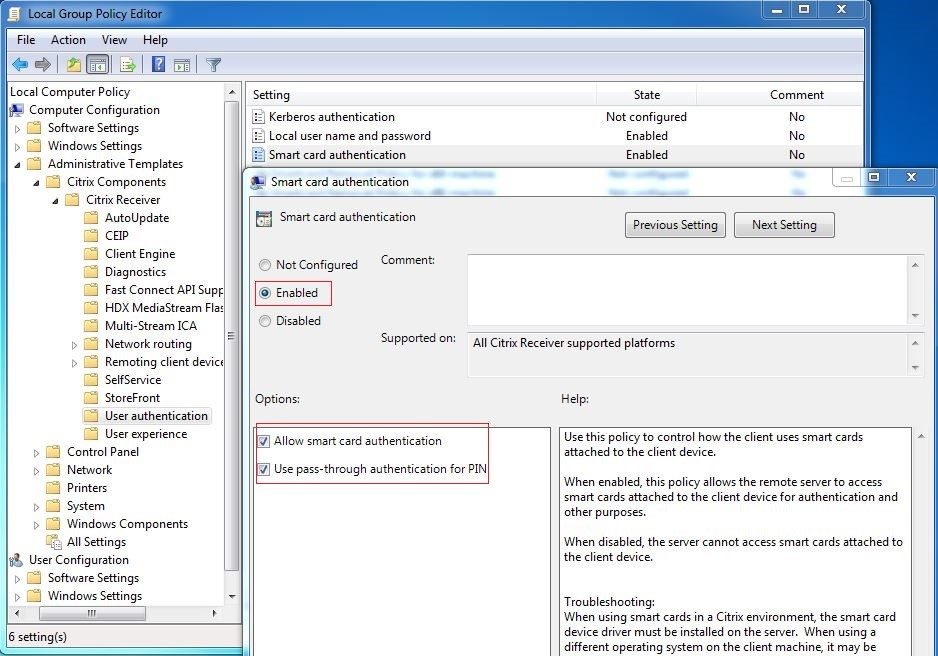
Single sign-on (SSO) is a Citrix feature that implements pass-through authentication with virtual desktop and application launches. This feature reduces the number of times that users type their PIN. To use SSO with the Linux VDA, configure Citrix Workspace app. The configuration is the same with the Windows VDA. For more information, see Knowledge Center article CTX133982.
Enable the smart card authentication as follows when configuring the group policy in Citrix Workspace™ app.
Fast smart card logon
Fast smart card is an improvement over the existing HDX PC/SC-based smart card redirection. It improves performance when smart cards are used in high-latency WAN environments. For more information, see Smart cards.
The Linux VDA supports fast smart card on the following versions of Citrix Workspace app:
- Citrix Receiver for Windows 4.12
- Citrix Workspace app 1808 for Windows and later
Enable fast smart card logon on the client
Fast smart card logon is enabled by default on the VDA and disabled by default on the client. On the client, to enable fast smart card logon, include the following parameter in the default.ica file of the associated StoreFront site:
[WFClient]
SmartCardCryptographicRedirection=On
<!--NeedCopy-->
Disable fast smart card logon on the client
To disable fast smart card logon on the client, remove the SmartCardCryptographicRedirection parameter from the default.ica file of the associated StoreFront site.
Run XDPing
After completing the preceding steps, you can use the Linux XDPing tool to check for common configuration issues that might exist in your Linux VDA environment.
Usage
Log on to the Linux VDA by using a smart card
You can use a smart card to log on to the Linux VDA in both SSO and non-SSO scenarios.
- In the SSO scenario, you are logged on to StoreFront™ automatically by using the cached smart card certificate and PIN. When you launch a Linux virtual desktop session in StoreFront, the PIN is passed to the Linux VDA for smart card authentication.
-
In the non-SSO scenario, you are prompted to select a certificate and type a PIN to log on to StoreFront.
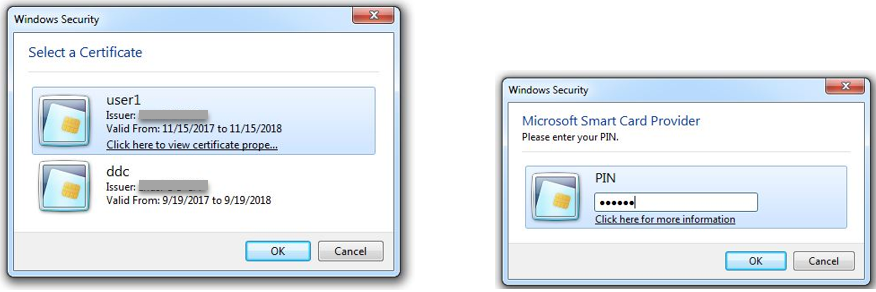
When you launch a Linux virtual desktop session in StoreFront, a dialog box for logon to the Linux VDA appears as follows. The user name is extracted from the certificate in the smart card and you must type the PIN again for logon authentication.
This behavior is the same with the Windows VDA.
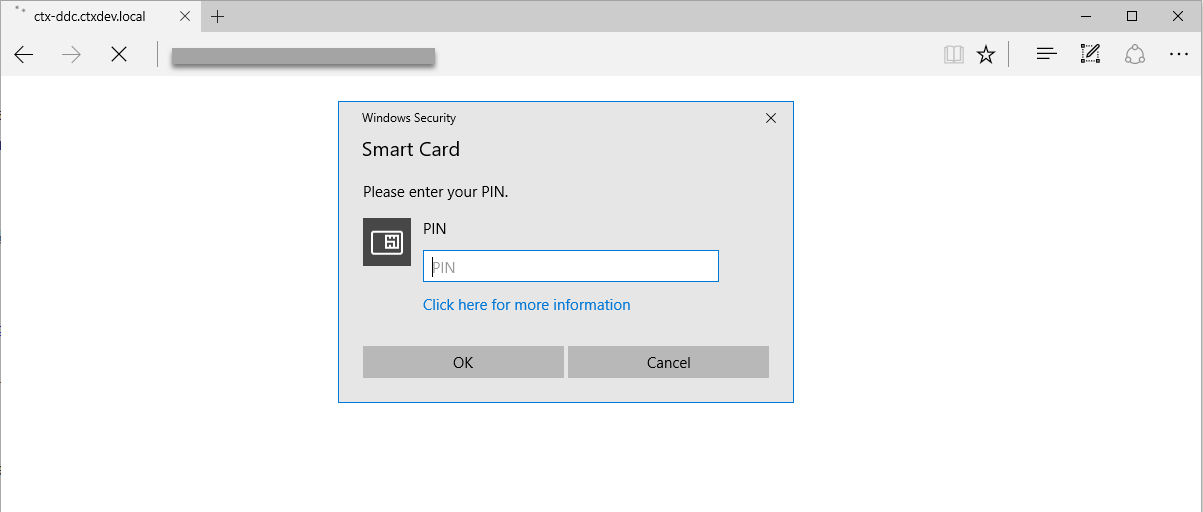
Reconnect to a session by using a smart card
To reconnect to a session, ensure that the smart card is connected to the client device. Otherwise, a gray caching window appears on the Linux VDA side and exits quickly because reauthentication fails without the smart card connected. No other prompt is provided in this case to remind you to connect the smart card.
On the StoreFront side, however, if a smart card is not connected when you reconnect to a session, the StoreFront web might give an alert as follows:
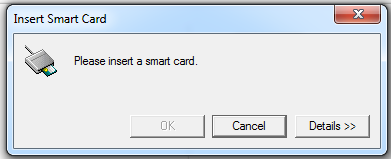
Limitation
Smart card removal settings
To specify the behavior when a signed-in user’s smart card is removed from the smart card reader during a session, edit the following registry key on the Linux VDA:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\LocalPolicies\SecurityOptions
| Value name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCardRemoveOption | REG_DWORD | 0x00000000 | This setting determines what happens when the smart card for a signed-in user is removed from the smart card reader during a session. The options are as follows. |
| 0 No Action | |||
| 1 Force Logoff: The user is signed out automatically upon removal of the smart card. | |||
| 2 Disconnect Session: The session is disconnected without signing out the user upon removal of the smart card. The user can reinsert the smart card to reconnect the session later. | |||
| 3 Lock workstation: The virtual desktop is locked. The user can subsequently reinsert the smart card and enter the PIN code to unlock the screen. | |||
| SCardRemoveActionDelaySeconds | REG_DWORD | 15 | If the removal option is set as Force Logoff or Disconnect Session, you can further specify a delay of several seconds before the action is taken. With this setting, a message box appears in the user session after the smart card is removed, indicating that the session will be force logged off or disconnected after the specified seconds. If you reinsert the smart card before that time, the session continues uninterrupted. |
Limitations
The Linux VDA supports only one smart card reader at a time.
Support for other smartcards and the PKCS#11 library
Citrix provides a generic smart card redirection solution. Although only the OpenSC smart card is listed on our support list, you can try using other smart cards and the PKCS#11 library. To switch to your specific smart card or the PKCS#11 library:
-
Replace all the
opensc-pkcs11.soinstances with your PKCS#11 library. -
To set the path of your PKCS#11 library to the registry, run the following command:
/opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/ctxreg update -k "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Citrix\VirtualChannels\Scard" -v "PKCS11LibPath" -d "PATH" <!--NeedCopy-->where PATH points to your PKCS#11 library such as
/usr/lib64/pkcs11/opensc-pkcs11.so -
Disable fast smart card logon on the client.