-
Installing and configuring Provisioning Services
-
Upgrading a Provisioning Services target device vDisk using in-place upgrade
-
Getting the bootstrap file
-
-
Deploying virtual desktops to VMs using the XenDesktop Setup Wizard
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
Getting the bootstrap file
A target device initiates the boot process by first loading a bootstrap program. A bootstrap program is a small program that runs before the operating system is loaded. Provisioning Services uses a special bootstrap program that initializes the streaming session between the target device and the Provisioning Server. After this session starts, the operating system begins to be streamed and loaded from the vDisk that was initiated.
There are three ways that a target device may load the bootstrap program.
- Over the network, via Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE)
- From a boot device stored on attached media
- From a BIOS Embedded bootstrap (OEM versions only)
After the target device’s BIOS is configured to allow it to boot from the network, the device can boot and get a vDisk assignment from the Provisioning Server. The target device firmware gets the bootstrap file using standard network protocols.
Note
The device firmware (NIC) must support PXE 0.99j, PXE 2.1or greater.
Network Booting a Target Device
The DHCP service delivers IP configurations to a target device. It can also deliver the bootstrap file location using options 67, and 60 or 66. Consider delivering the bootstrap file location with a DHCP service to reduce the number of services and increase reliability.
Note: The BOOTP service can deliver IP configuration to a target device according to BOOTP tab. It can also deliver the boot program location using optional fields. Use of this service is no longer typical. Use this service only if DHCP does not meet your requirements.
The PXE service can deliver the bootstrap file location to a target device according to the PXE Specification Version 2.1. Use this service if a DHCP service exists and cannot be changed, and another PXE service is not used.
The TFTP service delivers the bootstrap file to a target device on request. Use it if another TFTP service is not available.
The illustrations and steps that follow describe the boot process both with and without the use of PXE.
Using DHCP to Retrieve IP Address and Scope Options (Without PXE)
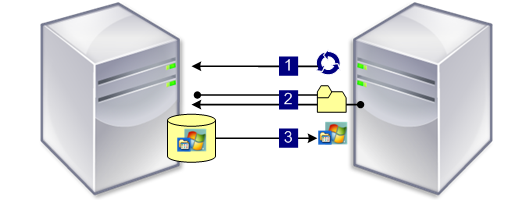
- When a target device boots from the network, DHCP sends a request to the Provisioning Server for an IP address and Scope Option settings (66 and 67). The Provisioning Server returns the information as requested.
- Using TFTP, a request for the bootstrap file is sent from the target device to the Provisioning Server. The Provisioning Server downloads the boot file on the target device.
- The target device boots the assigned vDisk image.
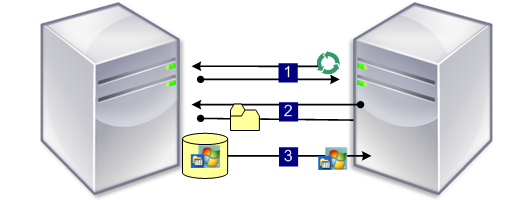
Using DHCP with PXE to Retrieve IP Address and Scope Options
- When a target device boots from the network, DHCP sends a request to the Provisioning Server for an IP address and Scope Option settings (option 60; PXEClient identifier). The Provisioning Server returns the information as requested.
- The target device sends a request to the Provisioning Server for the bootstap file name and location to the PXE service (options 66 and 67). The PXE service returns the information to the target device.
- Using TFTP, a request for the bootstrap file is sent from the target device to the Provisioning Server. The Provisioning Server downloads the bootstrap file to the target device and the target device boots.
Booting From an Optional Boot Device
As an alternative to using PXE, the Boot Device Manager (BDM) can create a bootstrap file on a local hard drive, USB flash drive, or ISO image. The bootstrap file will then be used to boot the target device.
Note: The BIOS Embedded Bootstrap boot method also exists to allow OEMs to embedded the bootstrap file on the target device.
Share
Share
This Preview product documentation is Citrix Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Citrix Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Citrix product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select Do Not Agree to exit.