Client certificate or certificate plus domain authentication
The default configuration for XenMobile® is user name and password authentication. To add another layer of security for enrollment and access to the XenMobile environment, consider using certificate-based authentication. In the XenMobile environment, this configuration is the best combination of security and user experience. Certificate plus domain authentication has the best SSO possibilities coupled with the security provided by two-factor authentication at Citrix ADC.
For optimal usability, you can combine certificate plus domain authentication with Citrix PIN and Active Directory password caching. As a result, users don’t have to enter their LDAP user names and passwords repeatedly. Users enter user names and passwords for enrollment, password expiration, and account lockout.
Important:
XenMobile doesn’t support changing the authentication mode from domain authentication to some other authentication mode after users enroll devices in XenMobile.
If you don’t allow LDAP and use smart cards or similar methods, configuring certificates allows you to represent a smart card to XenMobile. Users then enroll using a unique PIN that XenMobile generates for them. After a user has access, XenMobile then creates and deploys the certificate used to authenticate to the XenMobile environment.
You can use the Citrix ADC for XenMobile wizard to perform the configuration required for XenMobile when using Citrix ADC certificate-only authentication or certificate plus domain authentication. You can run the Citrix ADC for XenMobile wizard one time only.
In highly secure environments, usage of LDAP credentials outside of an organization in public or insecure networks is considered a prime security threat for the organization. For highly secure environments, two-factor authentication that uses a client certificate and a security token is an option. For information, see Configuring XenMobile for Certificate and Security Token Authentication.
Client certificate authentication is available for XenMobile MAM mode (MAM-only) and ENT mode (when users enroll into MDM). Client certificate authentication isn’t available for XenMobile ENT mode when users enroll into legacy MAM mode. To use client certificate authentication for XenMobile ENT and MAM modes, you must configure the Microsoft server, the XenMobile Server, and then Citrix Gateway. Follow these general steps, as described in this article.
On the Microsoft server:
- Add a certificate snap-in to the Microsoft Management Console.
- Add the template to Certificate Authority (CA).
- Create a PFX certificate from the CA server.
On the XenMobile Server:
- Upload the certificate to XenMobile.
- Create the PKI entity for certificate-based authentication.
- Configure credentials providers.
- Configure Citrix Gateway to deliver a user certificate for authentication.
For information about Citrix Gateway configuration, see these articles in the Citrix ADC documentation:
- Client authentication
- SSL profile infrastructure
- Configuring and Binding a Client Certificate Authentication Policy
Prerequisites
-
When you create a Microsoft Certificate Services Entity template, avoid possible authentication issues with enrolled devices by excluding special characters. For example, don’t use these characters in the template name:
: ! $ () # % + * ~ ? | {} [] - To configure Certificate-based Authentication for Exchange ActiveSync, see this Microsoft blog. Configure the certificate authority (CA) server site for Exchange ActiceSync to require client certificates.
- If you use private server certificates to secure the ActiveSync traffic to the Exchange Server, ensure that the mobile devices have all necessary Root/Intermediate certificates. Otherwise, certificate-based authentication fails during the mailbox setup in Secure Mail. In the Exchange IIS Console, you must:
- Add a website for XenMobile use with Exchange and bind the web server certificate.
- Use port 9443.
- For that website, you must add two applications, one for “Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync” and one for “EWS”. For both of those applications, under SSL Settings, select Require SSL.
Add a certificate snap-in to the Microsoft Management Console
-
Open the console and then click Add/Remove Snap-ins.
-
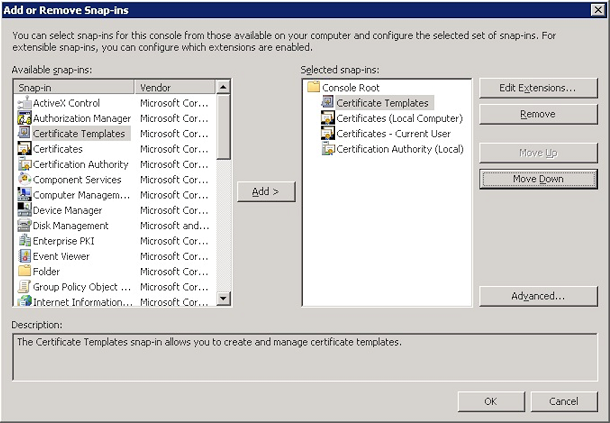
Add the following snap-ins:
- Certificate Templates
- Certificates (Local Computer)
- Certificates - Current User
- Certificate Authority (Local)
-
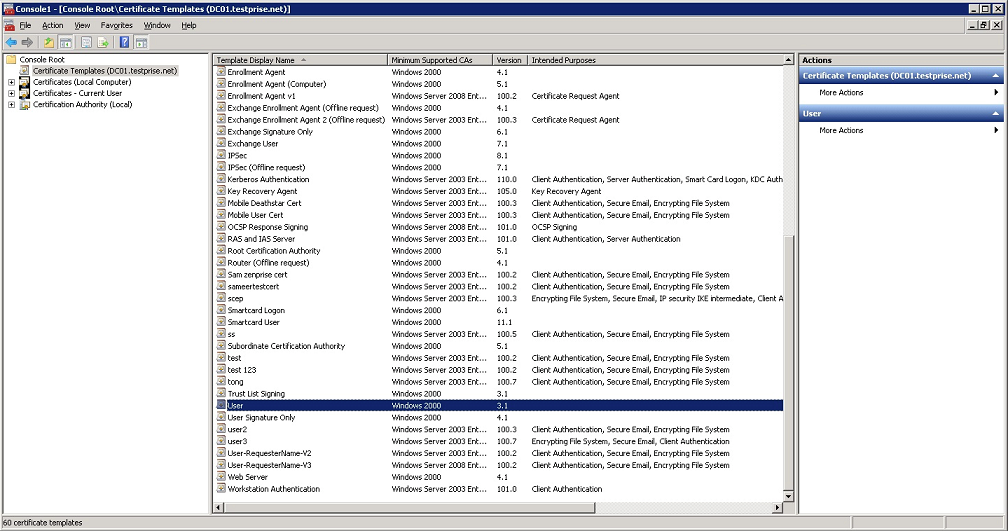
Expand Certificate Templates.
-
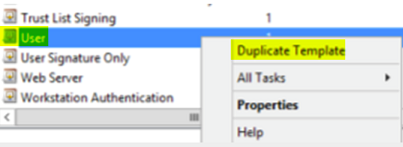
Select the User template and Duplicate Template.
-
Provide the Template display name.
Important:
It is not recommended to select the Publish certificate in Active Directory option. If this option is selected, it creates client certificates for all users in Active Directory, which might clutter your Active Directory database.
-
Select Windows 2003 Server for the template type. In the Windows 2012 R2 server, under Compatibility, select Certificate authority and set the recipient as Windows 2003.
-
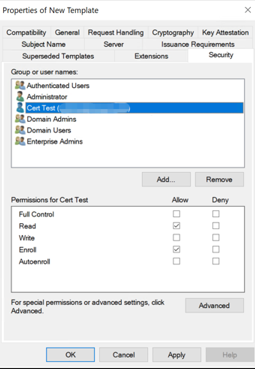
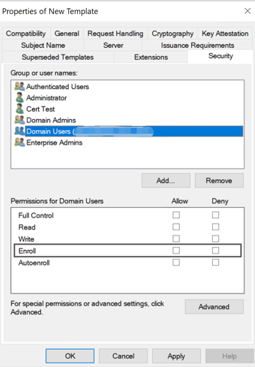
Under Security, configure the following:
-
Click Add and then select the AD user account that XenMobile Server uses to generate certificates.
Important:
Add only the service account user here. Add the Enroll permission only to this AD user account.
As described later in this article, you create a user .pfx certificate using the service account. For information, see Creating a PFX certificate from the CA server.
-
Revoke the Enroll permission from Domain Users.
-
-
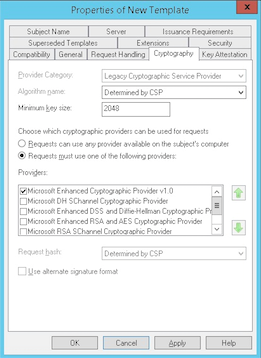
Under Cryptography, ensure that you provide the key size. You later enter the key size when configuring XenMobile.
-
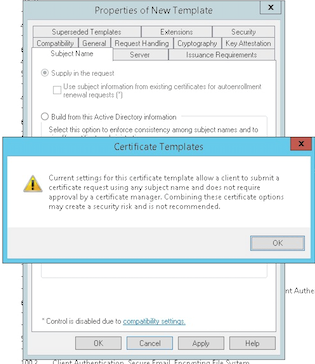
Under Subject Name, select Supply in the request. Apply the changes and then save.
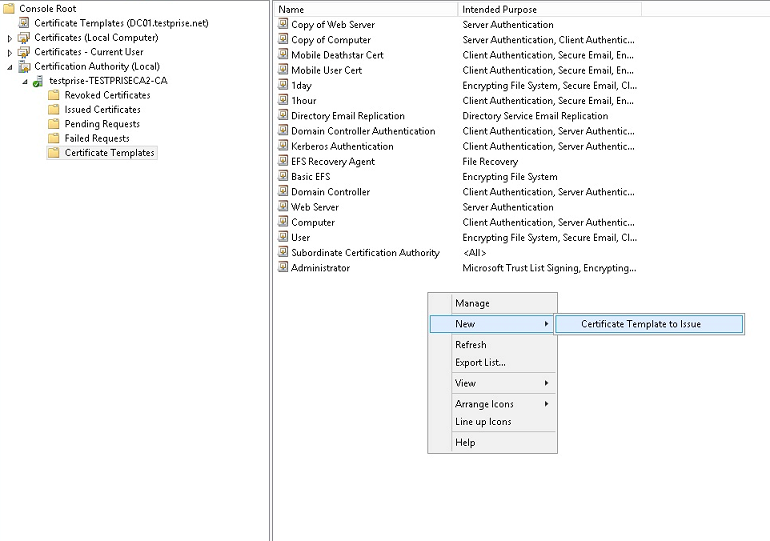
Adding the template to Certificate Authority
-
Go to Certificate Authority and select Certificate Templates.
-
Right-click in the right pane and then select New > Certificate Template to Issue.
-
Select the template that you created in the previous step and then click OK to add it into the Certificate Authority.
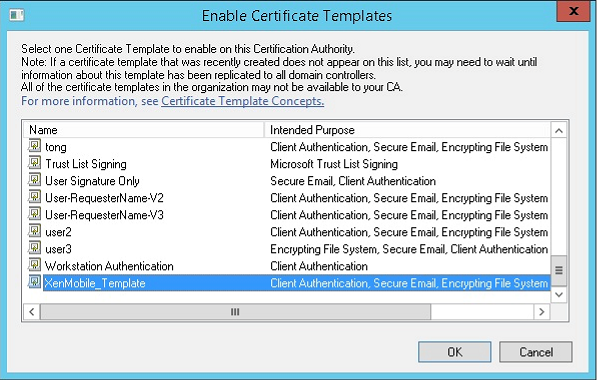
Creating a PFX certificate from the CA server
-
Create a user .pfx cert using the service account with which you logged in. The .pfx is uploaded to XenMobile, which then requests a user certificate on behalf of the users who enroll their devices.
-
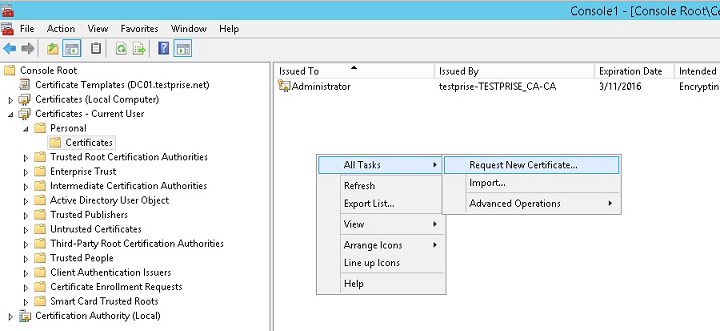
Under Current User, expand Certificates.
-
Right-click in the right pane and then click Request New Certificate.
-
The Certificate Enrollment screen appears. Click Next.
-
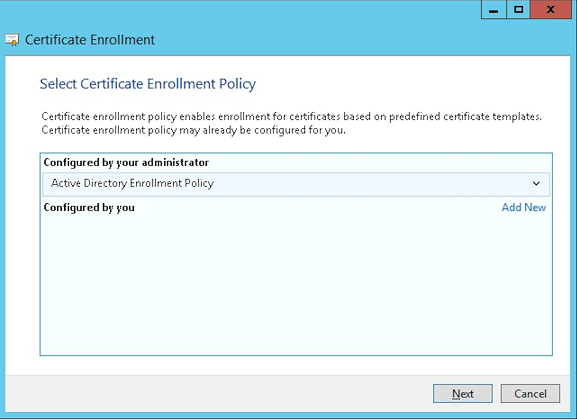
Select Active Directory Enrollment Policy and then click Next.
-
Select the User template and then click Enroll.
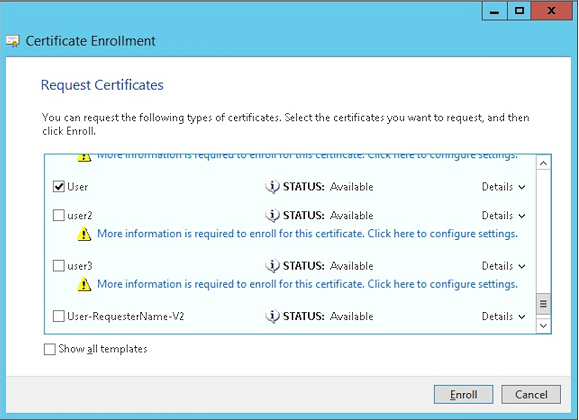
-
Export the .pfx file that you created in the previous step.
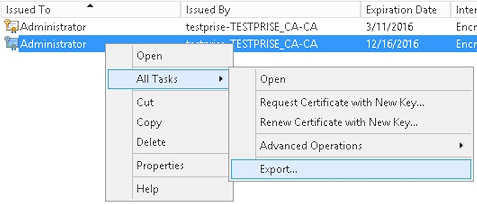
-
Click Yes, export the private key.
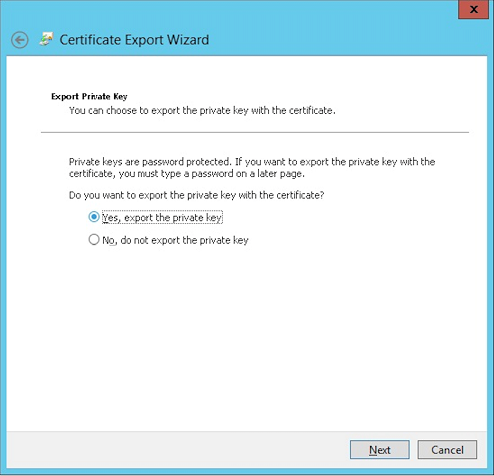
-
Select Include all certificates in the certification path if possible and select the Export all extended properties checkbox.
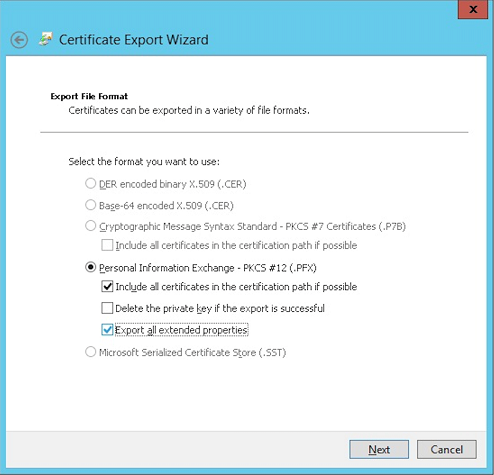
-
Set a password to use when uploading this certificate into XenMobile.
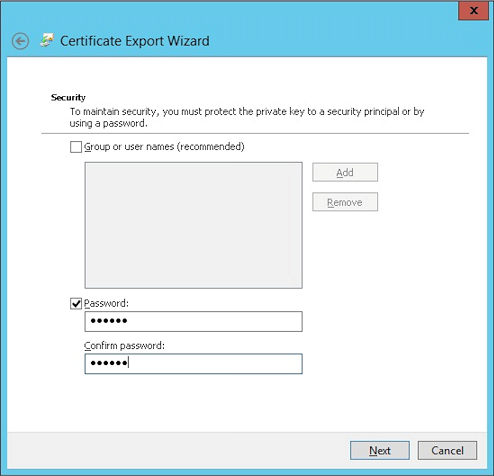
-
Save the certificate onto your hard drive.
Uploading the certificate to XenMobile
-
In the XenMobile console, click the gear icon in the upper-right corner. The Settings screen appears.
-
Click Certificates and then click Import.
-
Enter the following parameters:
- Import: Keystore
- Keystore type: PKCS #12
- Use as: Server
-
Keystore file: Click Browse to select the
.pfxcertificate you created. - Password: Enter the password that you created for this certificate.
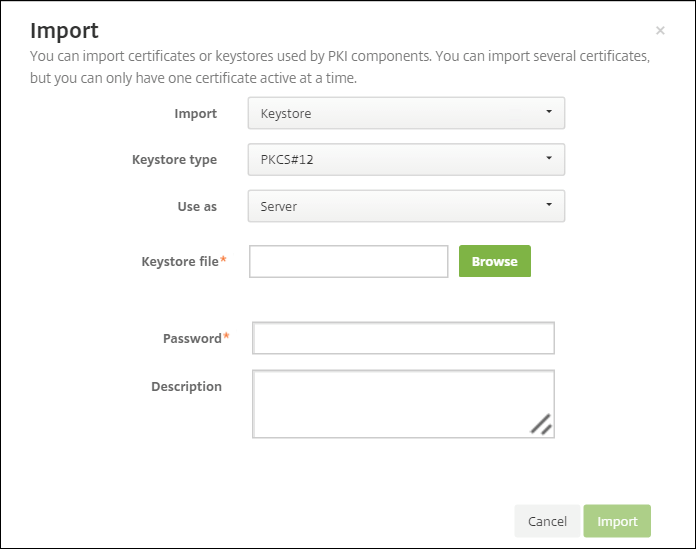
-
Click Import.
-
Verify that the certificate installed correctly. A correctly installed certificate displays as a User certificate.
Creating the PKI entity for certificate-based authentication
-
In Settings, go to More > Certificate Management > PKI Entities.
-
Click Add and then click Microsoft Certificate Services Entity. The Microsoft Certificate Services Entity: General Information screen appears.
-
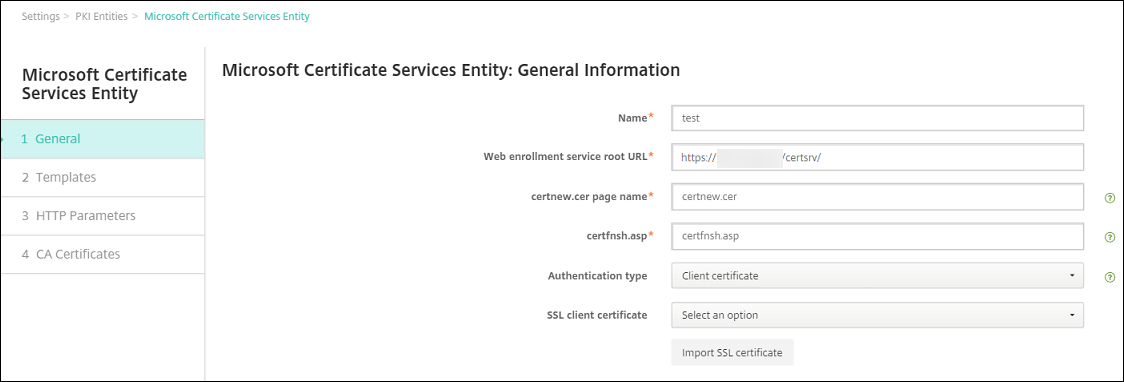
Enter the following parameters:
- Name: Type any name
-
Web enrollment service root URL:
https://RootCA-URL/certsrv/(Be sure to add the last slash, /, in the URL path.) - certnew.cer page name: certnew.cer (default value)
- certfnsh.asp: certfnsh.asp (default value)
- Authentication type: Client certificate
- SSL client certificate: Select the User Certificate to be used to issue the XenMobile client certificate.
-
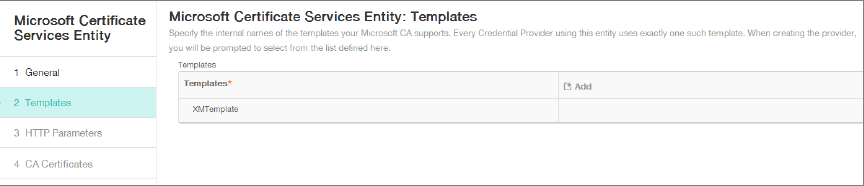
Under Templates, add the template that you created when configuring the Microsoft certificate. Don’t add spaces.
-
Skip HTTP Parameters and then click CA Certificates.
-
Select the root CA name that corresponds to your environment. This root CA is part of the chain imported from the XenMobile client certificate.
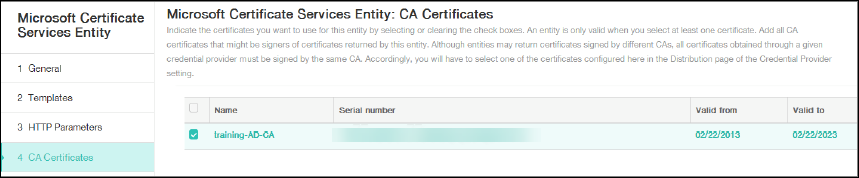
-
Click Save.
Configuring credentials providers
-
In Settings, go to More > Certificate Management > Credential Providers.
-
Click Add.
-
Under General, enter the following parameters:
- Name: Type any name.
- Description: Type any description.
- Issuing entity: Select the PKI entity created earlier.
- Issuing method: SIGN
- Templates: Select the template added under the PKI entity.
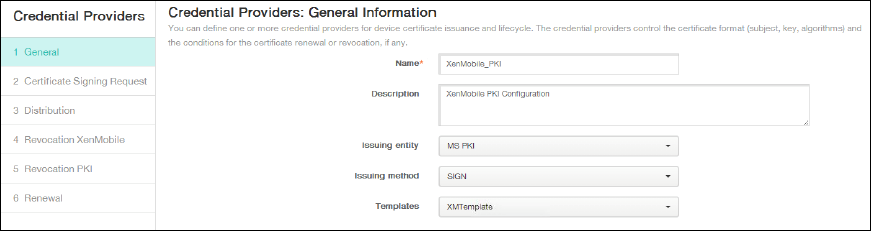
-
Click Certificate Signing Request and then enter the following parameters:
- Key algorithm: RSA
- Key size: 2048
- Signature algorithm: SHA256withRSA
-
Subject name:
cn=$user.username
For Subject Alternative Names, click Add and then enter the following parameters:
- Type: User Principal name
-
Value:
$user.userprincipalname
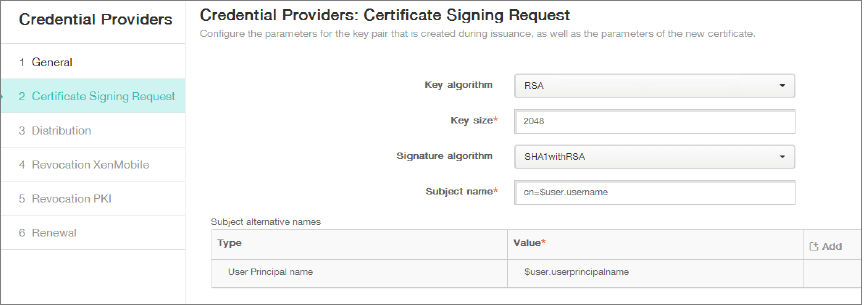
-
Click Distribution and enter the following parameters:
- Issuing CA certificate: Select the Issuing CA that signed the XenMobile Client Certificate.
- Select distribution mode: Select Prefer centralized: Server-side key generation.

-
For the next two sections, Revocation XenMobile and Revocation PKI, set the parameters as required. In this example, both options are skipped.
-
Click Renewal.
-
For Renew certificates when they expire, select ON.
-
Leave all other settings as default or change them as required.
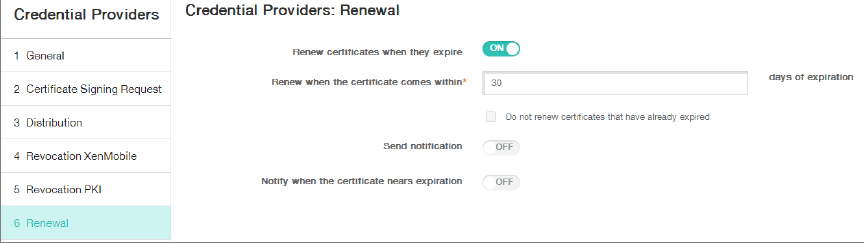
-
Click Save.
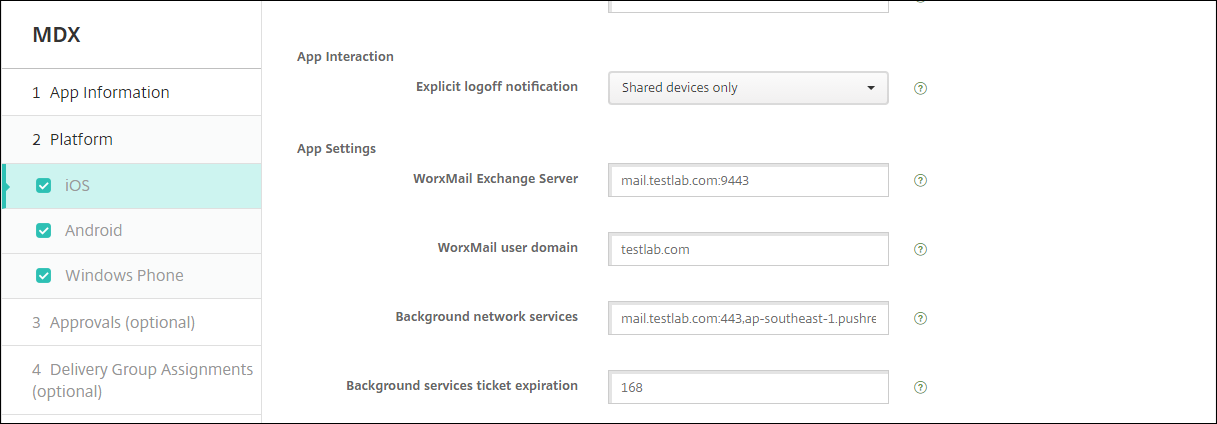
Configuring Secure Mail to use certificate-based authentication
When you add Secure Mail to XenMobile, be sure to configure the Exchange settings under App Settings.
Configuring Citrix ADC certificate delivery in XenMobile
-
Log on to the XenMobile console and click the gear icon in the upper-right corner. The Settings screen appears.
-
Under Server, click Citrix Gateway.
-
If Citrix Gateway isn’t already added, click Add and specify the settings:
-
External URL:
https://YourCitrixGatewayURL - Logon Type: Certificate and domain
- Password Required: OFF
- Set as Default: ON
-
External URL:
-
For Deliver user certificate for authentication, select On.
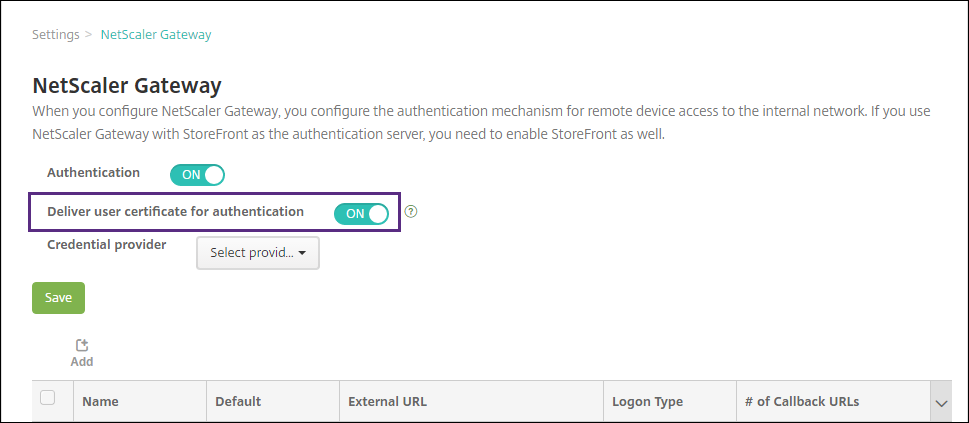
-
For Credential Provider, select a provider and then click Save.
-
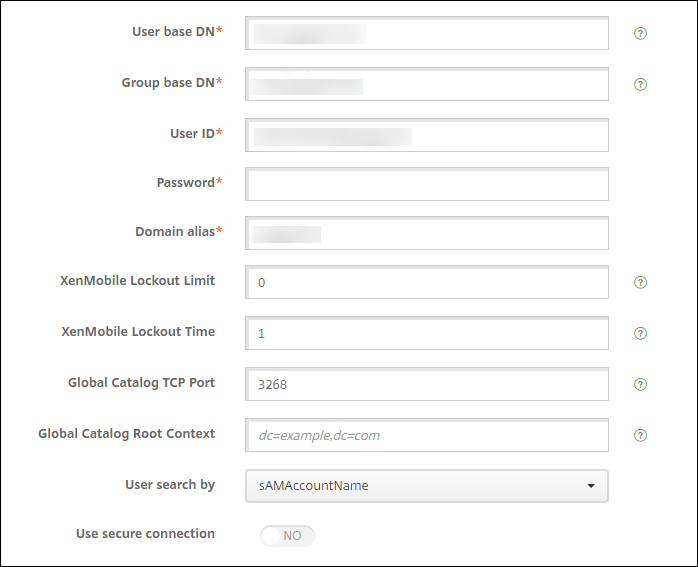
To use the sAMAccount attributes in the user certificates as an alternative to User Principal Name (UPN), configure the LDAP connector in XenMobile as follows: Go to Settings > LDAP, select the directory and click Edit, and select sAMAccountName in User search by.
Enable Citrix PIN and user password caching
To enable Citrix PIN and user password caching, go to Settings > Client Properties and select these checkboxes: Enable Citrix PIN Authentication and Enable User Password Caching. For more information, see Client properties.
Troubleshooting your client certificate configuration
After a successful configuration of the preceding configuration plus the Citrix Gateway configuration, the user workflow is as follows:
-
Users enroll their mobile device.
-
XenMobile prompts users to create a Citrix PIN.
-
Users are then redirected to the XenMobile Store.
-
When users start Secure Mail, XenMobile doesn’t prompt them for user credentials for mailbox configuration. Instead, Secure Mail requests the client certificate from Secure Hub and submits it to the Microsoft Exchange Server for authentication. If XenMobile prompts for credentials when users start Secure Mail, check your configuration.
If users can download and install Secure Mail, but during the mailbox configuration Secure Mail fails to finish the configuration:
-
If Microsoft Exchange Server ActiveSync uses private SSL server certificates to secure the traffic, verify that the Root/Intermediate certificates installed on the mobile device.
-
Verify that the authentication type selected for ActiveSync is Require client certificates.
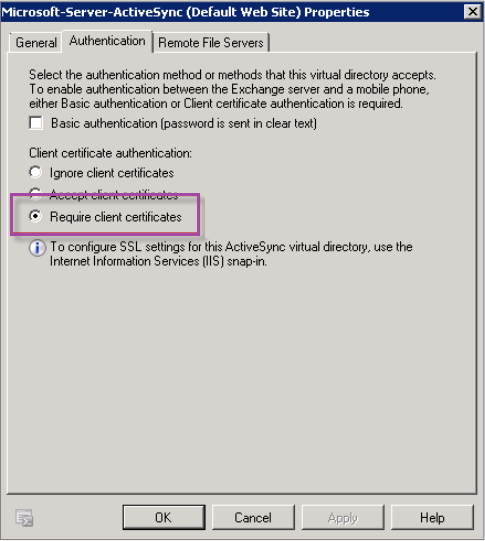
-
On the Microsoft Exchange Server, check the Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync site to verify that client certificate mapping authentication is enabled. By default client certificate mapping authentication is disabled. The option is under Configuration Editor > Security > Authentication.
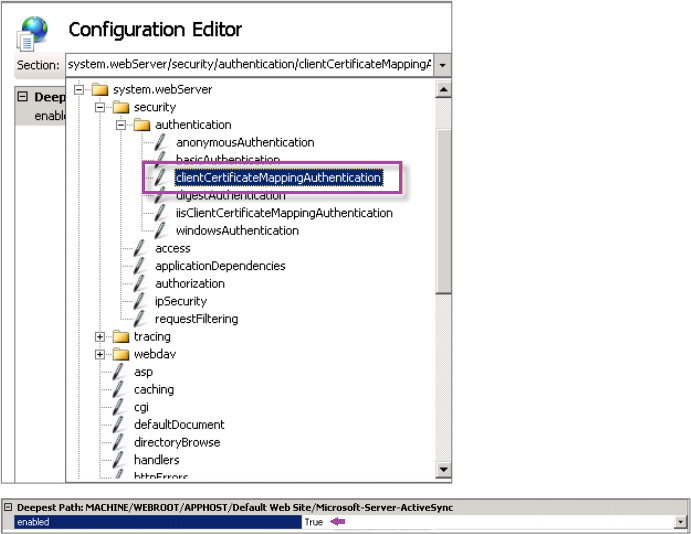
After selecting True, be sure to click Apply for the changes take effect.
-
Check the Citrix Gateway settings in the XenMobile console: Ensure that Deliver user certificate for authentication is ON and that Credential provider has the correct profile selected.
To determine if the client certificate was delivered to a mobile device
-
In the XenMobile console, go to Manage > Devices and select the device.
-
Click Edit or Show More.
-
Go to the Delivery Groups section, and search for this entry:
Citrix Gateway Credentials: Requested credential, CertId=
To validate whether client certificate negotiation is enabled
-
Run this
netshcommand to show the SSL Certificate configuration that is bound on the IIS website:netsh http show sslcert -
If the value for Negotiate Client Certificate is Disabled, run the following command to enable it:
netsh http delete sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=cert_hash appid={app_id} certstorename=store_name verifyclientcertrevocation=Enable VerifyRevocationWithCachedClientCertOnly=Disable UsageCheck=Enable clientcertnegotiation=EnableFor example:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=609da5df280d1f54a7deb714fb2c5435c94e05da appid={4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914} certstorename=ExampleCertStoreName verifyclientcertrevocation=Enable VerifyRevocationWithCachedClientCertOnly=Disable UsageCheck=Enable clientcertnegotiation=Enable
In this article
- Prerequisites
- Add a certificate snap-in to the Microsoft Management Console
- Adding the template to Certificate Authority
- Creating a PFX certificate from the CA server
- Uploading the certificate to XenMobile
- Creating the PKI entity for certificate-based authentication
- Configuring credentials providers
- Configuring Secure Mail to use certificate-based authentication
- Configuring Citrix ADC certificate delivery in XenMobile
- Troubleshooting your client certificate configuration