Create a Workspace
A workspace is created from the Workspaces Page. A workspace is, in essence, an online Cloud Development Environment (CDE) accessible via a Cloud IDE, a terminal or an SSH connection. Using an SSH connection is possible from a locally installed IDE supporting development from a remote container.
-
Basic Set-Up
- Basic info
- Resource Access Control
-
Data Loss Prevention
Permission: Security::Manage - Custom Work Schedule
- Launch it
- From an existing Workspace
- From a template
Basic Set-Up
You can create a workspace by pressing the “Create Workspace” button.
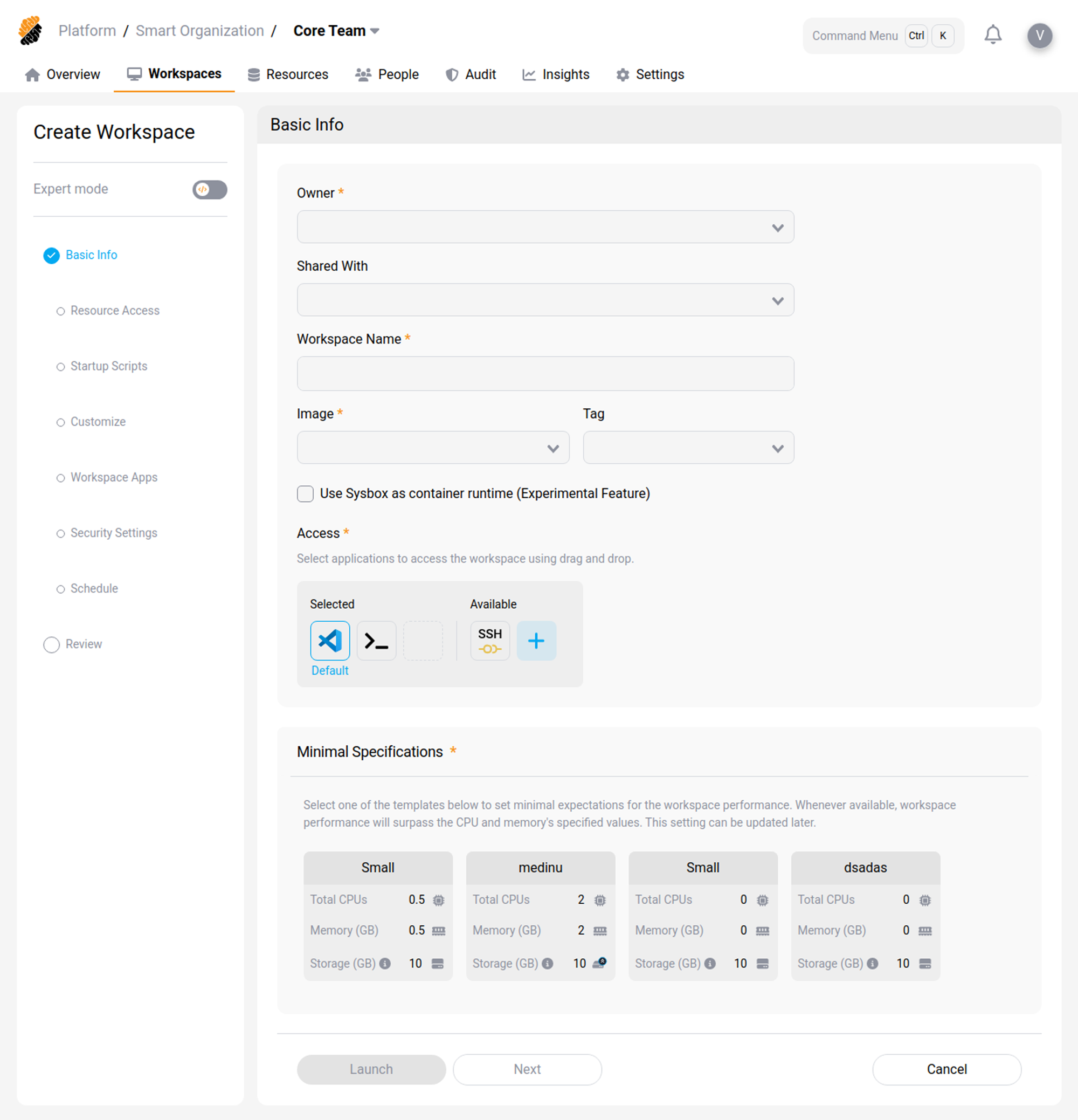
You will need to select the following information:
Basic info
- Workspace Name
- Embedded Cloud IDE
- User Sharing Options
- Docker Image
- Image Version
- Minimal Resource Specifications
Resource Access Control
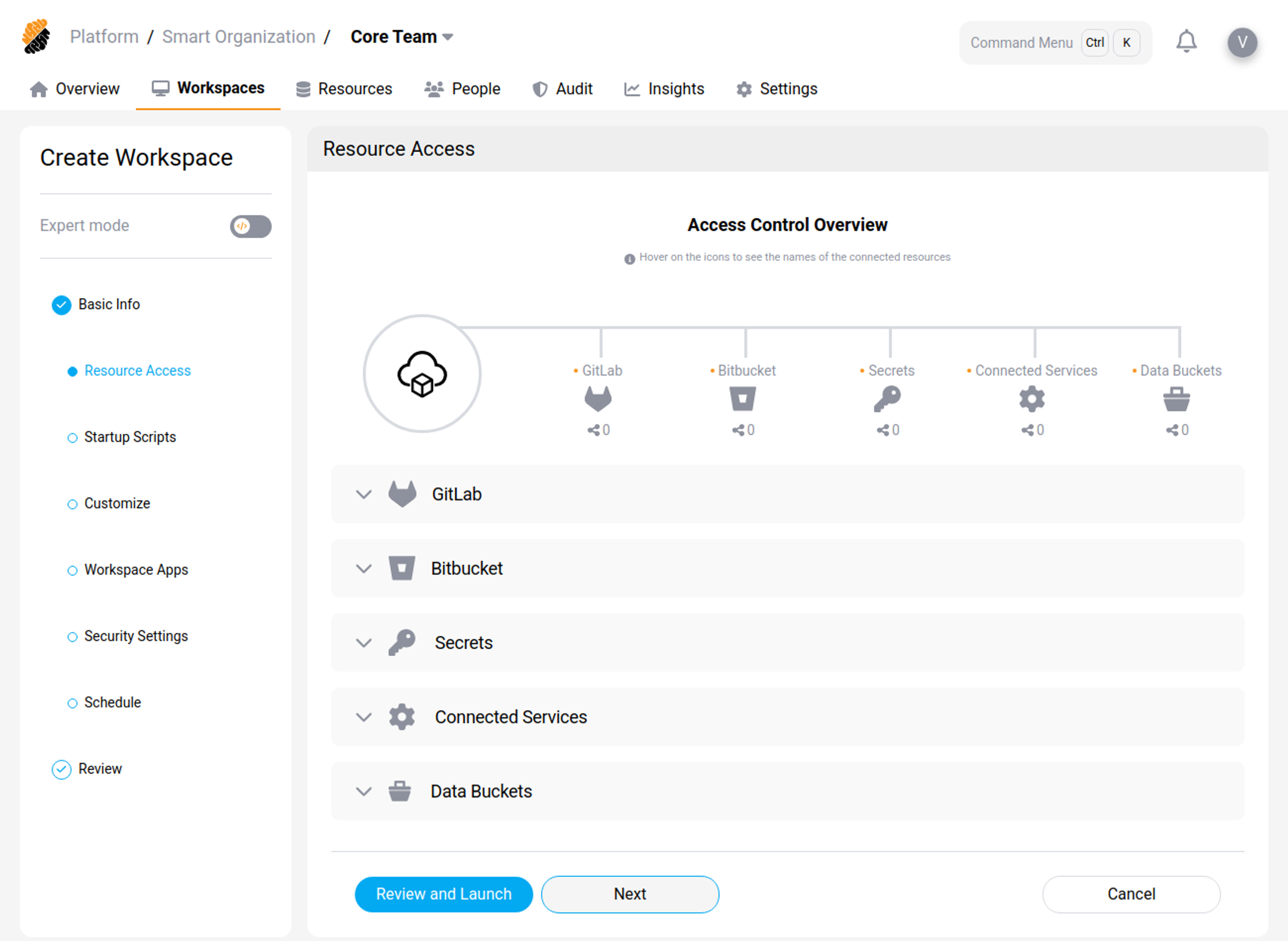
You can attach various project resources to your workspace. Resources must have been previously added to the project. In addition, you might need the appropriate access rights to access them.
You can add the following resource:
- Git Applications And Repositories: You can connect the entire GIT applications available from your platform or single repositories that have been previously imported to the project’s or organization’s resources. Additionally, you can specify a default folder location within your workspace where the Git files will be cloned.
- Secrets: You can import secrets to the workspace as files or environment variables in the workspace. Choose from existing secrets or create a new one.
- Connected HTTP and SSH Services: You can connect services to appear as environment variables in the workspace. Supported and available services are part of the project’s and organization’s resources and depend on the platform’s configuration.
Startup Scripts
While the base container image (Dockerfile) provides core tools like languages and compilers, a startup script handles dynamic configurations. Because these configurations are often user-specific, they shouldn’t be part of the shared image. You can use a startup script to automate environment configuration every time the workspace launches and run it either pre-startup or post-startup, depending on your requirements. This ensures your workspace is ready for development immediately, without requiring manual setup.
Startup scripts are useful for tasks such as:
Manage dynamic dependencies
Dependencies often change frequently or are specific to a branch, which makes them unsuitable for a static container image. You can use a script to:
-
Install dependencies: Run commands like
npm installorapt update. This ensures the environment has the latest libraries that match the code in your current branch. - Build binaries: Compile the latest version of the application or helper tools so they are ready to run.
Initialize services
A startup script can boot necessary background services that the container runtime doesn’t automatically manage. Use the script to:
- Start databases: Launch local instances of services like PostgreSQL, Redis, or MongoDB if you need them for development.
- Run daemons: Start background processes, such as file watchers, test runners, or local servers.
Run status checks
Scripts can provide feedback to let you know when the environment is fully ready. You can configure the script to:
- Perform health checks: Verify that all required services are running before giving you control of the terminal.
- Print a welcome message: Display a “Ready to code!” message or a list of available commands.
Data Loss Prevention Permission: _Security::Manage_
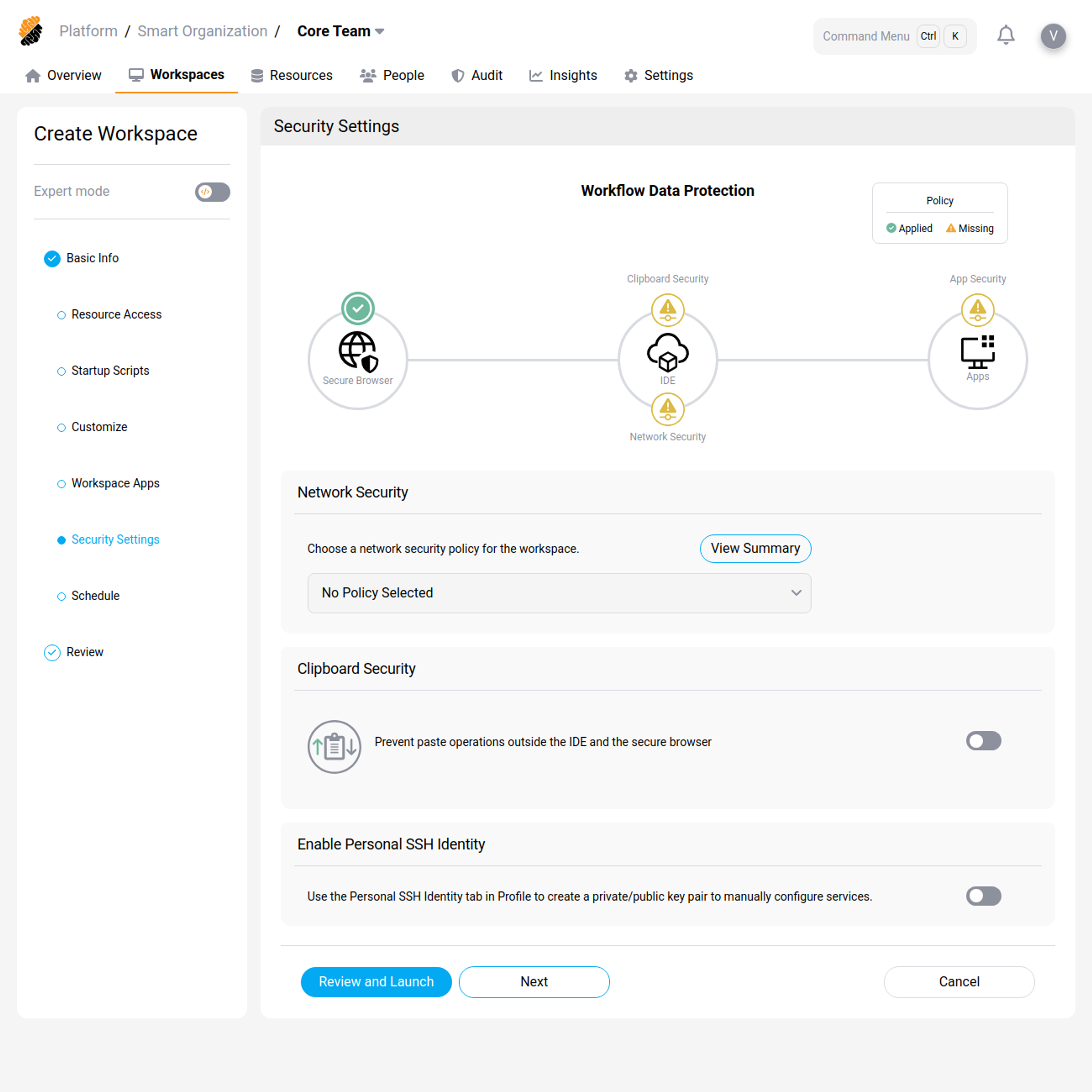
In the Data Loss Prevention section you can configure the security of your workspace.
Under Security Settings you can configure:
- Network Policy: Select a network policy to enforce on the workspace. Network policies are part of the project’s and organization’s resources and are defined by the user with the Security::Manage permission. In particular, policies allow you to control outbound network traffic from the workspace.
- Clipboard Security: Prevent pasting outside of the IDE and the Secure Browser for this workspace.
- Apps Security: Configure Workspace Apps to be accessed only through the Secure Browser.
Under Secure Access Management you can configure:
-
Enable Remote Development Over SSH: Allow connection to the workspace via SSH.
-
Enable Personal SSH Identity: Allow users to use their personal SSH identity from within the workspace.
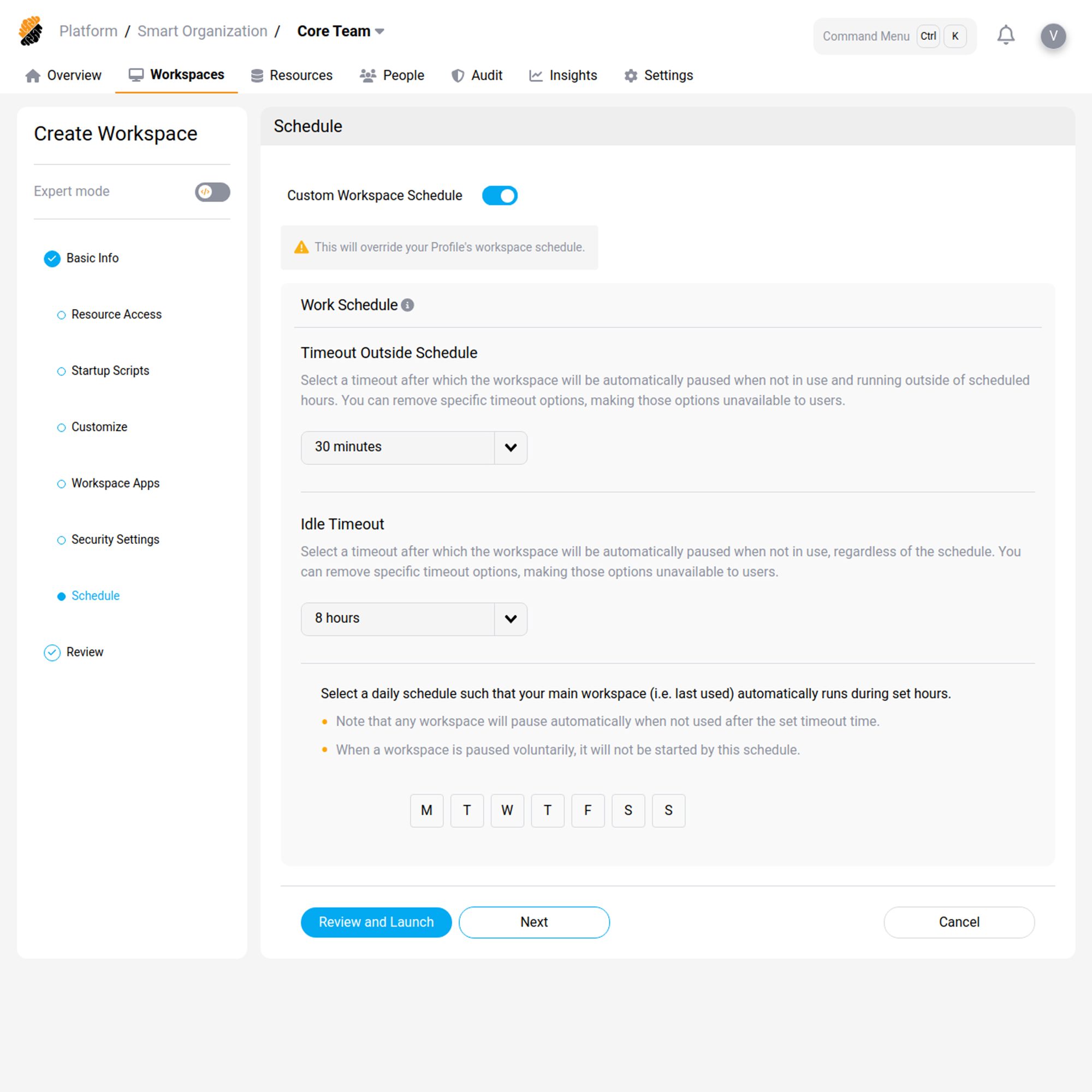
Custom Work Schedule
You can define a custom work schedule for your workspace.
Launch it
Finally, review your Workspace configuration, and launch it. Your workspace will be automatically deployed. You can edit its configuration at any time from the Overview or Workspaces pages.
From an existing Workspace
You can create a workspace from an existing one by pressing the “Create from Existing” button on the drop-down button of the “Create Workspace” button.
You will need to provide the following information:
- Workspace to Copy
- Owner for the Workspace
Tip
Click on “Customize” to edit the workspace as if you were creating it from scratch.
Once done, press the “Launch” button.
From a template
You can create a workspace from an existing one by pressing the “Create from Template” button on the drop-down button of the “Create Workspace” button.
You will need to provide the following information:
- Template Name
- Owner for the Workspace
Tip
Click on “Customize” to edit the workspace as if you were creating it from scratch.
Once done, press the “Launch” button.