-
-
WebSocket communication between VDA and Delivery Controller™
-
-
Migrate workloads between resource locations using Image Portability Service
-
-
HDX Direct
-
-
-
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
HDX™ Direct
When accessing Citrix-delivered resources, HDX Direct allows both internal and external client devices to establish a secure direct connection with the session host if direct communication is possible.
System requirements
The following are the system requirements for using HDX Direct:
-
Control plane
- Citrix DaaS™
- Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ 2503 or later
-
Virtual Delivery Agent (VDA)
- Windows: version 2503 or later
-
Workspace app
- Windows: version 2503 or later
- Linux: version 2411 or later
- Mac: version 2411 or later
-
Access tier
- Citrix Workspace™
- Citrix Storefront™ 2503 or later
- Citrix Gateway Service
- Citrix NetScaler® Gateway
Network requirements
The following are the network requirements for using HDX Direct.
Session hosts
If your session hosts have a firewall such as Windows Defender Firewall, you must allow the following inbound traffic for internal connections.
| Description | Source | Protocol | Port |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct internal connection | Client | TCP | 443 |
| Direct internal connection | Client | UDP | 443 |
Note:
The VDA installer adds the appropriate inbound rules to Windows Defender Firewall. If you use a different firewall, you must add the rules above.
Client network
The following table describes the client network for internal and external users.
Internal users
| Description | Protocol | Source | Source port | Destination | Destination port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct internal connection | TCP | Client network | 1024–65535 | VDA network | 443 |
| Direct internal connection | UDP | Client network | 1024–65535 | VDA network | 443 |
External users
| Description | Protocol | Source | Source port | Destination | Destination port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STUN (external users only) | UDP | Client network | 1024–65535 | Internet (see note below) | 3478, 19302 |
| External user connection | UDP | Client network | 1024–65535 | Data center’s public IP address | 1024–65535 |
Data center network
The following table describes the data center network for internal and external users.
Internal users
| Description | Protocol | Source | Source port | Destination | Destination port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct internal connection | TCP | Client network | 1024–65535 | VDA network | 443 |
| Direct internal connection | UDP | Client network | 1024–65535 | VDA network | 443 |
External users
| Description | Protocol | Source | Source port | Destination | Destination port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STUN (external users only) | UDP | VDA network | 1024–65535 | Internet (see note below) | 3478, 19302 |
| External user connection | UDP | DMZ / Internal network | 1024–65535 | VDA network | 55000–55250 |
| External user connection | UDP | VDA network | 55000–55250 | Client’s public IP | 1024–65535 |
NOTE:
Both the VDA and Workspace app attempt to send STUN requests to the following servers in the same order:
- stun.cloud.com:3478
- stun.cloudflare.com:3478
- stun.l.google.com:19302
If you change the default port range for external user connections using the HDX Direct port range policy setting, the corresponding firewall rules must match your custom port range.
Configuration
HDX Direct is disabled by default. You can configure this feature using the HDX Direct setting in the Citrix policy.
- HDX Direct: To enable or disable a feature.
- HDX Direct mode: Determines if HDX Direct is available for internal clients only or for both internal and external clients.
- HDX Direct port range: Defines the port range that the VDA uses for connections from external clients.
If needed, the list of STUN servers used by HDX Direct can be modified by editing the following registry value:
- Key: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Citrix\HDX-Direct
- Value type: REG_MULTI_SZ
- Value name: STUNServers
- Data: stun.cloud.com:3478 stun.cloudflare.com:3478 stun.l.google.com:19302
NOTE:
HDX Direct for external users is only available with EDT (UDP) as the transport protocol. Therefore, Adaptive Transport must be enabled.
Considerations
The following are considerations for using HDX Direct:
- HDX Direct for external users is only available with EDT (UDP) as the transport protocol. Therefore, Adaptive Transport must be enabled.
- If you are using HDX Insight, note that using HDX Direct prevents the HDX Insight data collection, as the session would no longer be proxied through NetScaler Gateway.
How it works
HDX Direct allows clients to establish a direct connection to the session host when direct communication is available. When direct connections are made using HDX Direct, self-signed certificates are used to secure the direct connection with network level-encryption (TLS/DTLS).
Internal users
The following diagram depicts the overview of the HDX Direct connection process of internal users.
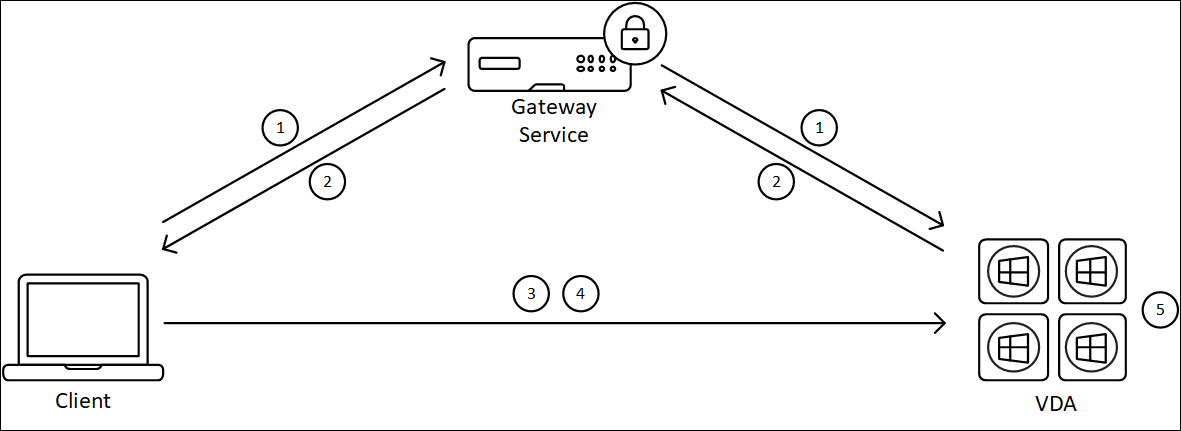
- The client establishes an HDX session through the Gateway Service.
- Upon a successful connection, the VDA sends to the client the VDA machine’s FQDN, a list of its IP addresses, and the VDA machine’s certificate via the HDX connection.
- The client probes the IP addresses to see if it can reach the VDA directly.
- If the client can reach the VDA directly with any of the IP addresses shared, the client establishes a direct connection with the VDA, secured with (D)TLS using a certificate that matches the one exchanged in step (2).
- Once the direct connection is successfully established, the session is transferred to the new connection, and the connection to the Gateway Service is terminated.
Note:
After establishing the connection in step 2, above, the session is active. The subsequent steps do not delay or interfere with the user’s ability to use the virtual application or desktop. If any of the subsequent steps fail, the connection through the Gateway is maintained without interrupting the user’s session.
Traditional direct connections
When using Storefront, Workspace with Direct Workload Connection, or Workspace configured for internal-only connectivity, direct connections are established between the client and the session host without the need to route through a Gateway first.
In these instances, HDX Direct is not triggered since the connections are inherently direct. However, if HDX Direct is enabled, these connections will leverage the HDX Direct certificates to secure the sessions.
External users
The following diagram depicts the overview of the HDX Direct connection process for external users:
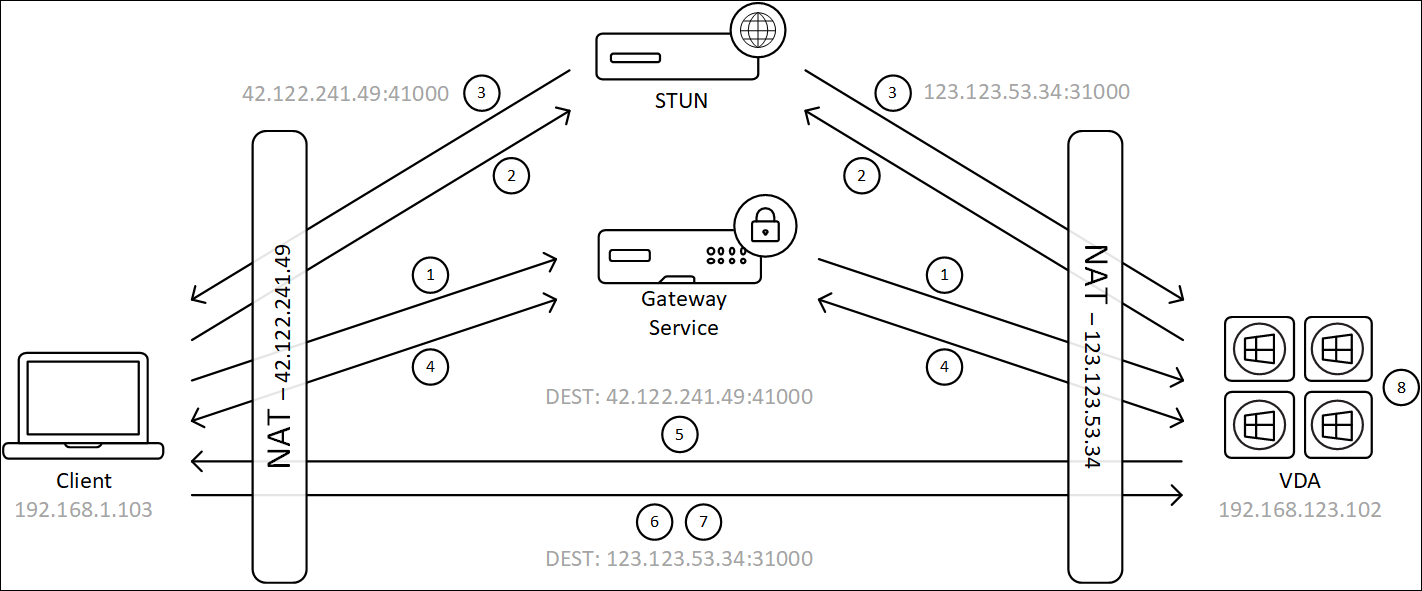
- The client establishes an HDX session through the Gateway Service.
- Upon a successful connection, both the client and the VDA send a STUN request to discover their public IP addresses and ports.
- The STUN server responds to the client and VDA with their corresponding public IP addresses and ports.
- Through the HDX connection, the client and the VDA exchange their public IP addresses and UDP ports, and the VDA sends its certificate to the client.
- The VDA sends UDP packets to the client’s public IP address and UDP port. The client sends UDP packets to the VDA’s public IP address and UDP port.
- Upon receipt of a message from the VDA, the client responds with a secure connection request.
- During the DTLS handshake, the client verifies that the certificate matches the certificate exchanged in step (4). After validation, the client sends its authorization token. A secure direct connection is now established.
- Once the direct connection is successfully established, the session is transferred to the new connection, and the connection to the Gateway Service is terminated.
Note:
After establishing the connection in step 2, above, the session is active. The subsequent steps do not delay or interfere with the user’s ability to use the virtual application or desktop. If any of the subsequent steps fail, the connection through the Gateway is maintained without interrupting the user’s session.
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Citrix Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Citrix Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Citrix product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.